Types of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
Modern dental technologies are very diverse.
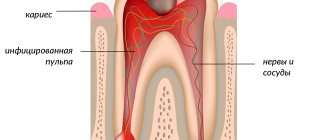
Hypnosis, musical sound analgesia, laughing gas, electroanesthesia, and infiltration anesthesia can be used as anesthesia for children during dental treatment. But more often they use methods based on proven medications and compounds. Protocols can be classified according to a variety of criteria. General gradation:
- local anesthesia;
- Oxygen sedation;
- deep sedation;
- general anesthesia.
There are also different methods of how dental anesthesia is given to children:
- topical anesthesia - smearing the gums with an anesthetic to locally “freeze” the nerve endings;
- injection anesthesia - administration of the drug using a carpule syringe with a particularly thin needle;
- mask for children - used in dentistry to administer anesthesia or a nitrogen mixture.
The names of drugs for pediatric anesthesia during dental treatment deserve special mention. Most often this is:
- Sevoran for general anesthesia is a highly effective inhalation anesthetic with the highest safety profile.
- Propofol for deep sedation is a completely safe composition for intravenous anesthesia.
The method of pain relief is selected taking into account the patient’s age, indications for use, and the amount of planned dental work.
Local anesthesia
For most dental procedures, the use of local anesthetics is sufficient. Children usually tolerate freezing well, and modern drugs are safe and have minimal contraindications. Sensitivity of soft tissues is easily relieved with lidocaine, dicaine, benzocaine, bumecaine. The drugs are produced in different forms: water-based, oil-based solutions, in the form of gels, sprays, ointments.
Types of local anesthesia
Depending on the procedure, age, psychological mood of the child, pain relief is carried out using the application or injection method, as well as a combination of both.
Applications. Soft tissues in the treatment area are often treated with solutions, gels, and sprays based on lidocaine. The agents penetrate well into the mucous membranes and dull sensitivity. For some procedures, for example, removal of a loose baby tooth, an application is sufficient; in more complex cases, an additional injection is given.
Injections. The drugs are administered using a syringe. From the age of four you can use products with articaine, which are several times more powerful than novocaine anesthetics and are also safer. In pediatric dentistry, conduction (acts on the branch of the trigeminal nerve) or infiltration (reaches the endings of the dental nerves) anesthesia is usually performed. The second method is acceptable from the age of six.
Injection instruments
Classic syringes are gradually leaving children's clinics. Modern instruments make it possible to give injections less painfully and without psychological discomfort.
Through a needle-free injector, the drug enters the soft tissues under high pressure. Since there is no needle, the child does not experience strong fear.
In this case, the analgesic effect occurs faster due to the uniform distribution of the product.
The computer syringe also does not look like a regular one, so the injection is more comfortable. The dosage is controlled electronically, which allows saving on anesthetic, and the feeling of numbness after the injection is less pronounced.
A thinner needle is placed on the carpule syringe, which minimizes discomfort. The solution is contained in a sterile capsule to ensure precise dosing.
Local anesthesia in dentistry for children
Local anesthesia is an anesthesia that temporarily blocks the transmission of nerve impulses. This means that during the treatment the child does not feel pain or discomfort. Dentists use local anesthetics as medications, selecting the composition after determining the patient’s allergic reactions.
Local anesthesia for children's teeth is usually carried out in two stages:
- application - for primary reduction of sensitivity;
- injection - administration of an anesthetic composition through an injection of an anesthetic.
Anesthesia for the treatment of baby teeth in very young patients takes place in three stages. The first is application “freezing”. The second and third are injection anesthesia. The first injection of anesthetic is performed with a minimum dose, a drop. Anesthesia takes effect almost immediately, after which the entire volume of the drug is administered.
Rodikova Tatyana
With children 3-4 years old we usually play a fairy tale - based on Frozen or invent our own. First, we smear the gums with “magic ice jam”, then we cast a spell like Elsa “to freeze microbes.” And after that we “make Olaf the snowman” or simply “freeze everything around.” Kids are happy to listen and help, which eliminates tears and whims during dental treatment.
We talk about important aspects of the child’s psychological preparation for the upcoming operation with the chief pediatric specialist - anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the St. Petersburg Health Committee, candidate of medical sciences, head of the department of anesthesiology and resuscitation Vladimir Vladimirovich Kopylov.
— Vladimir Vladimirovich, along with physical preparation for the upcoming operation and anesthesia, it is important for young patients to prepare psychologically. How can parents help them?
Children, as well as adults, are afraid of the new, of what they have never encountered before. Therefore, the child’s condition depends on how the parents themselves behave and what they say to their child.
“First of all, children must understand that everything is done only for their benefit.”
It’s good if in a conversation parents use the following words: “The doctor needs to fix something so that your body is healthy and beautiful.” You should choose your words carefully. Some medical terms may frighten a child. When talking about anesthesia with children, it is better to use expressions such as “breathe the sweet air”; with older children, you can talk about “introduction to a special medical sleep.” It is important to choose positive words: “prick” instead of “needle”, “crib on wheels” instead of “gurney”, “fix” or “repair” instead of “cut off” or “remove”.
— Often, parents themselves are worried, if not panicked, before the upcoming anesthesia.
It is very important to remain calm when communicating with a child. Unlike adults, a small child does not know what surgery is and whether he should be afraid of it. They absorb all worries with the anxiety of their parents. Recent research has shown that reducing anxiety in parents helps reduce anxiety in children. The ideal psychological preparation of a child for surgery is that the parents themselves are calm and wise about the upcoming process. Your voice, facial expressions, gestures and body movements should instill in your child calmness and confidence that everything will be fine. Ask your family not to focus on what the child is facing - even sympathetic sighs are of no use to him.
— What can help parents find peace of mind themselves?
First of all, parents should trust the medical staff. Before an operation or manipulation performed under anesthesia, parents and the child must meet with an anesthesiologist. These are specialists of the highest class. In order to obtain a certificate as an anesthesiologist in Russia, a doctor must not only obtain a diploma of higher medical education, but also complete a residency in the chosen specialty. The specialist’s tasks include not only choosing drugs for anesthesia, but mainly ensuring life safety and comfortable conditions for the patient.
“During the operation, the anesthesiologist constantly monitors and controls all the vital functions of the body: breathing, blood circulation, metabolism.”
When talking with an anesthesiologist, it is important to answer all questions honestly and as accurately as possible. This will help the doctor determine the plan for the necessary anesthetic examination and the method of anesthesia that will minimize the risk during the proposed operation or manipulation. After assessing the patient’s level of preparedness, the specialist will explain the features of the chosen technique and the rules for preparing for it.
— What questions need to be discussed with the anesthesiologist?
Parents must understand that the doctor can and should ask questions! The anesthesiologist will tell you what drugs will be administered to the child, what will be required of the child during induction of anesthesia, and what is its expected duration. The doctor will explain until what point you can be with the child and how to behave correctly after anesthesia in order to help the little patient recover as comfortably as possible, and what restrictions the child should follow before and after the operation.
— Can parents express their wishes about the method of anesthesia?
Parents have the right to express their wishes. However, it is important to understand that no matter how unique the case of their child may seem to the parents, something similar has already happened in the anesthesiologist's practice. And if parents impose restrictions, they must be aware that each doctor is responsible for the patient’s health. This is his professional responsibility. I repeat once again - communication with a doctor presupposes a high degree of trust in the competence of the anesthesiologist. The result of the conversation is always the signing of an informed consent by the child’s legal representative, which records the results of the conversation.
— The operation or manipulation is over, but the child’s well-being is still far from desired. How can I explain to him what is happening?
The process of awakening after general anesthesia consists of a gradual return to independent breathing and restoration of sensitivity. The anesthesiologist will try to make this process as comfortable as possible for the child. Often, in the first time after surgery, the child continues to experience pain. Tell your child that if he experiences pain after surgery, he must tell the doctor about it. It is important that children understand that after surgery they do not need to play heroes, walk around with a “happy” face and hide their worries. Explain to your child that it is possible and necessary to tell the doctor about your complaints and worries. The doctor will definitely listen to them and give the necessary medicine that will alleviate the condition.
“The most important thing is the peace and love of the parents.”
When you return home, praise your child and tell him that you are proud of his courage and how he managed to overcome the situation.
In conclusion, I want to repeat once again - children can and should be told about the upcoming manipulations. But this should be done in a form that is accessible to their age.
Oxygen-nitrogen sedation
ZAX is a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide, often known as laughing gas. Served through a mask. After inhaling the gas, the child falls into a relaxed, sleepy state, calmly perceives the surrounding reality, hears and understands speech addressed to him.
- maintains a positive mood - at the same time as treatment, the child watches cartoons and gets great pleasure from it;
- neutralizes pain - the pain threshold increases, which allows you to endure dental treatment comfortably and calmly;
- reduces natural reactions - the child is no longer frightened by bright lamps and the buzzing of the drill.
Superficial ZAX sedation is recommended for patients over three years of age and, with an experienced doctor, can replace pediatric anesthesia during dental treatment.
Sedation is an alternative to general anesthesia
If anesthesia is contraindicated or inappropriate, but the child cannot be persuaded to undergo dental treatment, then sedation is used. It comes in two types: inhalation with nitrous oxide or intravenous with Propofol or Dexdor.
In the first case, the child inhales the vapors of “laughing gas” and relaxes, plunging into a pleasant state of half-asleep. He remains conscious and can hear and comply with the doctor's requests. This does not exclude local anesthesia. Nitrous oxide is harmless to the body. Its effect begins immediately after the gas is supplied and stops just as quickly. The procedure is performed on babies, older children and even adults.
Intravenous sedation can be superficial, moderate, or deep. This depends on the dosage of the drug. After the drug is administered, the child’s consciousness is not suppressed, as with anesthesia, but he does not respond to treatment, as he sleeps.
Deep sedation with Propofol - drug-induced sleep
During dental treatment, anesthesia for children or deep sedation may be used. These concepts are often confused, since in both cases the child is immersed in medicated sleep. But the difference is significant:
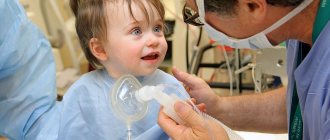
- General anesthesia in dentistry is given to children through a mask. Artificial sleep is as deep as possible, with complete loss of sensitivity.
- Sedation with Propofol involves intravenous administration of the drug and requires additional pain relief.
Propofol guarantees:
- natural physiological state of sleep;
- falling asleep in 1-2 minutes;
- exceptionally high safety for the child;
- simple awakening and rested state;
- extremely low risk of allergic reactions and side effects.
The quality and depth of sleep is controlled by an anesthesiologist. At this time, dentists treat and save teeth, remove completely destroyed units, and install prosthetic structures.
Preparation for general anesthesia
The preparatory stage includes the following procedures:
- orthopantomogram;
- oral cavity examination;
- drawing up a treatment plan based on an x-ray image;
- collecting anamnesis using a questionnaire filled out by parents;
- consultation with a pediatric anesthesiologist and pediatrician;
- necessary laboratory tests;
- registration of written voluntary consent to the procedure.
The child must refuse food and liquids for a certain period of time before anesthesia to prevent the pharyngeal reflex. This period is determined by the anesthesiologist. As a rule, it is 6 hours for food, including kefir, milk, juices and pulp, and 4 hours for liquids. For children under one year old it is reduced to four hours.
Deep sedation with Propofol - drug-induced sleep
Dental anesthesia for children
Dental treatment for young children under anesthesia raises the maximum number of questions among adults. The main ones relate to the safety of the procedure and side effects. Parents are also interested in what kind of anesthesia they give their children during dental treatment - whether there are high risks of negative consequences.
Is anesthesia harmful for dental treatment for children?
Sevoran is a non-narcotic, non-toxic, completely safe drug that is used in dentistry for treatment under general anesthesia. It is given to the child through a mask, instantly putting him to sleep.
Among the advantages of the drug, confirming its safety for young patients:
- excreted from the body unchanged;
- does not affect internal organs;
- does not depress the heart;
- maintains physiological blood pressure readings.
Sevoran simply turns off consciousness and does not cause side effects. Additional positive points:
- pain relief - doctors do not administer additional drugs to the child;
- pleasant smell - children themselves breathe through the mask with pleasure;
- quick recovery from anesthesia - awakening takes only 10-15 minutes.
The high quality of the composition ensures that the use of anesthesia for dental treatment for children eliminates any unpleasant consequences.
Anesthesia at the dentist for children: features
Having figured out whether it is possible to treat a child’s teeth under general anesthesia, parents begin to prepare the child for the procedure.
To do this, the young patient is prescribed a series of examinations:
- Consultation with a dentist.
The doctor must assess the amount of work - determine caries, pulpitis, and the intensity of tooth destruction. Together with the parents, a decision will be made on how many teeth to treat, what to remove, and whether prosthetics are necessary. - Testing, primary diagnostics.
The basic set of studies is general and biochemical blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Obtaining permission from a pediatrician.
If there are chronic diagnoses, the child is also sent for a consultation with a specialized specialist in order to eliminate any risks during dental treatment.
When all issues are agreed upon, the doctor sets a date for treatment and gives final recommendations.
Soldatenkova Alina
When removing baby teeth, it is very important to preserve space for future permanent ones. To do this, they either undergo prosthetics or go to an appointment with an orthodontist to install an orthodontic seat holder.
Contraindications to general anesthesia
Under certain conditions, general anesthesia is contraindicated:
- with decompensated heart disease;
- for renal failure and liver diseases;
- with diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- with severe forms of rickets;
- after the actual meal.
In case of increased bleeding and decreased blood clotting, before anesthesia, the patient should consult a hematologist and give the dentist permission to use this method for pain relief.
Rubber dam system for general anesthesia
Under conditions of general anesthesia, the patient's oral cavity remains open for a long time, which increases the risk of drying out the mucous membrane and developing stomatitis. The rubber dam system allows you to avoid such a scenario and speed up manipulations. It isolates the mucous membrane from the effects of irritating drugs, prevents burns and accidental ingestion or entry of small instruments into the respiratory tract.
The system can be fixed to the entire dentition or to a quadrant - the patient does not need to keep his mouth open all the time. In this condition, dentists still have a wide field of view and can work on multiple teeth.
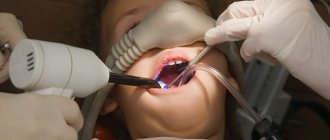
Features of dental treatment under general anesthesia
Manipulations are carried out “with four hands” - a doctor and an assistant, in order to achieve maximum accuracy. To work with filling materials, it is rational to involve a second assistant. Treatment is optimally carried out in segments, for example, first the upper right, then the upper central, etc. This allows you to reduce time, since closely spaced teeth have a similar treatment plan due to an identical diagnosis.
Sometimes, in addition to general anesthesia, the patient is given local anesthesia as indicated. For this purpose, articaine anesthetics without vasoconstrictors are used.