This article uses excerpts from the chapter of the same name in the Face Anatomy atlas. It is of particular importance for specialists involved in the correction of age-related changes and contouring using fillers. The title “Dangerous triangle of the face” was not chosen by chance; it is in this zone that there are prerequisites of an anatomical and functional nature that can interfere with medical manipulation and cause side effects, including severe ones. Let's look at the topography of this triangle and the reasons for its danger.
Content:
- Possible reasons
- Dental causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes on the chin
- How to understand that the problem is in the lymph nodes
- Diagnostic measures
- How are lymph nodes treated?
- Preventive measures
If the lymph nodes are inflamed, it is important to undergo a comprehensive medical examination.
This condition can be accompanied by many diseases, both related to the field of dentistry and not related to it. Lymph nodes are peripheral organs of the lymphatic system. They perform the functions of a biological filter. Passing through their tissues, lymph enters different parts of the body and internal organs.
If the lymphoid structure has increased, it means there is an inflammatory process. It is necessary to find out as soon as possible what functional disorders it is associated with. This will allow you to create an effective treatment plan and prevent the development of severe complications.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostic procedures involve identifying the primary source of the disease. The first instance that a person with inflamed nodes in the parotid area needs to visit is a family doctor or therapist; for children, a pediatrician.
The doctor conducts a preliminary examination of the patient with palpation of the inflamed area. Based on the examination and complaints of the patient, a preliminary diagnosis of “parotid lymphadenitis” can be made. Next, the patient will have to undergo a series of specialists to determine the source of infection, as well as undergo standard laboratory tests. Additionally, the patient may be prescribed an ultrasound examination of the inflamed segment.
Further diagnostic procedures depend on individual indicators specific to the patient. If the source of lymphatic inflammation is “on the surface,” then steps are taken to treat it. Otherwise, the search involves additional tests and a comprehensive examination of the body.
The international classification of diseases ICD-10 classifies lymphadenitis in the section “Infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.” Inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes in medical documentation is identified by code L 04.0, indicating the localization of infected lymph nodes on the neck, face or head.
Possible reasons
The lymphatic system is the basis of immunity . It prevents the spread of pathological microorganisms and blocks the occurrence of many disease processes. In various diseases, lymphocytes begin to actively multiply to slow down inflammation. Then the lymph nodes enlarge.
If structures localized under the jaw and in the neck area “grow,” it is most likely an infection, that is, the disorder is caused by bacteria. But sometimes the condition occurs in the absence of infection.
Among the most common infectious causes:
- Colds, viruses. Their pathogens affect the ENT organs, and general intoxication is observed. In this scenario, sore throats, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, sinusitis, otitis media, etc. occur.
- Tuberculosis. With lymphadenitis, the entire neck swells. In advanced cases, lymphoid tissues located in the abdominal cavity and chest increase. The pathology is treated conservatively and surgically.
- Dental problems. Pulpitis, caries, periodontitis - all these are provoking diseases.
- Toxoplasmosis. People become infected with it from domestic animals (most often from cats). In addition to the growth of nodes, with this diagnosis the following are observed: high body temperature, headaches, an increase in the size of the spleen and liver. But very often the disease is asymptomatic.
- Venereal pathologies. Transmitted sexually. The body reacts very sharply to most of them, so already in the first days the patient notices that the lymph nodes have become enlarged and began to hurt, and severe weakness has appeared.
- Herpes. It manifests itself as an increase in the volume of lymphoid tissue in the neck, under the jaw and in the groin. Requires competent antiviral therapy.
Among the factors of a non-infectious nature that lead to the appearance of an unfavorable symptom:
- Oncology. It does not matter whether cancer of the lymphatic system or any internal organ is diagnosed. But in the first case, cancer cells quickly spread with the lymph flow, which contributes to the formation of metastases.
- Autoimmune pathologies. These are conditions in which the immune system begins to malfunction, causing serious damage to the body. This group includes systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, etc.
- Allergy. It manifests itself differently in all people. The most common symptoms are skin rashes and itching. But lymph can also be involved in the allergic process.
- Traumatic injuries to the head and face. If a strong pathological process occurs, lymphocytes begin to be actively produced.
Triangle and arteries
One of the main arteries in this area is the facial artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The facial artery, immediately after its origin, goes upward and passes to the face in front of the masticatory muscle, where its pulsation can be determined by palpation. Next, it is directed medially and towards the lips, giving off branches - the superior and inferior labial arteries, then passes under the muscle that lifts the upper lip, and reaches the wing of the nose, where its course becomes superficial and ends with two terminal branches - the arteries of the wing of the nose and the angular . Up to this point, everything is clear and clear, but in reality this is not always the case [Fig. 2].
Rice. 2. Facial artery - angular artery.
I will explain more clearly: there are many works with cadavers that emphasize the fact of the existence of frequently encountered anatomical variations and the place of origin of the facial artery, the course of this vessel and its branches. Often such variations are more the norm than the exception. Therefore, it can be argued that even with in-depth knowledge of anatomy, there is a possibility of complications due to the abnormal arrangement of blood vessels. Therefore, it is necessary to use techniques that help to avoid possible side effects as much as possible.
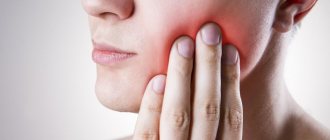
Dental causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes on the chin
Since very often in their work dentists are faced with huge lymph nodes in patients, let us dwell in more detail on the diseases that cause this symptom:
- Periodontitis. It can occur in acute or chronic form. Leads to tooth loosening and severe pain. If you do not receive qualified dental care in time, there will be a need to remove the affected unit.
- Stomatitis. Causes painful ulcers to appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It is the result of injuries, low immunity, vitamin deficiency. In advanced cases, the entire oral cavity becomes covered with wounds. Then active production of lymphocytes is observed.
- Pulpitis. Inflammatory lesion of pulp tissues. A very insidious disease. Through the pulp, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the lymph nodes and other tissues. It is important to clean the canals and seal them as soon as possible.
- Advanced caries. Despite the fact that many people do not take caries seriously, it is a rather insidious infectious process. If the deep tissues of the tooth are damaged, the lymph nodes come to the aid of the body - they try to neutralize pathological agents by producing lymphocytes. This can be understood by their increased size.
- Periodontal disease. Causes hypertrophy of periodontal tissues, leading to local hypoxia. Periodontal disease does not cause pain, so most often the patient learns about it by chance during a medical examination for some other condition. With periodontal disease, the gums become lighter, the interdental papillae atrophy, and the dental necks become exposed. If treatment is not started in time, the teeth will begin to loosen and fall out.
- Periodontitis. A disease that develops due to metabolic disorders, neurosomatic abnormalities, poor oral hygiene, and deficiency of vitamins and minerals. It manifests itself as bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth.
- Gingivitis. Inflammatory reaction in the gums. Appears against the background of gastrointestinal pathologies, allergies, infections. The patient experiences bleeding gums even with minor mechanical stress. A burning sensation in the mouth bothers me. Ulcerative-necrotic areas may form.
These are not all dental conditions in which the lymph nodes under the chin become inflamed. In medical practice there are many more such diagnoses. This once again proves that the patient himself will not be able to understand why his submandibular area is swollen.
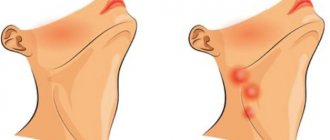
How to understand that the problem is in the lymph nodes
Among the symptoms indicating damage to the lymph nodes:
- pain in the area where they are located;
- migraine;
- weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- discomfort under the chin;
- unpleasant pulsation in the lower jaw;
- difficulty chewing food;
- swelling noticeable to the naked eye.
If a purulent process develops, the skin in the area of inflammation becomes red and becomes very hot to the touch. Additionally, symptoms characteristic of the disease that provoked the disorder may appear.
Diagnostic measures
Detecting the problem is very simple - the doctor just needs to feel the area under the chin and carefully examine it. To establish the exact cause of the disease, you need:
- Take blood and urine tests. From them you can understand the nature of the “provocateur” (viral or bacterial).
- Donate blood biochemistry.
- Get an ultrasound of the lymph nodes.
If the doctor suspects oncology, the patient is referred for a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan or a puncture biopsy. These diagnostic measures allow you to make a correct diagnosis and select adequate treatment.
How are lymph nodes treated?
The treatment tactics chosen by the doctor directly depend on the characteristics of the clinical symptoms and the diagnosis. If it's all about a bacterial infection, you can't do without antibiotics. For viruses, antiviral drugs and immunostimulants are indicated. In the case of an autoimmune disorder, the focus is on reducing the activity of specific culprit markers. If cancer is confirmed, chemotherapy, surgery, and immunomodulators are necessary.
If the lymph nodes are enlarged due to a certain dental disease, its step-by-step treatment is carried out. Almost immediately after this, the problem of increased lymphocyte production disappears by itself.
It is extremely important that the patient does not warm the lymph node or apply any compresses unless the doctor has prescribed it. Such actions can aggravate the situation and lead to the development of health-threatening complications.
Indications
There are many indications for the procedure:
- Node over 1 cm;
- Soreness;
- Inflammatory process for no apparent reason;
- Suspicion of a malignant tumor;
- The lymph node does not change, although treatment has been carried out for a long time;
- Sarcoidosis or lymphogranulomatosis, etc.
This procedure provides an understanding of:
- What is the specificity of the course of the disease;
- What is the level of infection;
- If a patient with cancer has metastases.
Preventive measures
No one is immune from the problem described. But there are ways to minimize the risk of its occurrence. Among them:
- receiving qualified medical care for any ailments;
- annual laboratory tests;
- timely treatment of emerging dental diseases;
- sanitation of the oral cavity every six months;
- following medical prescriptions.
Take care of your health, and the risk of enlarged lymph nodes will be minimized.
Symptomatic therapy
Before prescribing special treatment, rinsing with antiseptic solutions is effective in order to more quickly restore the size and density of the submandibular lymph nodes in case of ARVI, sore throat, and other inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. In the presence of combat syndrome, it is possible to take analgesics. In other cases, therapy is selected only after the causes of the condition have been established. The combination of lymphadenopathy with fever, rapid deterioration in health, headache, or detection of tumor formations in the head area is an indication for emergency medical attention.