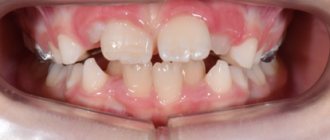
If you go to the mirror and open your mouth wide, you can see two formations that are located on the side surfaces, in the depths of the pharynx, which are shaped like an almond. This is why the tonsils are called tonsils. And since the tonsils are located in the soft palate, they are called palatine tonsils.
Also, in common parlance, the palatine tonsils are also called tonsils. They are one of the important organs of the pharyngeal immune system and form an important part of the Pirogov-Waldeer lymph-epithelial pharyngeal ring.
Palatine tonsil, tonsila palatina. It is located in the tonsillar fossa between the palatoglossus and velopharyngeal arches.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
What other tonsils are there in the pharynx?
Other tonsils that form the lymphoid pharyngeal ring are: adenoid vegetations, or, more simply, adenoids, which are not a paired organ. They are located in the dome of the nasopharynx. It is impossible to see them with the naked eye. In order to recognize the condition of the adenoids, it is necessary to perform an endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx. Inflammation of the adenoids is called adenoiditis and is more common in children.
Also in the pharynx there is a lingual tonsil, located at the root of the tongue, which, like the adenoids, is an unpaired organ.
There are also tubal ridges, which are also called tubal tonsils. They are located at the entrance to the pharyngeal mouth of the auditory tube. The tube ridges are located deep in the nasopharynx, on the lateral (medial) surfaces of the nasopharynx on the right and left. Tubal tonsils perform an important function - they protect against infection entering the auditory tube. Since each of the tonsils of the lymphoepithelial pharyngeal ring deserves separate close attention, in this article we will only talk about the palatine tonsils and chronic tonsillitis. Other tonsils and the pathology they cause will be described in detail separately, in other relevant ENT articles.
Read more about tonsils
It must be said that the palatine tonsils are the largest lymphoid formations of the entire pharyngeal ring, and they play, perhaps, the leading role in the disposal of bacterial and viral infections that enter the pharynx by airborne droplets.
Due to their size, the palatine tonsils are the first to stand in the way of microbes that enter the oral cavity from the external environment, and protect the body from infection by viruses, bacteria, spirochetes, protozoa and other microorganisms.
The palatine tonsils have depressions - lacunae, which in turn are exit holes for deep and sharply convoluted canals - crypts, which are located in the thickness of the palatine tonsil, leading to its root. The number of lacunae and crypts can vary from 1 to 14, but on average, in each amygdala there are from 4 to 7 lacunae. The diameter of the lacunae can also vary, depending on gender, age, individual characteristics of the patient, as well as the duration and severity of the disease and the presence of scar changes in the tonsils themselves.
It is believed that the wider the exit hole - the lacuna - the higher the likelihood of the palatine tonsil to self-cleanse. This statement is true. Accordingly, the smaller the diameter of the lacuna, the more pronounced and severe the tonsillitis. Moreover, if the tonsil produces a large amount of caseous-necrotic detritus (plugs), the severity of the course also noticeably increases.
Normally, on the mucous membrane of the palatine tonsils, as well as in the thickness of the palatine tonsils, in the lacunae and crypts, there is a growth of non-pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora, in normal (permissible) concentrations. If there are more microorganisms (for example, due to intensive growth, or the addition of other pathogenic microflora from the outside), the palatine tonsil immediately destroys and utilizes the dangerous infection and normalizes a dangerous condition for the body. At the same time, the macroorganism, that is, the person, does not notice this in any way.
The tissues of the palatine tonsils produce the following main protective substances: lymphocytes, interferon and gamma globulin.
The palatine tonsils act as a serious infectious and inflammatory barrier and are an important component in creating not only local, but also general immunity in the human body. Therefore, when it comes to removing the palatine tonsils, you first need to think ten times, weigh the pros and cons, and only after that make a decision about removing the tonsils.
Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is an autoimmune disease that occurs as a result of frequent sore throats and a decrease in the body’s overall resistance since childhood. With the development of the disease and its exacerbation, a person does not have enough general immunity to keep the palatine tonsils “in working order” and adequately fight the infection.
If harmful microbes get onto the surface of the mucous membrane and into the lacunae of the palatine tonsil, a real battle occurs between the microbes and the human immune system.
The palatine tonsil fights all pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic infections, but not being able to fully resist attacking microbes, it provokes either a new outbreak of sore throat or an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis (treatment cannot be delayed in any case), thereby triggering an infectious-inflammatory process in palatine tonsils.
As a result of a lost fight, pus accumulates and stagnates in the lacunae of the tonsils, that is, dead leukocytes that come to the aid of the tonsil in the fight against a dangerous infection. The purulent masses irritate and inflame the tonsil tissue from the inside and have a toxic effect on it, thereby causing a sore throat - a severe infectious outbreak of inflammation of the tonsils.
In the absence of quick and adequate treatment, the contents of the lacunae and crypts of the palatine tonsils serve as a breeding ground for pathogenic microbes and a constant source of infection, even after an attack of tonsillitis.
Disease Prevention
Strengthening the immune system prevents inflammatory processes from developing. In order to prevent the development of diseases, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle: avoid bad habits, eat right, and monitor the general condition of the body. To maintain normal tonsils, it is enough:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Avoid cold drinks.
- Eliminate all possible sources of infection: sinusitis, caries, sinusitis.
- At the first signs of infection, contact a medical facility.
Forms of the disease
- recurrent form, that is, with frequently recurring sore throats;
- protracted form, when the inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils is characterized by a sluggish and prolonged course;
- compensated form, when episodes of sore throat and exacerbation of tonsillitis are not observed for a long time.
Chronic tonsillitis is the most common disease among all diseases of the pharynx and one of the most common diseases of all ENT organs, along with such a diagnosis as acute sinusitis.
Chronic tonsillitis can affect both adults and children, from the moment the palatine tonsils begin to develop (from 2-3 years). Moreover, the incidence of this disease in childhood is much higher.
Some respiratory diseases can also be classified as social diseases. For example, sinusitis and tonsillitis are among them. Poor environment, stress, lack of sleep, overwork, monotonous and poor nutrition, as well as poor heredity are predisposing factors to the development of the disease.
Causes
The development of the disease is closely related to frequent sore throats (acute tonsillitis). Very often, incompletely cured tonsillitis leads to chronic tonsillitis. Very often, tonsillitis is an exacerbation due to the accumulation of plugs in the tonsils - caseous-necrotic masses, which are often confused with food debris.
Main reasons for development
- Unfavorable working conditions. The greatest influence is exerted by gas and dust levels in the air at work.
- Poor environmental conditions, pollution from vehicle exhaust gases, harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
- Low quality of consumed water.
- Weak (low) immunity.
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- Stressful situations.
- The presence of chronic diseases in the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and oral cavity - dental caries, purulent sinusitis, etc., which often leads to infection of the tonsils.
- Irrational or poor nutrition, in which excess amounts of proteins and carbohydrates are consumed.
- Heredity (mother or father suffers from chronic tonsillitis). It is very important for a woman to undergo one or two courses of treatment for tonsillitis during pregnancy (depending on the severity of the process) in order to minimize the likelihood of the disease developing in the unborn child.
- Frequent overwork, fatigue syndrome, inability to fully rest.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
Resection of the palatine tonsils (tonsillotomy) in children
Hypertrophied palatine tonsils, as well as adenoids, can cause breathing problems, snoring and even sleep apnea (stopping breathing) during sleep. A child’s tonsils often become a source of inflammation during a cold or sore throat. If a child gets sick up to seven times in a year, especially with sore throat, which is dangerous with serious complications, an otolaryngologist may advise solving the problem surgically. Today, tonsillotomy is performed using several methods: surgically, using a laser, or by freezing the tissue (cryodestruction of the tonsils).
Symptoms
How to independently recognize chronic tonsillitis? Symptoms and treatment in adults and children can only be correctly determined by an ENT doctor. Below are characteristic signs - if you find them in yourself, consult a doctor.
The disease is characterized by symptoms such as:
- Headache.
- Feeling of something foreign in the throat, as if something was stuck in the throat. In fact, this is nothing more than large accumulations of caseous masses, that is, plugs in the thickness of the palatine tonsils.
- Increased fatigue, weakness, decreased performance. All this is due to the so-called tonsillogenic intoxication, or in other words, intoxication syndrome.
- Aching pain in the joints and muscles (with severe illness).
- Aching pain in the heart, with interruptions in heart function - extrasystole (with severe illness).
- Pain in the lower back, in the kidney area (with severe disease).
- Bad mood, and in some cases increased body temperature, and for a long time.
- Persistent skin rashes, provided that there was no previous skin pathology.
All these symptoms appear due to the entry of waste products of microorganisms into the blood from the palatine tonsils, i.e. staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, poisoning the entire body.
Bad breath appears due to the accumulation of organic substances and the decomposition of bacterial infection in the lacunae (recesses of the tonsils) and crypts (their canals). Tonsils become a source of bacterial infection, which can spread throughout almost the entire body and cause inflammation of the joints, myocardium, kidneys, paranasal sinuses, prostatitis, cystitis, acne and other diseases.
If the tonsils do not cope with their function as an immune organ, then even slight overwork, stress, or mild hypothermia can significantly reduce the immune defense and open the way for microbes and exacerbation of the disease.
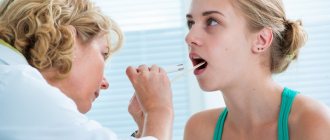
Rules for examining the throat
To assess the condition of the throat, it is necessary to follow a certain algorithm:
- The patient should be placed near a window, and if there is insufficient lighting, use a flashlight.
- If you don’t have a sterile medical spatula, take a spoon, wash it thoroughly and pour boiling water over it.
- Use the back of the spoon to press on the middle of the tongue (if you press on the base, you can cause a gag reflex).
- To assess the condition of the tonsils, you need to press your tongue to your lower lip and open your mouth wider.
If the examination is being performed on a child, you need to wait a few seconds. During breathing, the tongue will reflexively lower. This way you can better see the tonsils and lateral walls of the larynx.
Complications
Chronic tonsillitis is very dangerous due to rapidly occurring complications. The most severe of them are heart disease - myocarditis, inflammation of the joints - rheumatism and serious kidney damage - glomerulonephritis.
Some toxins that are produced by microbes in the tonsils and then enter the bloodstream can damage cartilage and ligament tissue. The result is inflammation and pain in the muscles and joints. Other toxins often cause persistent fever, changes in blood tests, fatigue, depression, and severe headaches.
Chronic tonsillitis can affect the functioning of such a vital organ as the heart. The tonsils are often parasitized by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the protein of which is very similar to the protein found in the connective tissue of the heart. Because of this, the immune system can show retaliatory aggression not only to the emerging streptococcus, but also to its own heart. As a result, heart rhythm disturbances, heart valve prolapses, and even the development of severe myocarditis and bacterial endocarditis occur.
For the same reason, articular surfaces and kidney tissue are at great risk. Unfortunately, the development of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and glomerulonephritis is extremely high.
Due to the fact that the source of infection remains in the tonsils for a long time, a distortion of the body’s reactivity occurs, resulting in allergic changes. In some cases, just one course prescribed by a doctor can get rid of itching and allergic rashes, and in some cases stop the development of bronchial asthma attacks.
Changes you can't ignore
Throat diseases have pronounced symptoms, but clinical manifestations are individual for everyone. There are a number of symptoms that may indicate a serious illness:
- elevated temperature;
- abnormal color of the tongue and larynx;
- pain that gets worse when swallowing;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- swelling of the throat;
- headache;
- ulcers, inflamed blood vessels;
- purulent and necrotic formations.
The appearance of several symptoms at once is a signal to consult a doctor. If the patient's condition worsens, emergency medical attention may be required.
Important! Some pathologies can provoke swelling of the larynx. If help is not provided in time, a person may die as a result of suffocation.
Chronic tonsillitis during pregnancy
It is very important to pay attention to the disease during pregnancy. When planning a pregnancy, even in the case of a compensated condition, that is, a condition outside of an exacerbation of tonsillitis, it is highly advisable to carry out a planned course as prescribed by a doctor. This will reduce the bacterial load on the entire body in general and on the palatine tonsils in particular.
It is very encouraging that doctors are now referring pregnant women and women who are just preparing for pregnancy for treatment of tonsillitis. Unfortunately, in some cases one of the reasons for not carrying a pregnancy to term is this disease, although at first glance it is hard to believe, tonsillitis is a traffic jam, the treatment of which and other manifestations may seem in no way related to pregnancy.
Before conceiving a child, it would be correct to examine the future father of the child for the disease and, if necessary, treat it as well. This will significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic tonsillitis in the unborn child. And, on the contrary, the worse the condition of the future father and especially the mother, the risk of developing the disease in the child increases many times over.
Before pregnancy, it is very important to carry out comprehensive treatment of the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis. But even during pregnancy, it is recommended to repeat the course, preferably in the second trimester, when the woman’s condition is perhaps the most comfortable. It is important to note that physiotherapeutic procedures cannot be carried out during pregnancy, but it is highly desirable to wash the palatine tonsils using a vacuum method, followed by treatment with antiseptic solutions.
The right approach
Sore throat, tonsillitis - treatment in children and adults is important to carry out immediately for all diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx that bother you. If breathing through the nose is impaired, and mucus or mucopurulent discharge flows down the back wall of the pharynx, then these symptoms should be given special attention.
Chronic tonsillitis - treatment (effective) can be conservative and surgical. Due to the fact that the removal of tonsils can cause serious harm to the defenses and immunity of the human body, otolaryngologists should try their best to preserve the tonsils and restore their functions without resorting to surgery to remove the tonsils. Modern methods of treating tonsillitis provide a greater chance of recovery without intervention.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Chronic purulent tonsillitis - treatment of a conservative type must always be carried out in an ENT clinic, performing a complex, pathogenetically based course of treatment, as well as using a medicinal approach - medications prescribed by an ENT doctor.
What are the dangers of adenoids if you ignore them?
- Chronic oxygen starvation. When a child breathes through the mouth, less oxygen enters the lungs, and therefore into the blood, than when breathing through the nose. Oxygen starvation is especially dangerous for the brain. Children study poorly, have poor memory, and reduced attention and performance; they are restless and irritable, and sleep poorly.
- Hearing loss. Due to the fact that with adenoid hypertrophy, the mouth of the auditory tube is blocked, its ventilation is disrupted. And also due to recurrent catarrhal and purulent otitis media.
- Constant source of infection. Chronic inflammation in the tonsil can give rise to the development of autoimmune and allergic diseases. Sinusitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, and bronchitis often appear. All these diseases are frequent “companions” of adenoid hypertrophy in children.
- Frequent colds. There is no normal breathing through the nose and the protective function of the mucous membrane - there is mucus and conditions for the emergence of infectious diseases. A child with adenoids gets sick longer and has a harder time recovering.
- Changes in speech. Nasality, the habit of speaking “out of the nose”, even the inability to pronounce individual letters, impaired growth of facial bones - all this has an unfavorable effect on speech.
The order and stages of treatment.
Initial appointment. Complaints and anamnesis.
The doctor asks what exactly is bothering you or your child.
Tell us when difficulty breathing through your nose and snoring at night, especially strong and intermittent, began. Do not hide other symptoms - fatigue, sleep disturbances, decreased memory and attention, headaches, digestive problems. Find out how often your child gets sick, how quickly he recovers, and how you treat a cold. If you have already had such symptoms and you have sought help from specialists, been tested, been examined and treated in another clinic, take the card and test results with you. The ENT doctors at the Energo Clinic care about all the details to help you and your child. Objective examination
During a general examination, especially with significant hypertrophy of the adenoids, a typical “adenoid” face attracts attention: an open mouth, an enlarged and swollen nasolabial triangle, due to chronic hypoxia, bruises under the eyes, a drooping lower jaw, changes in the skin under the nose, deformation of the facial bones and bite. Breathing through the nose is difficult or impossible. The degree of hypertrophy is clarified during a special study using a mirror - anterior rhinoscopy. Adenoids are located in the posterior superior part of the nasopharynx. They often spread down the side walls, to the pharyngeal openings of the auditory tubes, sometimes completely blocking the choanae. The wide base is attached to the roof of the nasopharynx; the tissue growths are divided into several parts by deep crevices; they are soft and pale pink in color. In approximately half of patients with grade 2-3 adenoid hypertrophy, regional lymph nodes—submandibular and cervical—enlarge. This means that the infection has “passed the barrier”, and the outflow of lymph is difficult.
A complex approach
First stage
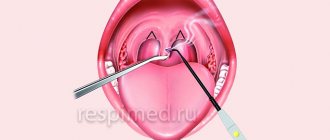
Viral tonsillitis - treatment with a good and pronounced effect is obtained by washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils. There are two ways to wash the tonsils.
A very old method is to rinse the tonsils with a syringe. Previously, this method was widely used, but today it is used for lack of a better one or when the patient’s gag reflex is very pronounced.
The disadvantages of this method are that during the process of washing the palatine tonsils, the pressure created by the syringe is not sufficient to effectively wash out caseous masses from the lacunae of the tonsils. Also, this technique is contact and traumatic, since when using a straightened attic needle, its thin and sharp end can prick the inner surface of the palatine tonsil, namely the crypts - the channels into which the needle enters. Also, the tip from the set with a syringe is used for rinsing the tonsils and injecting into the larynx. On the contrary, it is very wide in diameter and injures the tonsil tissue when inserting the tip into the lacuna, or in general, due to the large outer diameter, it cannot always get there.
Practice has shown that today, the best results are achieved by the approach when the ENT uses the Tonsilor attachment.
First, it is necessary to rinse the lacunae of the palatine tonsils with a modified attachment of the Tonsilor apparatus with a transparent antiseptic solution, for example, saline solution (also known as isotonic sodium chloride solution). This is necessary so that the doctor can clearly see what he is washing out of the palatine tonsils.
Second phase.
Since the tonsils are washed from pathological secretions, it is necessary to immediately influence the tissues of the palatine tonsils with low-frequency ultrasound. At the same time, a medicinal solution passes through the ultrasonic tip of the “Tonsilor” apparatus, which, due to the ultrasonic effect of cavitation, turns into a finely dispersed medicinal suspension, which, due to hydraulic shock, hits the tissues of the palatine tonsil and the posterior wall of the pharynx with force and impregnates the medicinal solution into the submucosal layer of the tonsil.
The procedure for exposure to ultrasound is correctly called: Ultrasonic medicinal irrigation. In our clinic we use a 0.01% solution of Miramistin. This drug is good because it does not lose its properties under the influence of ultrasound. Miramistin is a very strong antiseptic drug, and ultrasound exposure further enhances the durability of the physiotherapeutic effect.
Third stage.
It is necessary to treat (lubricate) the palatine tonsils with Lugol's solution, which is also a strong antiseptic based on iodine and glycerin.
Fourth stage.
The otorhinolaryngologist at our clinic conducts a laser therapy session on the tissue of the palatine tonsils and the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. Laser treatment of tonsillitis in adults is very effective. Its action is aimed at reducing swelling and inflammation of the tissues of the palatine tonsils.
The laser radiation source can be installed in the oral cavity and acted in close proximity to the palatine tonsils and the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall, thereby achieving the best results.
You can also install the laser emitter on the skin of the anterolateral surface of the neck in the projection of the location of the palatine tonsils and the posterior wall of the pharynx.
Fifth stage.
It is recommended to conduct sessions of vibroacoustic influence. They are carried out with the aim of normalizing microcirculation in the tissues of the palatine tonsils and improving the trophism (nutritional function) of the palatine tonsils themselves.
Sixth stage.
Effectively sanitize the microflora located on the surface of the palatine tonsils using ultraviolet irradiation (UVR).
This method has long been known, has proven itself very well and is still in service in many city (especially children's) clinics.
In this case, it is necessary to approach courses. The number of procedures in each specific case is determined individually at the first consultation with an ENT specialist. But for a lasting effect to occur, at least five sessions must be performed. If, during the fifth procedure, caseous and mucous masses are still washed out of the lacunae of the palatine tonsils, rinsing and other procedures must be continued “until clean rinsing waters”. As a rule, the number of ENT procedures does not exceed 10 treatment sessions.
After a full course, the lacunae of the palatine tonsils restore their ability to cleanse themselves, and the patient feels much better and more energetic.
In order to have a lasting result, it is necessary to carry out conservative treatment 2 to 4 times a year, as well as independently once every 3 months, take homeopathic and antiseptic medications.
In this case, you will most likely be able to avoid exacerbations of this disease and the need to remove the tonsils.
If, 2-4 weeks after the end of the course, caseous detritus again begins to accumulate in the thickness of the palatine tonsils, and the patient’s ENT complaints begin to bother them, as before the start of the course, conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis in children and adults is considered ineffective. In this case, the patient is asked to consider the option of surgical removal of the tonsils. But fortunately, such an outcome (result) is quite rare.
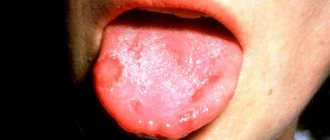
What should a healthy throat look like?
- The oral cavity does not contain visible changes, there are no ulcers or wounds.
- The surface of the tongue is clean, with a slight coating.
- The tonsils are the same size, pale pink in color.
- There are no tubercles, seals, plaque, or bubbles on the surface of the tonsils.
- There are no purulent formations, spots, plaque on the surface of the palate and palatine arches, the color is pinkish.
- The lateral area of the larynx is without swelling, pink.
- The posterior wall of the larynx is more saturated in color due to the location of a large number of vessels.
- There is no plaque, vesicles, or ulcers on the surface of the larynx, and the vessels are not enlarged.
Drug treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Dear patients! In this article I will describe only general principles and approaches.
More precise treatment will be offered to you at the initial ENT consultation, where an accurate diagnosis, form and degree of the disease will be made, as well as an optimal recovery plan will be proposed and a prognosis for the duration of remission will be given.
So:
- Antibacterial approach. Antibiotic therapy is important and necessary. But the decision to prescribe antibacterial drugs is made individually and only after a visual examination.
Antibiotics can be either light, prescribed for a short course and have no effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, or heavy, which must be prescribed under the guise of probiotic medications. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of chronic tonsillitis and the microflora that supports this condition. - Probiotic treatment is prescribed in case of taking aggressive antibiotics, as well as in the presence of concomitant gastritis, duodenitis, reflux esophagitis.
- Antiseptic approach. Antiseptic sprays, aerosols, and rinses also give a very good effect and are therefore mandatory in the fight against chronic tonsillitis. I prefer a 0.01% solution of Miramistin, a 1% solution of Dioxidine (1 ampoule diluted - 10 ml + 100 ml of boiled warm water) and Octenisept, which must be diluted with boiled warm water or saline in a dilution of 1:5 , or 1:6.
- Decongestant (desensitizing) therapy is mandatory. It is needed to relieve swelling of the palatine tonsils and the surrounding tissue, as well as the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. This is also necessary for better absorption of all medications used. Such modern medications as Cetrin, Claritin, Telfast can cope with these tasks. But if a certain desensitizing drug helps you for a long time, you should not change it to another.
- Immunostimulating therapy. Here I want to draw your attention to the fact that the doctor prescribes drugs that stimulate the immune system. These drugs should not be confused with immunomodulators, which are strictly prescribed by an immunologist based on the results of a blood test. There are not so many drugs that stimulate local immunity at the level of the palatine tonsils and the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. Of the well-known drugs, Imudon comes first. The course must be at least 10 days. You need to take (dissolve) Imudon 1 tablet 4 times a day.
- Homeopathic treatment. In addition to conventional drug therapy of a chemical nature, it is necessary to take homeopathic medications that improve the trophism and, as a result, the nutritional function of the palatine tonsils. The drugs of choice may be tonsillotren and tonsilgon, as well as rinses, steam and ultrasonic inhalations with infusions and herbs: propolis, string, sage, chamomile and some other herbs.
- Emollient therapy is used symptomatically, when, against the background of exacerbation of tonsillitis, as well as taking medications, there may be dryness, rawness and soreness in the throat. In such cases, you can use peach oil, which must be instilled a few drops into the nose, throwing back the head. You can rinse your mouth with 3% hydrogen peroxide (VERY IMPORTANT! 6% and 9% hydrogen peroxide CANNOT be used!!!). To do this, you need to pour half a bottle of peroxide (10 ml) into a cup, put it in your mouth and rinse the entire solution once, for as long as possible. Then the solution is spat out and rinsed from foam and bitterness with warm boiled water. After gargling with hydrogen peroxide, you will feel a significant softening and comfort in your throat. You can gargle twice a day, but no more.
- Analgesic therapy is used if necessary, as symptomatic therapy, depending on the severity of the pain syndrome. Of the tablet forms, it is better to give preference to Nurofen or Ketanal and its derivatives: Ketarol, Ketalar, Ketanof, Ketanal.
- Diet therapy. Nutrition also plays a significant role in recovery. It is necessary to limit the intake of spicy, fried, sour, salty and peppery foods. During treatment, you should exclude hard foods from your diet. It is also recommended to protect yourself from very hot and very cold foods. Drinking alcohol, especially strong alcohol, is also contraindicated.
First aid
It is difficult to swallow, the temperature has risen, when examining the throat, redness or pustular rashes are found - call a doctor. Before a specialist arrives, patients should not take fever-reducing pills, but only if it does not exceed 39 °C. High temperature will help the body cope with infection and destroy harmful microorganisms.
Scheme for relieving the patient’s condition:
- Drink plenty of warm drinks.
- Gargling with salt water, decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula).
- Rinse with Furacilin, Miramistin, Dioxidin and other products recommended by your doctor diluted with water.
- Dissolving lozenges with a calming and analgesic effect.
- Bed rest.
You should take antibiotics, and preferably all other drugs, only as prescribed by your doctor.
Surgical removal of tonsils
If we talk about the removal of the tonsils, then the operation to completely remove the tonsil tissue is called a bilateral tonsillectomy.
Partial removal of the tonsils is called a bilateral tonsillotomy.
It is extremely rare that the palatine tonsil is removed routinely on one side. There is also a practice of a number of hospitals (they like to do this in the Pirogov City Clinical Hospital No. 1) of removing the palatine tonsil or tonsils in case of a paratosillar abscess. This operation is called abscessonsillectomy. But it must be remembered that against the background of severe pain caused by an abscess, removal of the tonsil is extremely painful. Due to the purulent process, it is impossible to provide adequate anesthesia. Therefore, it is necessary to anesthetize the peri-almond tissue only with strong anesthetics: Ultracaine and Ultracaine DS-forte.
Routinely, palatine tonsils can be removed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. Previously, this operation was performed only under local anesthesia.
Fortunately, there is now modern equipment that allows removal of palatine tonsils under general anesthesia or under anesthesia using cold plasma coagulation - Coblator.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis
- Drug therapy
. If an ENT patient undergoes treatment courses in the clinic once every 6 months, then in addition to six-month procedures, he is recommended to take the drug Tonsilotren, with a frequency of once every 3 months, i.e. 4 times a year. The course of taking (resorption) of the drug is for 2 weeks (more precisely 15 days). It is also possible to instill 0.01% Miramistin solution, 4 pumps 4 times a day for 2 weeks, in courses 4 times a year. - Climatotherapy and spa therapy
. An important point in the prevention of chronic tonsillitis is visiting seaside resorts. Sunbathing, humidified sea air, swimming and, as a result, the inevitable entry of sea water into the mouth have a beneficial effect on the prevention of chronic tonsillitis. - Work and rest schedule
. In order for the periods of remission to be long, it is necessary to fully rest and not expose yourself to stress. It is not without reason that chronic tonsillitis, like sinusitis, is classified as a social disease, in which the more stress and workload there is at work, the higher the likelihood of exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. - Diet
. It is very important to eat right. Under no circumstances should you get carried away with fried, salty, peppery, sour, bitter, i.e. that food that irritates the mucous membrane of the back of the throat and palatine tonsils. Citrus fruits are contraindicated. The consumption of alcoholic beverages, especially strong ones, is also contraindicated. It is not advisable to eat very hot and very cold and solid foods.
Treatment or removal of tonsils?
Dear patients! If you have visited several specialists in this field, if a course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis has been carried out and none of the methods has brought the expected result, then only in this case should you think about removing the tonsils.
If a conservative approach gives lasting results for 4-6 months or more, then the palatine tonsils are able to fight on their own. Your task is to help the tonsils by regularly sanitizing them and stimulating their work physiotherapeutically.