Symptoms and treatment of lip jams in adults and children
The popular name for angulite is zaeda.
The disease is characterized by the presence of cracks in the corners of the mouth, erosion and irritation. In some cases, slight bleeding may occur. Common causes of sticking at the corners of the mouth include infection, irritation, and damage to the skin at the corners of the lips. Angulitis is rare in children. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in adults. Predisposing factors:
- decreased general immunity;
- deficiency of B vitamins;
- the presence of a bacterial infection;
- habit of licking lips, malocclusion;
- hypothermia;
- long-term use of corticosteroid drugs;
- eating unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- presence of caries;
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, anemia, HIV, liver disease).
Your pediatrician will tell you at your appointment what causes seizures in babies.
Why does a child have jams?
Almost every wound in the area of the outer and inner surfaces of the lips, as well as the corner of the mouth, can be called a jam. The exception is traumatic injuries to the skin and mucous membranes, which are quite common in children. Although such wounds resemble jams, they have a completely different origin.
In short, seizures in a child can occur due to infection, allergic reactions, or vitamin deficiency. In most cases, seizures in children are caused by streptococci.
Although, according to pediatricians, the most common cause of seizures in a child is a deficiency of riboflavin, which is necessary for healthy skin and normal growth of hair and nails. Also, seizures often occur due to decreased immunity and certain diseases. Many children suffering from binge eating also have a history of chronic tonsillitis, caries, and frequent colds and viral diseases. Among the causes of seizure in a child may also be staphylococci, streptococci, fungal diseases, and helminthic infestations. Timely treatment of such skin lesions helps to get rid of such unpleasant consequences.
In the etiology of true seizures in children, several factors are important. The most important of them are:
- Microbes;
- Allergic reactions;
- Various diseases and pathological abnormalities in the body;
Regardless of the root cause of seizures in children, its central link is the microbial factor. In this case, the pathogens become ordinary microorganisms that normally live on the surface of the skin. But when the child’s body is healthy, such microbes do not cause any manifestations. As soon as the protective forces decrease, they immediately begin to actively multiply, causing inflammation of the skin with the formation of wounds on the lips or in the corners of the mouth (jams).
With regard to specific types of pathogens that provoke the formation of jams, the main role belongs to streptococcal and fungal infections. It is these two classes of microbes that live on the surface of the skin in children and can cause inflammatory damage to the surface layers of the skin, which ends in the formation of a small ulcerative surface, which is called a jam.
Important! For seizures to occur, there must be a decrease in the immune function of the child’s body, against the background of which opportunistic microflora (fungi and steptococci) are activated. Sometimes this condition occurs as a result of infection with these microbes from the environment.
The following factors can lead to this very decrease in immune surveillance:
- Colds;
- Increased body temperature;
- Allergic reactions;
- Food, toys and objects infected with pathogenic microbes that the child puts into his mouth;
- Anemia of various types and origins;
- Hypovitaminosis;
- Immune system diseases;
- Diseases of the blood system;
- History of chemotherapy.
The most important thing is that seizures in children are not a common occurrence. But, if they occur, they usually last a long time. Children in transitional age periods (6-8 years and 13-17 years) are most prone to their appearance.
Symptoms of seizure in a child
Among the first symptoms of jamming, small bubbles appear in the corners of the child’s mouth, which over time burst, and erosion forms in their place. The skin of the corners of the lips becomes wet and bleeds, microcracks appear. The erosion either heals or becomes inflamed again. Children may experience pain that makes it difficult for them to eat or talk.
Treatment of seizure in a child
Treatment for seizures should be comprehensive. Before starting treatment, laboratory diagnostics are performed to identify the pathogen and provide more effective treatment. They also do a general blood test, stool culture for enterobiasis and dysbacteriosis, and examine the thyroid gland. In addition to antibacterial ointments and antiseptic lotions, multivitamins, immunostimulants are prescribed, and dysbacteriosis is treated. Correct the diet: increase the consumption of dairy products, vegetables and fruits.
If a child’s seizures do not go away
Sometimes it happens that seizures do not respond to local treatment for a long time. This is possible even despite the use of different combinations of agents, the action of which is aimed at different causes and mechanisms of development of this problem. This situation clearly indicates a serious weakening of the body’s immune and protective resources. Therefore, every mother must take this fact into account. After all, children with such problems are subject to careful examination:
- Examination by a pediatrician;
- Consultation with a dermatologist;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Biochemical blood tests;
- Sowing from the jam for microflora and its sensitivity to the action of specific drugs;
This will help to establish the true cause of the formation of ulcers in the child and their resistance to local treatment.
Serious health problems are always hidden behind a long-term non-healing lesion. The main thing is to identify them in time. This will not only relieve the jam, but also prevent the progression of the causative disease.
Additional measures
For wounds that are resistant to treatment, the following may be prescribed in combination with local medications:
- Antibiotics for systemic use: azithromycin, flemoxin, augmentin in small dosages;
- Antifungal agents: fucis, fluconazole, nystatin;
- Products to strengthen the immune system;
- Vitamin preparations: vitamins A, E, C, B, multi-tabs, kinder biovital.
You cannot self-medicate; consultation with a dentist is required.
Types of angulite
Considering the etiology, seizures can be primary and secondary. In turn, the primary ones are divided into: streptococcal, viral and candidiasis.
Viral seizures. They are caused by a viral infection (herpes virus). In this case, a doctor will help you choose an ointment for sticking in the corners of an adult’s lips.
Streptococcal seizures are caused by streptococcal infection. A characteristic manifestation is the formation of a yellowish-red crust.
Candidiasis angulitis. The cause is a fungal infection. This type is characterized by a chronic course and the absence of a crust.
Prevention of streptoderma
To reduce the likelihood of developing streptoderma in a child, follow the rules of prevention:
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- treat skin lesions with antiseptics;
- strengthen your immune system with vitamin complexes and good nutrition;
- do not wash your child with soap too often;
- At the first symptoms of any disease, consult your doctor.
Streptoderma is a curable disease, but you need to see a doctor in time. The sooner treatment is started, the easier it is to avoid complications and transition to a chronic form. You can undergo a qualitative examination of your skin condition at the SM-Doctor clinic. Qualified pediatric dermatologists will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Angulitis during pregnancy: how to get rid of it
Pregnant women are very vulnerable to various infections. Risk factors in this case are vitamin deficiency and increased stress on the body.
Causes of angulitis during pregnancy:
- licking lips in the cold;
- allergic reactions;
- caries;
- dry lips;
- general decrease in immunity.
On our website Dobrobut.com you will find more information on this issue. Here you can make an appointment with a doctor, who will tell you how to get rid of the jam and which ointment is best to use in your case.
Causes of streptoderma
The causative agent of the disease is group A streptococcus. The bacterium affects the surface of the skin. But not every encounter with a microorganism leads to the development of a disease. Infection occurs if there are aggravating factors:
- cuts, abrasions, cracks and other damage to the skin into which pathogens easily penetrate;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- weak immunity;
- endocrine pathologies;
- concomitant dermatological diseases;
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- washing the skin too often, as a result of which the protective film is washed off;
- intense exposure to low or high temperatures;
- intoxication;
- blood flow disturbance.
If at least one of the listed causes of streptoderma in children is present, the likelihood of developing pathology increases significantly.
Angulitis: clinical manifestations
The symptoms of angulitis are very similar to the manifestations of herpes, so it is extremely important to promptly contact a specialist who will make the correct diagnosis and tell you how to quickly cure angulitis.
Symptoms of seizure:
- redness in the corners of the mouth;
- cracks;
- multiple blisters with purulent contents;
- slight bleeding (not always);
- purulent crusts.
Treatment of lip jams in adults depends on the etiology and form (acute or chronic). It is very important to start treatment on time, because without it, the affected area can increase, causing significant discomfort to the patient.
General information
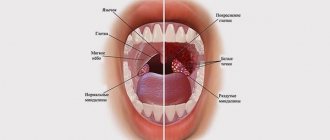
Streptoderma is a disease caused by streptococci.
Damage to the skin is characterized by the appearance of a rash. Blisters and ulcers form on the surface of the skin, which itch and cause discomfort. Streptoderma in children can be acute or chronic. The first is characterized by an aggressive course with severe symptoms. Chronic is characterized by periodic exacerbations and periods of subsidence of the inflammatory process.
Based on the depth of the lesion, streptoderma is divided into superficial, deep and intertriginous (the rash develops in the skin folds). Each of the forms has its own characteristics.
Diagnosis of the disease
Unfortunately, patients with angulitis very rarely turn to a specialist for help, but in vain. After all, the acute form of the disease is easier to cure, thereby preventing the disease from becoming chronic.
Required research:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood sugar test;
- biochemical analysis and liver tests;
- ELISA blood test for herpes viruses;
- blood test for syphilis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Consultation with highly specialized specialists may also be required.
Treatment of streptoderma
Even if the initial examination was carried out by a pediatrician, a dermatologist should prescribe treatment for streptoderma in children.
A specialist in this profile is aware of narrow-spectrum drugs that will help to quickly cope with the disease. The first step is to transfer the child to a therapeutic diet with restrictions on sweets, fatty and salty foods. The course of therapy involves avoiding bathing: water procedures contribute to the spread of the disease. It is recommended to wash healthy areas with chamomile decoction, and never touch inflamed areas.
It is important to choose the right clothes for a sick child. Synthetic and wool items should be excluded from your wardrobe. These tissues cause discomfort and contribute to the spread of the disease.
Doctors recommend opening the blisters that form on the skin with a sterile needle, then treating the opening erosions with brilliant green 2 times a day. Areas of skin not infected with bacteria are wiped with a boron solution. Weeping erosions are lubricated with silver nitrate or resorcinol.
If crusts form on the skin, they are treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In severe cases, a number of other oral medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics of the tetracycline or chloramphenicol series;
- anti-allergy medications;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin complexes;
- antipyretic drugs.
The list of medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. Only a specialist knows how to treat streptoderma in children correctly. Self-medication can provoke the pathology to become chronic. With an adequate course of therapy, the symptoms disappear after 7 days, but after curing the deep form of the pathology, scars remain on the skin. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible.
Treatment of lip jams in adults
After examining the patient and studying the test results, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, usually consisting of medications (local or general action) and vitamin-mineral complexes. It is extremely important to give up bad habits and avoid irritating factors during treatment.
If there is an infection, the patient will be prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy (taking into account the type of pathogen). For a viral infection, antiviral drugs are recommended, and for candidiasis angulitis, antimycotic drugs, such as nystatin and lamicon. Trimistin and tetracycline are prescribed for mixed forms of the disease. All this applies to the treatment of the disease in adults. Your pediatrician will tell you how to treat jams in the corners of the mouth in children. After examining the baby, the pediatrician will prescribe drug therapy and suggest the most effective traditional medicine.
Manifestations and stages
Cheilosis is a common inflammatory problem. When the lip tissue is damaged, signs such as increased dryness and redness, the development of wounds and ulcers, and pain appear. Often develops due to poor ecology, irritation caused by food or chemicals. In some cases, it is caused by other diseases, that is, it acts as a symptom.
The following types of lesions are observed in children:
- traumatic;
- exfoliative;
- contact;
- meteorological;
- grandular and angular cheilitis in children;
- microbial.
The traumatic form occurs due to mechanical, chemical and other influences, after which infection develops. Swelling appears, the mucous membrane becomes tense, and lip movements become limited. In some cases, this type of cheilitis is caused by herpes in the acute stage. For treatment, antibiotics, antiseptics or anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
The exfoliative type of the disease is accompanied by increased dryness and peeling. The reason is a lack of vitamin B, ascorbic or nicotinic acid. The problem arises with dysfunction of the endocrine or nervous system, impaired lip closure, or mouth breathing. Therapy is prescribed depending on the cause of the lesion; multivitamins and softening creams are often used.
Allergic, or contact, cheilitis in most cases develops in adolescents. The causes are chemicals and other external factors. Manifestations of the disease include itching or burning, blisters on the surface, and dryness. To eliminate the problem, you need to avoid contact with the substance that caused the allergy and take antihistamines.
In addition, there are:
- atopic cheilitis in children, which is accompanied by peeling, swelling, erythema and edema;
- hypovitaminosis, characterized by cracks, soreness, the causes are bad habits, for example, frequent licking of lips;
- Eczematous cheilitis is not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of an inflammatory process affecting the skin.