December 3, 2020
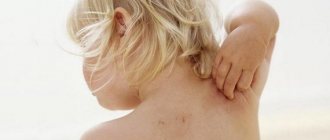
Contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin in an area that has come into contact with an irritating substance or environmental factor. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The point is the structural features of children's skin and the weakness of its protective mechanisms. The disease manifests itself in any area that has been in contact with the irritant, but more often on the face, arms, neck, and groin area.
If the provoking agent is recognized in time and the child is protected from it, the inflammation is well treated and the symptoms quickly pass. When the cause is difficult to identify or parents do not consult a doctor on time, the course of the disease becomes more severe.
Contact dermatitis occurs:
- simple - local irritation by some factor;
- allergic.
The second option will appear when the child has an increased sensitivity to this substance. The first interaction with it is outwardly unnoticeable, but chemicals are formed in the skin that bind to immune cells - T-lymphocytes. Immune cells remember the stimulus. Upon repeated contact, which can occur after a long time, T-lymphocytes trigger an allergic reaction and cause skin symptoms.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
How to cope with unpleasant symptoms?
It is important to avoid consuming raw vegetables and fruits that cause reactions, especially during allergy season. This is due to the fact that for many people, oral allergy syndrome develops more often and is more difficult during the flowering season of certain plants. You can reduce cross-reaction with food by boiling or baking vegetables and fruits, since proteins that cause allergies are destroyed at high temperatures.
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis and oral allergy syndrome can be managed with antihistamines. However, when it comes to treating a child, the choice of medications must be approached with great caution. First generation antihistamines can cause severe sedation and impaired psychomotor activity.
External causes of the development of allergic dermatitis in children
The disease can be caused by one of the factors or a combination of several.
- Physical - friction or pressure on the skin of fabrics, leather products, high or low temperatures, humidity, electric current, ultraviolet or x-rays.
- Chemical - various acids and alkalis, substances included in creams and hygiene products, medicines, tobacco smoke.
- Biological - sap and pollen of plants, bites and secretions of insects and animals.
Of the plant agents, the most dangerous are the juice of celandine, hogweed, nettle, pollen of meadow and weeds.
In industrial cities in winter, there are widespread cases of contact dermatitis under the eyes and on the hands of children. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air and touching the skin with wet mittens.
In infants, allergic inflammation can be caused by a combination of high humidity in diapers, fabric friction and the action of inappropriate cream.
A special type of contact dermatitis is phototoxic, when sunscreens degrade in sunlight and cause allergic damage to the epidermis.
What is oral allergy syndrome?
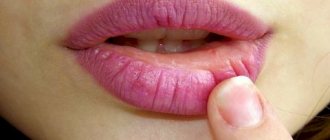
Another little-known reason why a child's palate itches is oral allergy syndrome. It occurs in patients with pollen allergies (50-75% of cases). The syndrome is accompanied by itching and subsequent swelling of the mucous membrane of the lips and oral cavity, including the palate, after eating vegetables, fruits or nuts.
This health problem occurs because the proteins found in some fruits and vegetables are very similar to the proteins found in pollen. They can confuse the immune system, causing an allergic reaction or worsening existing symptoms, which is called cross-reactivity.
When oral allergy syndrome develops, children and adults may react to different foods depending on what type of seasonal allergy they suffer from. For example, if you are allergic to birch pollen, apples, celery, carrots, almonds and hazelnuts can cause a reaction. If your child's palate is red and itchy after eating nuts, you should consult an allergist, as mild symptoms may only be the beginning of a more serious allergic reaction to nuts.
Children with grass allergies may have the same reaction to peaches, tomatoes, melons and oranges. Those who react to ragweed may experience itching and swelling of the oral mucosa when eating foods such as banana, cucumber, melon and zucchini.
Dermatitis in a child and psychosomatics
Skin health directly depends on a person’s mental well-being. Stress changes hormonal levels and metabolism, causing disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, a calm emotional state will prevent exacerbation of the disease and delay the first appearance of symptoms.
When faced with contact dermatitis, analyze the causes and identify the allergen that caused it.
It's not always easy. To be sure of the correct diagnosis, conduct the necessary tests and receive treatment, come for a consultation at our center. In addition to treatment, you will learn how to properly prevent this disease. December 3, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Diagnostics
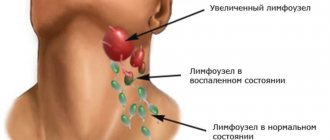
There is no specific test or examination to confirm the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis; the diagnosis is made clinically. The doctor will examine the rash and ask about the child's symptoms and family history of atopy and allergies. A history of eczema in family members (either as a child or still today) will be an important clue.
Your doctor will rule out other conditions that may cause your skin to become inflamed or itchy. In case of difficulties with diagnosis or severe course of the disease, the pediatrician will refer the child to a pediatric dermatologist or pediatric allergist.
The doctor may ask you to eliminate certain foods (such as eggs, milk, soy, or nuts) from your child's diet for 2 to 3 weeks before reintroducing them and monitoring symptoms. If the diet leads to relief of the rash, and provocation leads to its obvious exacerbation, this will confirm the diagnosis and the need for a diet.
Since there are no accurate laboratory methods for confirming the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, there are criteria for standardizing the clinical diagnosis (the best known are the Hanifin and Raika criteria).
The criteria are divided into “large” and “small”. To make a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, it is necessary and sufficient to detect three major and three minor criteria in the patient.
The big ones include:
- itching;
- dermatitis affecting the flexor surfaces in adults, or the face and extensor surfaces in infants;
- chronic or recurrent dermatitis;
- a personal or family history of skin or respiratory allergies.
Small ones include:
- specific facial features: facial pallor, erythema, hypopigmented spots, dark circles under the eyes, cheilitis, infraorbital folds, recurrent conjunctivitis, anterior neck folds;
- typical triggers: emotional factors, environmental factors, food, skin irritants;
- typical complications: susceptibility to skin infections, impaired cellular immunity, predisposition to keratoconus and anterior subcapsular cataracts, immediate skin reactivity;
- other signs: early age of onset, dry skin, ichthyosis, hyperlinearity of the palms, piliary keratosis, dermatitis of the hands and feet, nipple eczema, white dermographism, white pityriasis, perifollicular accentuation.
An explanation of each of these symptoms is beyond the scope of this article; The criteria are given here to help you understand what the doctor is guided by when making a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis.
There are also various scales for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis used by doctors and scientists, the most famous of which is the SCORAD scale. In this scale, the doctor must note the number, prevalence and severity of symptoms of atopic dermatitis, express them in points, sum up the points and, based on this sum, set the severity of the disease.
Pinworms - Baby food
“Sadikov's disease” - enterobiasis?
When a child’s body is affected by worms, the mother must take care of the baby’s specific nutrition. Eating the right foods can speed up the healing process. It is worth including in the diet:
- Spicy dishes. Pepper and spicy dressings worsen the habitat for pinworms.
- Sour vegetables and fruits. In an acidic sphere, parasites die faster.
- Horseradish with mustard. Not all kids will like such a specific product. But it undermines active reproduction and temporarily paralyzes the worms.
- Walnuts, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds. Such products help destroy parasites in the intestines.
- Olive and vegetable oil. Relieves irritation of the intestinal walls.
- Dairy products. With their use, medications are better absorbed and the intestinal microflora is not disturbed.
During the period of illness, it is recommended to exclude sweets, fatty foods, and foods with a chemical composition - the consumption of harmful foods creates all the conditions for the further proliferation of pinworms in the child’s body.
Main causes of food allergies
8 foods cause 9 out of 10 food allergies.
In the first year of a child's life: cow's milk, soy milk and egg.
Older children: peanuts, tree nuts, fish, seafood and wheat.
Seafood includes shrimp, crab, lobster, clams, oysters and scallops.
Tree nuts include all nuts (such as almonds and cashews) except peanuts. Peanuts and tree nuts are the most common triggers for severe reactions.
Of children with a proven food allergy, 40% have severe reactions. The remaining 60% have a mild reaction.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading allergists in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
Eruption of baby teeth. Symptoms.
Teething in children is not a disease, but a natural physiological process. It can be accompanied by different symptoms in different children.
Typical symptoms of teething:
- Swollen gums and increased salivation are a characteristic sign of the onset of teething. These phenomena can be observed 3-6 weeks before the appearance of the first tooth. Drooling is due to irritation of the nerve endings in the mouth. Redness, swelling and inflammation of the gums are caused by increased blood supply to the areas above the growing teeth. These manifestations cannot be avoided, but their intensity can be reduced. The drug Dantinorm Baby reduces swelling and soreness of the gums, relieves inflammation.
- The child makes intense chewing movements with his gums - this is how he tries to get rid of the obsessive itching. To help your baby relieve discomfort, offer him a special chewing ring. You can use any dense rubber toy if you are sure that the material from which it is made is safe. The item should not have sharp edges or crumble into small pieces. You can pre-cool the ring or toy in the refrigerator.
- A wet cough in a baby during this period may be caused by an increase in the amount of saliva. Cough associated with teething does not require treatment. However, if he becomes intrusive, wheezing and profuse sputum are observed, it is worth showing the baby to the pediatrician.
- A child’s runny nose appears due to the activation of the glands of the nasal cavity. Normal nasal discharge in this case should be watery and clear. You can help your baby by promptly clearing his nose of secretions.
- The increase in temperature during teething is short-term and transient. Low-grade fever (37-38 °C) should not be “brought down” with narrowly targeted medications. To reduce temperatures above 38 °C, it is recommended to use paracetamol-based medications, drink plenty of fluids, and wet wipes. A high temperature for more than two days is a reason to urgently consult a doctor!
- Digestive disorders and loss of appetite are caused by the restless state of the child and a change in the usual diet. Diarrhea can be caused by excessive swallowing of saliva. In this case, the stool should not be too frequent, watery, without a pronounced unpleasant odor. If bloody or mucous streaks appear, stools become more frequent and the temperature rises, you need to show your baby to a pediatrician to rule out infection. One of the accompanying symptoms may be diaper rash in the baby's perineum, the reason for this is excessive salivation during teething, and as a result, more acidic and fermented stools, affecting the delicate skin of the baby's bottom, resulting in a rash and irritation. By the way, a rash from excessive drooling can also appear around the baby’s mouth.
- Older children may complain of nagging pain in the ears, while younger children may complain of pulling or scratching their ears.
- Behavioral disturbances when feeding and falling asleep - the child becomes more restless and irritable
Dantinorm Baby helps to quickly relieve all the main symptoms of teething in a child. It contains plant components that help reduce inflammation and soreness of the gums and normalize digestion.
The drug is available in a convenient form, is easy to use and has virtually no contraindications. In any case, do not hesitate to show your child to the pediatrician once again, so as not to confuse the symptoms of teething with a more serious cause of the baby’s illness.
The order of eruption of baby teeth:
Timing and sequence of teething in children. One of the important milestones in the development of a baby is the eruption of the first teeth, which begins at the age of about 3 months and lasts until 2.5-3 years. Normally, a baby (i.e., up to one year) should erupt eight teeth in the following order.
- The two lower incisors usually erupt first. This occurs between 3 and 9 months.
- Next, they are joined by the upper incisors with a one-month delay, i.e., between 7 and 10 months.
- At the age of 9 to 12 months, first the lateral incisors on the upper jaw and then the lateral (second) incisors on the lower jaw should erupt in your baby’s mouth. Thus, a one-year-old child normally moves from the status of an infant to a toddler with eight incisors . After a year, teething occurs almost continuously in a child.
- In the interval of 12-18 months, the first upper molars (the so-called “first molars”) erupt, and 13-19 months – the first molars on the lower jaw.
- At 16-20 and 17-22 months, the eruption of canines should be expected on the upper and lower jaws, respectively.
- At 20-23 and 24-26 months, the child’s second molars erupt, first on the lower and then on the upper jaw (“second molars”). However, due to hereditary factors, as well as the child’s nutritional characteristics, these dates can significantly degree to change. Therefore, there is no need to panic with minor deviations. If in doubt, you should consult a specialist.
What else do parents need to know?
One in five people suffers from allergies at some point in their lives. Hay fever is the most common type of allergy. It is easily treated by avoiding allergens, washing the child in the shower after returning from outside during flowering season, over-the-counter medications, and sometimes additional prescription medications. Most children with hay fever only need allergy medication during seasonal outbreaks.
Allergy symptoms often change with age. Allergy symptoms can worsen during early childhood and often disappear as people get older.
Drug labels list the ingredients of allergy medications. Use the lowest dose possible to treat symptoms, and check with your child's doctor if he is younger than 6 years old before giving him an over-the-counter antihistamine.