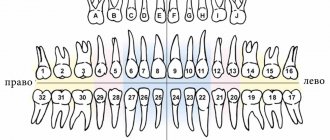
Untimely treatment of caries in children leads to the development of pulpitis - inflammation of tooth tissue, including blood vessels and nerve bundles. The lower molars are most often affected, but the disease occurs even on the anterior elements. Therefore, pulpitis in children occurs even more often than in adults. This is due to a number of factors:
- thin weak enamel;
- large volume of pulp;
- wide root canals;
- less mineralization;
- weak immunity.
In addition to caries, pulpitis can be caused by trauma, including poor treatment.
Treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis in children by our experienced pediatric therapists:
- treatment with a smile, no stress for the child , no tears
- pediatric doctors become friends for young patients
- doctors save baby and permanent teeth
- more than 7,890 children who are happy to have their teeth treated with us
- While the child is getting his teeth treated, the parents go about their business
- quality treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo
Treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth
Treatment of periodontitis in a permanent tooth involves removing the infection inside and outside the tooth, located in the ligament that holds the tooth.
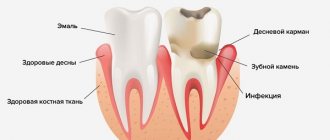
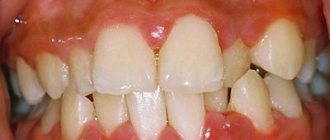
Complaints. With this type of disease, complaints appear when biting on a tooth, a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth, pain in the gum next to the tooth, swelling and swelling of the gum, discharge of purulent contents from the tooth or from the gum. Signs of general intoxication of the body: fatigue, weakness, lethargy, temperature, enlarged regional lymph nodes.
Treatment method. Before dental treatment for periodontitis, local anesthesia is performed (if necessary). Demineralized tissue is removed from the carious cavity and access to the root canals is created for the purpose of high-quality mechanical, chemical and medicinal treatment. A medicinal paste is injected into the tooth canals for 7-10 days for the purpose of antiseptic and osteotropic effects, the treatment ends with the installation of a temporary filling. On the second visit, the medicinal paste is removed from the tooth, the root canals are filled with modern sealers (pastes) and fillers (gutta-percha pins) under X-ray control. After the treatment, the issue of restoring the crown part of the tooth is decided: a filling or a crown. Only a dentist, having assessed the condition of the tooth, will suggest one or another method of restoring the tooth.
Recommendations. Visit a dentist at least once every 6 months to examine the oral cavity in order to identify foci of inflammation, prevent complications and sanitation.
Reviews about the clinic on independent portals:
Answers to popular questions
Where to remove a child's tooth?
It is worth knowing that only pediatric surgeons perform removal of baby teeth in dentistry. Experience and increased caution are required when working with baby teeth, so only specially trained doctors undertake this. At the Azabuka clinic we remove children's teeth of any complexity.
How to properly remove a baby tooth?
Removing children's teeth requires care and attention. I first numb the pain, then apply and fix the forceps on the coronal part - I dislocate and extract the tooth. I give it to the child for the Tooth Fairy, and I treat the hole. It may sound scary, but in reality it’s not even painful.
How to prepare a child for tooth extraction?
At Aza&Buka we recommend an adaptation technique. Our doctors have psychological training and easily prepare children for treatment and even removal of baby teeth. The reception takes place in a game format and is aimed at combating children's fears.
How is dental treatment performed for very young children?
How is dental treatment performed for very young children?
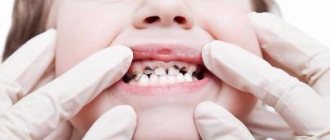
Treatment of primary teeth in children 2-3 years old is carried out under sedation - the child breathes through a mask with a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen: he is conscious, but relaxed and calm. Or under general anesthesia. More accurate information is possible only during a consultation - after examining the baby.
What treatment methods for baby teeth exist?
What treatment methods for baby teeth exist?
At Azabuka they rarely treat teeth using a drill. I usually use more modern methods of dental treatment for children - Icon technology, ozone therapy, remineralization. A laser is suitable for the treatment of complicated caries of primary teeth. All methods are effective and completely painless.
Is treatment of children's baby teeth really necessary?
Treatment of baby teeth is a necessity. If you don't do this, you can lose your teeth and have problems with your bite. Or permanent units will be at risk of caries. But even worse is the pain and discomfort experienced by a child with bad teeth. At the Aza&Buka clinic, teeth are treated without pain and even without drilling - with ozone, laser, and minerals.
Did not find an answer to your question?
Treatment with a smile, no stress for the child, no tears
Pulpitis of primary and permanent teeth in pediatric dentistry is quite common; approximately 90% of children with advanced caries suffer from symptoms of this disease. Children's pulpitis is accompanied by excruciating toothache, which deprives you of joy. The use of painkillers will not solve the problem, so the only correct solution is to visit a dentist. The Novodenta dental clinic offers the services of a pediatric dentist who will not only treat pulpitis or periodontitis, but will also find an approach to every little patient.
Reviews
After reading reviews about the treatment of pulpitis at the Natadent clinic, you can be sure that our little patients and their parents are always satisfied with both the treatment process and the quality of the result.
Don't forget to leave your review, we will be very grateful!
LEAVE FEEDBACK
What is pulpitis
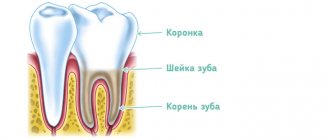
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the connective tissue that contains nerve endings, blood and lymphatic vessels. The pulp itself is located under a layer of dentin inside the tooth, consists of a cellular part, vascular and nerve bundles, the defeat of which causes severe and acute pain. In children, pulpitis occurs many times more often than in adults. The reason for this is the fact that baby teeth, like permanent teeth, have a thinner layer of enamel and dentin, which allows infection to quickly penetrate into the deep tissues of the tooth. The pulp is very important because it provides growth and nutrition to tooth tissue.
How to prepare your child for a doctor's appointment
If the child has attended adaptation appointments, additional communication about the benefits of dental treatment will be unnecessary. Otherwise, parents should gently and correctly tell:
- about dentists - doctors who know how to save teeth from disease;
- about the positive effect in the treatment of dental pulpitis in a child.
And:
- choose a convenient time for the appointment;
- play dentists at home;
- do not scare the baby with scary terms;
- do not panic yourself;
- do not deceive or be cunning;
- take your favorite toy to visit the doctor.
If the task seems difficult or impossible, then you should simply sign up for an adaptation appointment at Aza&Buka and entrust the conversation with the child to trained doctors. All dentists at the medical center are proficient in psychological communication techniques and can find a common language with any patient.
Causes and symptoms of pulpitis in children
Inflammation of the pulp, according to pediatric dentists, can occur for several reasons, including:
- caries;
- acute infectious diseases that led to decreased immunity and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- dental injuries.
Symptoms of pulpitis in children are manifested by the following signs:
- sharp and throbbing pain in the area of the diseased tooth;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling, redness of the gums;
- general weakness, fever;
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
The main symptom of the disease is throbbing pain, which can occur at any time of the day. If you do not pay attention to the problem, this can lead to complications in the form of purulent inflammation, periodontitis and other consequences.
Potential complications of pulpitis in primary teeth
Not treating baby teeth (“after all, they will fall out anyway”) is the biggest mistake that parents can make regarding their child’s dental health. In particular, pulpitis that is not treated in time leads to a number of serious complications:
- periodontitis, purulent abscess, infection entering the bloodstream, which can even lead to death;
- deep infection can affect the primordia of the molars;
- Early loss of baby teeth affects the eruption of permanent teeth. As a result, the child may develop significant bite problems;
- pain and discomfort prevent the child from eating and communicating normally.
Classification
Pulpitis in children can affect both milk and permanent teeth and manifest itself in several forms - acute and chronic.
Acute pulpitis of milk teeth or permanent teeth is divided into several types:
- Focal - attacks of pain last up to 30 minutes, most often appear after consuming cold or hot food or drinks.
- Diffuse – the middle layer of the pulp is damaged, the pain can last for several hours, and intensifies in the evening.
- Purulent - inflammation affects not only the pulp, but also affects the gums. Upon examination, you may notice a discharge of grayish or yellow liquid.
If you do not pay attention to the problem, the acute form quickly turns into chronic, which also has several forms:
- Fibrous – inflammation affects the root canals, tooth enamel quickly turns black, there is a reaction to hot and cold food, pain is practically not a concern.
- Hypertrophic – a polyp forms in the tooth cavity, the gums bleed, and there is a putrid odor from the mouth.
- Gangrenous is a dangerous type of disease when the pulp completely dies, and healthy tissue begins to be damaged.
Regardless of the form and type of the disease, treatment of pulpitis in milk or permanent teeth should be carried out as quickly as possible, this will help to eliminate the development of complications.
Treatment methods
The treatment of primary teeth in general does not differ from the treatment of permanent elements. If the child’s condition is serious, there is a threat of infection spreading throughout the body, amputation is performed. In most cases, the tooth is preserved to prevent malocclusion. Therapy is carried out in different ways:
- traditional. Involves treatment in three visits. During the first one, the nerve is opened, a devitalizing paste with arsenic is applied for 24-48 hours or without it for a period of up to 7 days. On the second visit, a pulp mummification mixture based on resorcinol-formalin is placed into the canals. At the last visit, a permanent filling is installed;
- modern. It takes place in 1 – 2 visits. If the child can sit quietly for a long time at the doctor and the roots of the tooth are formed, extraction is performed. The nerve is removed either on the first visit or after applying the paste. Next, the canals are carefully processed, infected tissue is removed, an anti-inflammatory paste (for example, zinc eugenol) is applied and closed with a filling. The composition will gradually dissolve along with the roots when changing teeth;
- partial vital amputation. The doctor removes the upper portion of the nerve and applies an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory medication that seals the remaining living pulp.
When treating teeth with immature roots, a different approach is chosen. This is due to several reasons:
- the apex of the roots has not yet closed and there is a risk of infection of the permanent tooth germ;
- the roots are short and the channels are wide;
- trauma to the upper zone of the root can lead to disturbances in its formation;
- It is impossible to remove the entire pulp and perform a complete canal treatment.
Most often, they choose amputation of the pulp by any method or biological treatment, when the tooth is cleaned of the affected tissue and a paste with calcium hydroxide is applied for several days. After this, a filling is installed.