What is the trigeminal nerve
The human face has many muscles and nerve endings. Not only the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx, and conjunctiva, but also the nerve endings can become inflamed. This is most often associated with neurological disorders that change the sensitivity of the fibers that conduct impulses.
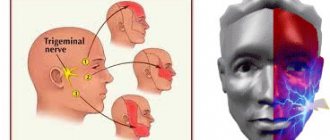
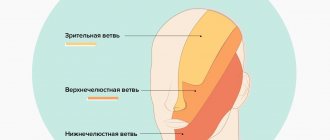
With neuropathy of the facial area, acute shooting pain occurs on the right or left. Mirror inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is extremely rare. It is located in the temporal region, near the base of the auricle. And from it there are branches along the entire half of the face:
- jaw nerve (upper and lower);
- optic nerve;
- infraorbital nerve.
The trigeminal nerve passes through the bone tissue in several places, which plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammation associated with pinching. Thus, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can result in acute pain both in the upper and lower jaw, and in the forehead area, covering the eye sockets.
Sciatica pain
The pain caused by sciatica is quite varied. There are burning and shooting ones. There are piercing and pulling. And there are also whining ones. But usually they come in fits and starts. In other words, unbearable pain and periods of relative peace follow each other.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
There are several reasons leading to inflammation of the nerve ducts:
- Poor blood supply associated with physical compression of the nerve. First of all, this is swelling caused by diseases of the ENT organs. The resulting tumor can also pinch the nerves.
- Inflammation associated with dentistry. This includes gingivitis, periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and eruption of wisdom teeth. Each of these diseases can lead to suppuration, abscesses, swelling and bacterial infections of tissues.
- Medical error by an anesthesiologist - if the injection was given unsuccessfully and the needle got into a nerve, pain cannot be avoided.
- Hypothermia causes muscles to lose their elasticity, which leads to pinching of the nerves passing between the fibers.
- Bacterial infections, in particular tetanus and polio.
- The cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is difficult to diagnose, is the psychological state of a person - frequent experiences, stress, and nervous disorders.
To determine the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a specialist.
Disease prevention
To prevent optic neuritis, it is recommended to give up bad habits, promptly treat infectious diseases, avoid eye and head injuries, and visit specialized doctors in the presence of chronic pathologies.
Article sources:
- Retrobulbar optic neuritis. Kukhtik S.Yu., Popova M.Yu., Tantsurova K.S. Bulletin of the Council of Young Scientists and Specialists of the Chelyabinsk Region, 2016
- Visualization of the optic nerve in the diagnosis and monitoring of retrobulbar neuritis. Yuryeva T.N., Burlakova E.V., Khudonogov A.A., Ayueva E.K., Sukharchuk O.V. Acta Biomedica Scientifica, 2011. p. 133-136
- Modern view on the problem of optic neuritis (systematic review). Krivosheeva M.S., Ioileva E.E. Saratov Scientific and Medical Journal, 2022. p. 602-605
- Results of treatment of optic neuritis. Latypova E.A. Saratov Scientific and Medical Journal, 2022. p. 875-879
Treatment methods
Depending on what caused the inflammation, a course of treatment is prescribed. For bacterial lesions, the emphasis is on antibacterial therapy through systemic administration of drugs.
However, regardless of the reasons, the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It could be:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- ketorol;
- diclofenac.
All of the listed drugs can be prescribed either in the form of tablets for oral administration, or prescribed in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration.
When conservative methods are not possible, the help of a surgeon may be needed. This primarily concerns abscesses due to the eruption of wisdom teeth, pulpitis or other dental diseases. In this case, the abscess will be opened, pus will be removed, the wound will be treated with antiseptic, and the tooth will be removed, if necessary. If a pinched nerve occurs as a result of pathologies in the structure of the skull, the surgeon will perform an operation to correct the situation and free the nerve bundles.
As a complex therapy, massage, heating or exposure to a magnetic field and electric current can be prescribed. You cannot massage or warm the inflamed area yourself, because this can lead to complications associated with rupture of the purulent capsule, blood poisoning and paralysis of the facial nerve.
Separately, you may need to consult a neurologist who will determine the cause of the inflammation if other specialists have not found obvious foci of infection and abscesses.
Traditional methods of treatment are permissible only as an addition to the main therapy. For example, rinsing with chamomile decoction will relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. But you can resort to such procedures only with the permission of the attending physician.
Which specialist can help with sciatica?
In the treatment of sciatica, the help of a neurologist is needed. It may also be necessary to consult other doctors:
- vertebrologist;
- neurosurgeon;
- vascular surgeon.
The “main” doctor to contact for sciatica is a neurologist, but he can also refer you to other specialists
During the treatment process, you also need the help of a physiotherapist, exercise therapy and massage specialist. The services of an osteopath may be helpful.
Possible complications
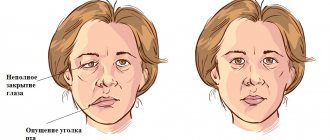
Doctors call facial paralysis the first complication that appears in the absence of adequate treatment. This means that a person who does not receive medical care in a timely manner is deprived of the opportunity to express his emotions through facial expressions on one side of his face. This condition can no longer be corrected, which will certainly affect the quality of life. Distortion of facial expressions will lead to the development of depression and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. Not every patient can come to terms with irreversible changes in their appearance without deep distress.
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of paralysis is the inability to close the eyelids on the injured side of the face. In this case, the eye will have to be regularly instilled with artificial tears to prevent the cornea from drying out, since natural hydration through blinking becomes unavailable for this eye.
Symptoms
A common characteristic sign of the disease is immobilization and distortion of part of the face, in which it turns into a sedentary or completely motionless mask. Additional symptoms depend on where the inflammation occurs.
The facial nerve is a paired nerve; when it leaves the brain, it divides into two symmetrical branches. One of them is responsible for the innervation of the right side, and the other is responsible for the innervation of the left side of the face.
As a rule, inflammation affects only one of the two symmetrical parts, so the symptoms of neuritis are almost always unilateral. Contractions of the facial muscles become difficult or impossible, this manifests itself when trying to frown, smile, close an eye or raise an eyebrow. The face becomes distorted and asymmetrical.
The corner of the mouth and the edge of the eye are lowered, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out. When you try to close your eyelids, the eyeball turns upward (Bell's palsy). When you try to close your eyelids, a gap remains between them, this is called lagophthalmos or “hare's eye.”
Since the facial nerve consists primarily of motor fibers, inflammation of the facial nerve results in muscle symptoms. Sensitive, painful symptoms (in the form of neuralgia) are not typical for such neuritis.
However, the common nerve cord includes the intermedius nerve, which consists of sensory fibers and provides the sensation of taste to the outer two-thirds of the tongue, as well as the functioning of the salivary glands. Therefore, with neuritis of the facial nerve, symptoms such as disturbance, partial loss of taste, and increased salivation (drooling) are possible.
Another possible symptom is tear gland dysfunction, dry eye, or watery eyes. A combination of these two symptoms is possible - the so-called “crocodile tears”, when the eye becomes abundantly moisturized when eating, but remains dry the rest of the time (Bogorad syndrome).
Paresis or paralysis of the face usually develops within 24 hours after the appearance of pain behind the ear - the first sign of neuritis. As the disease progresses, symptoms such as hearing loss or intolerance to loud sounds (hyperacusis) are possible.
Ear pain with neuritis can radiate to the back of the head, temple, and be accompanied by loss of coordination, dizziness, and hearing loss. The complex of these symptoms is called Hunt syndrome.
Disruption of the innervation of the external eye muscle with neuritis of the facial nerve is manifested by convergent strabismus. Along with the characteristic signs of inflammatory damage to the facial nerve, symptoms of concomitant diseases may be observed, for example, shooting pain in the ear with otitis media. Or symptoms of cerebrovascular accident due to atherosclerosis.
From the point of view of Tibetan medicine, inflammation of the facial nerve, like other neuritis and neuropathies, refers to disorders of the governing basis Wind (Rlung - Tib.).
This is a light and cold base that has a great influence on other control systems of the body. Its disorder usually manifests itself not only with local symptoms (neuralgia, numbness, paresis, paralysis), but also with metabolic, immune, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, excretory, reproductive systems, as well as hormonal regulation.
Sanzhizhapova Avgustina Dondopovna Reflexologist, neurologist Experience 39 years
Prevention of inflammation
To prevent the risk of developing inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to follow a number of measures:
- monitor oral hygiene and consult a dentist in a timely manner;
- do not stay in the cold for a long time or protect your face from freezing with a scarf;
- do not self-medicate otitis media.
At the first manifestations of pain on the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will stop the development of inflammation. In addition, early diagnosis allows for conservative treatment methods.
How is sciatica diagnosed?
Mild symptoms of sciatica in the form of tolerable pain in the legs/lower back can go unnoticed for a long time. In this case, a person may not contact a specialist. In a sense, this is even understandable: the sensations are not fatal, and it is not necessary to be examined. But it is strictly necessary to treat this disease. Otherwise, you may become disabled. And inflammation of the nerves is not the only problem worth attention, the signal of which is sudden attacks of pain. This happens, among other things, with neoplasms and spinal injuries.
When diagnosing sciatica, it is necessary to remember that it can be similar to pain from spinal tumors, myeloma, ankylosing spondylitis, and spondylitis.
If symptoms similar to sciatica are noticeable, you need to be examined by a neurologist. First of all, he will ask the patient about what his symptoms are, what the pain is like, and what his medical history is. With sciatica, the following diagnostic syndromes are noticeable:
- Sicard syndrome;
- landing syndrome;
- Legace's syndrome.
With Sicard syndrome, the patient experiences increased pain when bending the foot upward, which prevents him from making such a movement. With sitting syndrome, it is difficult for the patient to sit down when the leg is extended. Legace's syndrome is when a person has difficulty lifting his leg while lying on his back.
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve is extremely necessary to cure, but before that, diagnose it
When diagnosing sciatica, the most widely used are: