Palate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that forms from the mucous membrane of the hard and soft palate. This is a fairly rare disease. It is more common between the ages of 40 and 60 years. Men get sick 4 times more often than women.
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern research methods. The oncology clinic is equipped with modern equipment from leading American and European manufacturers, which allows you to quickly establish an accurate diagnosis. To treat malignant tumors of the palate, surgical interventions, chemotherapy drugs and innovative methods of radiation therapy are used.
The most malignant tumor of the palate occurs due to metastases of cancer of the nasopharynx and nose. The neoplasm affects the periosteum of the hard palate, lower and upper jaws, muscles and tissue of the oral cavity, and tongue. Atypical cells spread to the submandibular, mental and cervical lymph nodes.
What is the palate and where is it located in the oral cavity?
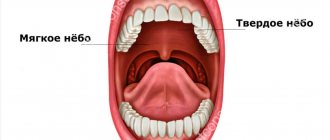
As mentioned above, this is a horizontally located partition that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. Approximately 2/3 of its surface suggests the presence of a bone base. These are solid processes in the form of plates that have a concave shape and are located in a horizontal position on the upper jaw. They are covered by a thin mucous membrane, which turns into the velum palatine. This is already a muscular formation with a fibrous membrane, also covered with mucous membrane.
The upper palate is the wall located in the mouth from above in the horizontal plane
It is the soft part that represents the barrier between the mouth and pharynx, and on its far edge there is the uvula. The palate is directly involved in the process of chewing food and swallowing, helps in the reproduction of sounds, which makes it an important component of the articulatory apparatus.
Reasons for the development of the inflammatory process
Inflammation of the palate near the tooth can occur:
- due to mechanical damage when eating crackers, seeds, nuts and other solid foods,
- thermal burn,
- some diseases - candidiasis, stomatitis,
- frequent smoking,
- pathologies of the jaw joints,
- inaccurate tooth extraction, violation of the rules for installing a microprosthesis.
Inflammation can develop under the influence of one or more factors. The problem cannot be ignored, as this can lead to blood poisoning, problems with breathing and swallowing.
Causes and symptoms of inflammation
At the initial stage of the pathological process, primary inflammation is diagnosed. First, blood circulation in the tissues is disrupted, and the person begins to experience moderate discomfort or even pain, which is especially noticeable when touching the palate with the tongue. Slight swelling appears. When the problem enters the stage of secondary inflammation, the pathological process takes over more space, and the pain noticeably intensifies. When the upper palate hurts, there can be a variety of reasons. Let us consider the main prerequisites in more detail.
Infections in the mouth
Infections of a bacterial and fungal nature (candidiasis) can provoke inflammatory processes, including on the mucous membrane of the palate. With this clinical picture, a whitish coating usually appears, painful ulcers, red areas and swelling may appear. If the problem is not addressed in time, the burning and pain will intensify, which will subsequently create serious difficulties in chewing food and swallowing.
The photo shows candidiasis in the mouth
Mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries to the mucous membrane
The palate is easily scratched by hard foods, such as seed shells or crackers. The problem may also be the appearance of a thermal or chemical burn after eating too hot food/drinks or sour, salty, spicy foods. Such microtraumas in conditions of insufficient hygiene become a favorable aid for the formation of pathogenic microflora and infection of tissues. The result will be redness and soreness. The mucous membrane usually swells, ulcers and blisters appear.
Dental diseases
Pathologies such as caries, pulpitis and stomatitis can also lead to the appearance of painful ulcers on the palate and along the entire perimeter of the mucous membrane. The inflammatory process often spreads to the surrounding soft tissues, including the palate and tongue, causing corresponding complications. A similar clinical picture also occurs with severe periodontitis or periodontal disease.
Another possible problem is leukoplakia, the development of which is accompanied by the formation of compactions in the mucous membrane and the appearance of dense whitish plaques, which can also be localized in the palate. The cause of this pathological phenomenon may be trauma, frequent rough mechanical impact on the mucous membrane, excessive smoking and consumption of low-quality alcohol.
The photo shows leukoplakia
Other Possible Prerequisites
In some cases, symptoms of inflammation appear after the installation of metal crowns or braces. Here, the appearance of redness, itching, and swelling can be provoked by the influence of galvanic currents and a corresponding change in the natural environment in the oral cavity. The reason why the soft palate in the mouth hurts may be associated with infectious diseases of the ENT organs.
It should also be noted that adult heavy smokers and those who abuse low-quality alcohol are especially susceptible to frequent dental problems. It also happens that inflammation of the palate is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the submandibular, sublingual and minor salivary glands. Sometimes, as a result of such disorders, various neoplasms arise in the oral cavity - from small benign to serious malignant tumors, including fibromas, papillomas, lymphangiomas and other painful phenomena. In any case, if you suspect a problem, you should definitely contact a specialist.
Diseases of the ENT organs can cause this symptom
Why does inflammation occur?
The muscular structure of the palate is covered on top with a mucous membrane, which is subject to the development of an inflammatory process. Inflammation often occurs under the influence of such factors:
- burn of the mucous membrane as a result of consuming excessively hot food and drinks;
- damage to the palate due to dental diseases - periodontitis, stomatitis, caries, pulpitis;
- disruption of the oral environment due to the action of metals - when wearing braces or installing crowns;
- smoking;
- allergic reactions to medications;
- neurological diseases affecting the joints of the upper or lower jaw;
- osteomyelitis - an infectious lesion of the bone tissue of the jaw;
- malignant neoplasms;
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract - sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis.
The development of the inflammatory process of the palate may be facilitated by some of these causes in their entirety or separately from each other.
The nature of the pain and the need to contact a specialist
If the roof of your mouth hurts, the nature of the course of this symptom usually depends on the cause that led to the inflammatory process. To understand what exactly caused this reaction, you will have to seek medical help. If this is simple damage from rough food, the wound may swell for several days, but the sensations will be tolerable, and the discomfort should gradually subside.
To speed up the healing process, experts recommend being careful when eating and rinsing your mouth with a light antiseptic solution or a soothing herbal infusion. You should consult your doctor personally about suitable medications for symptomatic therapy.
If the pain does not go away within 3-4 days and only gets worse, you should definitely visit a dentist. If the situation is ambiguous, the specialist will suggest undergoing a diagnostic examination. To determine the cause of the pathological process, you may have to undergo x-ray diagnostics, as well as visit other specialized doctors, for example, an ENT specialist, an infectious disease specialist, a therapist or an oncologist.
Main symptoms of laryngeal edema
Despite the fact that in most cases laryngeal edema itself is a symptom, it is not always possible to detect it promptly. Professional medical diagnostics or special signs characteristic of laryngeal edema3 come to the rescue:
- Severe cough, most often of the “barking” type;
- Hoarseness, loss or severe changes in voice - given that the human voice apparatus is located in the larynx, this is a quite obvious sign;
- Gradual progression of suffocation, breathing becomes difficult.
Laryngeal edema does not always develop slowly and unnoticeably. In rare cases, an emergency condition occurs in which swelling occurs immediately (laryngospasm). In such a case, the symptoms of laryngeal edema will be pronounced:
- The appearance of cyanosis on the face;
- Severe suffocation and oxygen starvation, complete asphyxia is possible.
Additional signs of the development of laryngeal edema may include more general symptoms that are characteristic of many other diseases:
- Temperature increase;
- Feeling of a foreign object in the throat, while the exact position cannot be determined;
- Discomfort and pain in the larynx area, especially when swallowing;
- Intoxication of the body - general weakness, nausea, headaches, muscle pain, etc.;
- Shortness of breath, even at rest.
How is differential diagnosis performed?
As mentioned above, if the doctor has doubts about the cause of the symptoms, the patient will have to undergo a differential diagnosis. It is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, excluding all other pathologies with similar symptoms. As part of such a survey, the following activities may be required:
- visual examination and medical history,
- x-ray examination,
- general blood tests and allergy tests,
- consultation of specialized specialists,
- full examination of the body, including ultrasound and CT.
For diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo tests.
But such in-depth diagnostics are not needed in all cases. If the clinical picture is obvious, the doctor will not require additional procedures. However, it is very important to establish an accurate diagnosis, because the further course of treatment will directly depend on it.
Diagnosis of laryngeal edema
In most cases, an experienced doctor (otolaryngologist, pulmonologist or even a therapist) can easily diagnose laryngeal edema. A visual examination or laryngoscopy will give an understanding of the condition of the sick person’s larynx. Endoscopy will show the most complete condition of the larynx. With edema, redness is almost always present, as is swelling of the laryngeal mucosa, and the glottis will be noticeably narrower4.
However, it is not recommended to diagnose this condition yourself. A doctor should examine it, since complications or severe forms are possible, in which there is a risk of suffocation, and swelling can directly indicate the development of a dangerous disease.
What to do if your palate hurts. Treatment methods
First of all, it is necessary to treat exactly what served as the impetus for the development of the pathological process. As part of supportive symptomatic therapy, special solutions for oral baths and mouth rinses are usually prescribed. These may be antibacterial, anti-inflammatory or antifungal agents, depending on the nature of the problem.
Gels and ointments are also often prescribed for external use, with a similar therapeutic effect or, for example, antihistamine action, if swelling, redness and itching are an allergic reaction. If a serious infection occurs, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. It is important to remember that only a professional doctor can select adequate treatment in your particular case.
Various gels may be prescribed for treatment
What drugs are used in different clinical cases
The choice of treatment must be justified by the cause of the problem. So, all the drugs that are prescribed if the palate is inflamed or if the gums also hurt can be divided into 3 large groups:
- antifungal: these include broad-spectrum antimycotics that effectively combat the development of candidiasis and trichomonas. They are usually prescribed for trauma to the mucous membrane, for stomatitis and thrush - “Levorin”, “Nystatin”, “Candide”,
- antibacterial: these include antibiotics that specifically prevent the proliferation of bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms. So, for example, “Metronidozole” and “Amoxicillin” can only be prescribed by a doctor, and their help is usually resorted to when there is a serious infection of tissues and an increase in temperature. But antibacterial rinsing solutions are used as maintenance therapy, and these include “Chlorhexidine”, “Stomatofit” and others,
- antiviral - as a rule, used in the early stages of the disease and for preventive purposes, they suppress the reproduction of viruses. Such drugs include “Acyclovir”, “Oxolin”, “Interferon”1.
Drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Any of the above drugs, and especially antibiotics, can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Remember, if suspicious symptoms appear, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. The longer you delay visiting a specialist, the higher your chances will be of encountering very serious consequences and complications.
Gels and ointments for treating inflamed mucous membranes
External agents, which include gels and ointments, are also prescribed to relieve pain and acute signs of inflammation. Below, as an example, are the most effective and popular drugs from this pharmacological group:
- “Nystatin” ointment - it is prescribed for candidiasis. The active ingredients in the composition destroy fungal cells and create a reliable barrier that prevents the further spread of infection,
- "Levomekol" ointment - has an antibacterial effect and promotes tissue regeneration processes. The active components of the product help reduce inflammation and actively fight the population of harmful microorganisms,
- “Solcoseryl” – this product contains an extract of calf’s blood (dialysate), which has a powerful therapeutic effect. The gel restores oxygen metabolism, triggers tissue regeneration processes at the cellular level and promotes collagen production, thereby accelerating damage processes,
- "Cholisal" is an anesthetic gel with a slight cooling effect. Helps relieve swelling and inflammation, destroys pathogenic microflora.
Gels and ointments are prescribed to relieve pain and acute signs of inflammation.
The choice of a suitable remedy remains at the discretion of the attending physician and directly depends on the cause of the development of the inflammatory process in the palate. Before use, you should carefully read the instructions and then follow all the instructions of the treating specialist.
A Brief Overview of Mouthwashes
Pharmacy rinses help relieve acute signs of inflammation, relieve pain and reduce swelling. Among the most effective drugs in this category, experts identify the following medications:
- Chlorhexidine is an inexpensive antimicrobial agent that helps to significantly reduce inflammation and stop the spread of infection. It is recommended to use for rinsing no more than 3 times a day,
- “Stomatofit” is a herbal remedy that helps with gingivitis and periodontitis,
- "Furacilin" - prescribed for inflammatory processes in the throat, palate and oral cavity. Has a pronounced antimicrobial effect and ensures the destruction of pathogenic microflora,
- “Chlorophyllipt” - a composition based on eucalyptus helps to soothe an irritated throat and palate during colds.
Pharmacy rinses help relieve acute signs of inflammation
“For some reason, my palate gets irritated about once every six months. I don't know, maybe it's too sensitive. And it happens that the pain is simply unbearable, you have to swallow painkillers. But in such cases, I usually rinse my mouth with chlorhexidine and after a week everything goes away completely.”
MariaS., from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
You should start using any of the drugs described above only after consulting a specialist. First, you should visit your dentist and determine the exact cause of the inflammation.
What does traditional medicine offer?
Some remedies prepared from herbal ingredients based on folk recipes also help relieve inflammation and reduce pain in the palate. Tannins and astringents in their composition have a disinfectant and analgesic effect. The most popular and proven recipes are described below, but it is better to first discuss their use with your doctor.
Calendula tincture
Used for pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis and fungal infections in the oral cavity. To prepare the tincture, you can dissolve a teaspoon of the product in 200 ml of warm water. Or pour raw calendula flowers with a tablespoon of boiling water, strain and use for rinsing while warm.
Calendula tincture will relieve pain
Chamomile decoction
Soothes, relieves acute inflammation, helps with colds and fungal infections. A tablespoon of dried flowers is brewed in 200 ml of boiling water, allowed to cool, filtered and used for rinsing 3-4 times a day.
Chamomile decoction helps well in treatment
Sage based rinse solution
Recommended for laryngitis, as well as for scratches on the palate, pharynx or larynx. The solution perfectly relieves inflammation and relieves pain. Sage leaves and flowers (1-2 tablespoons) are brewed in 200 ml of boiled water. The product is infused until it cools completely, then filtered and then used for rinsing up to 6-7 times a day.
Oak bark decoction
Effectively relieves bleeding and inflammation, eliminates swelling. To prepare the solution, 2 tablespoons of crushed oak bark are diluted in 200 ml of water and heated in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. Remove, leave to brew for an hour, filter and then use for rinsing 4-5 times a day.
Gargling with a decoction of oak bark will help in treatment
Honey with tea or milk
Honey has an enveloping and soothing effect and effectively fights the proliferation of fungi and the spread of infection. To enhance the healing effects, it is recommended to eat honey with a warm drink or dilute it in tea.
You can relieve pain in the palate and reduce inflammation with the help of a medicinal mixture, for the preparation of which butter and honey should be mixed in equal proportions. The composition must cool completely, after which it can be taken 0.5-1 teaspoon 5-7 times a day.
Tea with honey is used to treat throat
How to prevent inflammation of the palate
A swollen upper palate is an unpleasant symptom that is easier to prevent than to treat. To do this, you need to follow simple rules of prevention:
- brush your teeth twice a day, after each meal, rinse your mouth with mouthwash or at least water;
- consume warm food and drinks;
- eat a balanced diet, walk more, toughen up, that is, increase immunity, which will prevent the development of inflammation;
- give up bad habits to prevent injury to the mucous membrane;
- visit the dentist periodically - this will allow you to identify diseases at an early stage of their development and provide timely treatment;
- minimize stressful situations.
You should stop eating crackers, chips and candies. Not only are these foods not part of a healthy diet, but they can also injure the palate. The child needs to be explained that he should not put foreign objects in his mouth.
Possible complications
Severe consequences of the pathological process are possible if you ignore obvious symptoms for too long and do not consult a specialist in time. The following manifestations become frequent accompaniments of inflammation of the palate mucosa:
- increased salivation,
- further spread of the lesion,
- the appearance of bad breath,
- bleeding gums,
- purulent processes.
In severe cases, the body temperature rises and there is a real risk of developing sepsis, that is, a general infection of the body. Such dangerous complications can result from tonsillitis, stomatitis, candidiasis or any other dental disease.
Therefore, if you experience pain in the oral cavity, you should immediately see a specialist. If it is a simple wound, the doctor will recommend suitable disinfectant, anti-inflammatory and wound-healing rinse solutions. If the reason is not so obvious, you will have to undergo a full examination and receive direct recommendations from a specialist.
1Lukinykh L.M. Diseases of the oral mucosa, 2000.