Dental hyperplasia is an excessive increase in the structural components of dental tissues due to their excessive formation. The exact causes of such defects, including the most pronounced one, enamel hyperplasia , have not yet been established, although it is assumed that they lie in the area of impaired cell differentiation during the development of tooth germs and the growth of dental tissues. Provoking factors can be various effects on the reproduction and differentiation of dental tissues: metabolic disorders, violations of correlations in the process of growth and reproduction of tissue components, etc. Based on this, it is clear that for the identification and treatment of dental tissue hyperplasia, it is very important timely preventive examinations and sanitation of the oral cavity.
Dental hyperplasia can be hereditary (for example, focal enamel hyperplasia) or acquired (for example, hypercementosis - excessive formation of cement in the roots, observed against the background of certain pathologies). It is estimated that this defect of varying severity is observed on average in 1.5% of the population.
Dental hyperplasia in children: causes and treatment
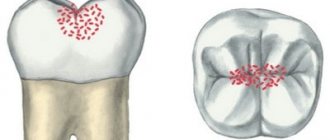
Dental hyperplasia externally looks like small growths on the enamel, formed due to excessive tissue formation.
In children, the defect is detected during examination by a dentist or by radiographic methods. Tubercles measuring 3-5 mm are located in the neck of the tooth, near the roots and are often covered by the gums. There is also localization on the crown. The causes of hyperplasia are not fully understood. Among the possible options for the formation of an enamel defect:
- improper development of the rudiments of mammary and permanent units;
- pathologies of dental tissue growth;
- metabolic disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- heredity.
The incidence of hyperplasia in children is less than 1%.
The defect does not bother the patient and therefore does not require special treatment. If there are “enamel drops” on the surface of the chewing teeth, the doctor will recommend fissure sealing to reduce the risk of caries.
If the localization of the anomaly is unsuccessful and the gums are injured, the pediatric dentist will carefully remove the tubercles with special burs, treat the enamel with remineralizing compounds, and return the dental crown to its anatomically correct shape.
Sensitivity due to gum disease, what is it?
Gum disease
is an inflammation of the gums that can progress to affect the bone that surrounds and supports your teeth, which also causes sensitivity, which we often confuse with tooth sensitivity. It is caused by bacteria in plaque, which always forms on tooth enamel. If plaque is not removed by daily brushing and flossing, thick plaque will form and bacteria will then infect the entire mouth. This can lead to weakening of the gums and, as a result, teeth falling out or being removed by the dentist.
Stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease and is caused by the formation of plaque on the gums. If daily brushing is not carried out promptly or does not meet all hygiene standards, plaque produces toxins (poisons) that can irritate the gum tissue, causing gingivitis. You may notice some bleeding during dental hygiene. If gum problems are detected early, the damage may be localized because the bone and connective tissue that holds the teeth in place are not yet affected.
- Periodontitis: At this stage, the bone and fibers are irreversibly damaged. Your gums may begin to form a pocket under the gum that traps food and plaque. Proper dental treatment and improved home care usually help prevent the disease from developing. Advanced periodontitis: In this final stage of gum disease, the fibers and bone that support the teeth are destroyed, which can cause the teeth to shift or become loose. This can affect your bite, and if aggressive treatment cannot save them, your teeth may need to be removed.
Hypoplasia of primary teeth: what is it and its causes
Hypoplasia is characterized by thinning of the enamel and a pronounced change in relief. On the crown of a baby or permanent tooth there are depressions, dots, pits, and grooves. Affected teeth differ from healthy ones already at the moment of eruption - the enamel is covered with white, yellowish or brown spots.
Hypoplasia of primary and permanent teeth is observed in 40% of patients. And the number of children with this pathology is growing steadily. Scientists associate the development of the anomaly with poor ecology, lack of a balanced diet, and hereditary factors. And all because the development of the defect occurs already at the stage of formation of the tooth germ.
A tooth—deciduous or permanent—is made up of pulp, dentin, enamel, and other tissues. Special cells, ameloblasts, are responsible for the proper development of enamel. In the absence of pathologies, one ameloblast forms one enamel prism. And it is these “prisms” that make up the outer tissue of the erupted tooth. As soon as the ameloblasts complete the task assigned to them, the destruction of the building cells occurs. After this, the tooth enamel of the erupted unit loses its ability to recover.
Ameloblasts are only the first stage in creating strong enamel of a child’s tooth. After eruption, it takes about a year for another stage of formation - final mineralization - to be completed. If all stages of development are successful, the child pleases his parents with strong, snow-white, healthy teeth.
Failure at any stage means potential enamel hypoplasia.
Causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in children
There are three risk factors for the development of hypoplasia:
- features of fetal development during pregnancy;
- illnesses of the child himself;
- external circumstances.
The health of the expectant mother is the basis for the child’s excellent well-being. The risk of hypoplasia can be provoked by:
- Rh conflict - negative Rh factor of the mother and positive Rh factor of the child;
- severe pregnancy, toxicosis;
- acute viral infections or toxoplasmosis during pregnancy;
- taking tetracycline drugs during pregnancy;
- smoking, drinking alcohol.
Among the diseases of the child himself, the risk of defects in the formation of teeth increases:
- CNS lesions, Down syndrome;
- rickets, vitamin deficiency;
- digestive disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
External factors include poor nutrition of the child and injuries to the jaws, which prevent the normal development of tooth germs.
Intrauterine factors provoke hypoplasia of primary teeth. The rest have an equally negative impact on both temporary and indigenous units.
Plaksina Margarita
My patients really like dental remineralization. Pastes rich in minerals have a pleasant taste and smell, and the procedure itself is painless and even pleasant.
How do you know if you have gum disease?
Gum disease is most common in adults. If detected in the early stages, the problem can be corrected with minimal consequences, please contact your dentist if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Gums that are red, swollen, or swollen or tender
- Gums that bleed when brushing or flossing
- Teeth that look longer because your gums have receded
- Gums that have separated or pulled away from your teeth, creating a pocket
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you cleave them together
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Constant bad breath
- How is gum disease treated?
When you detect the first symptoms of gum disease and proper oral hygiene, you will rid your teeth of plaque and avoid the development of the disease. Professional cleaning with a Doctor is the only way to remove plaque that has accumulated and turned into tartar. Your Doctor will clean your teeth and remove tartar from above and below the gum line.
Hypoplasia of primary teeth: treatment
Since one of the reasons for the abnormal development of enamel is low tissue mineralization, doctors have found an opportunity to help young patients. During treatment, two goals are set - to stop pathological changes, reduce or eliminate the severity of existing defects.
The following methods are used in pediatric dentistry in Moscow:
Enamel remineralization
The procedure allows you to replenish the deficiency of missing minerals and strengthen the child’s teeth. At the appointment, the doctor sequentially treats healthy and damaged teeth with a special gel. Treatment is continued at subsequent appointments or even at home. For home procedures, the doctor prescribes the child the optimal paste composition.
Fluoridation of teeth
Treatment of hypoplasia differs in the choice of drug. When fluoridating, the dentist uses a gel with a high fluoride content - up to 65-70%.
The method of restoring baby teeth with hypoplasia is chosen by the dentist after assessing the condition of the enamel and the indications.
Varieties
Depending on the prevalence, generalized and focal hyperplasia . If overgrown gums cover a large surface of several or all teeth, then this type of disease is called generalized. If it grows only near one tooth, then this type is called focal. It should be noted that generalized hyperplasia is much more common than focal hyperplasia.
Depending on the causes of hyperplasia, it can be medicinal or fibrous.
- Drug-induced hyperplasia occurs as a result of taking medications, the side effect of which is the extensive proliferation of gingival tissue.
- The fibrous form is rare and is a hereditary disease. The first symptoms appear in infancy during teething. In the future, the disease progresses, the gums gradually grow, become thicker, and over time, pockets begin to form, which are similar in appearance to the manifestation of periodontitis.
Hypoplasia of permanent teeth in children: treatment
Sometimes the process of hypoplasia cannot be stopped by applying mineral and fluorine-containing compounds. In such cases, pediatric dentists offer options for reconstructing tooth enamel or even the crowns of permanent teeth themselves.
Restoration is carried out using one of the following methods:
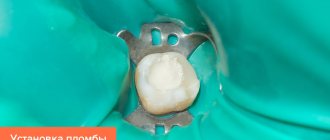
Filling children's teeth
Using grinding, dentists clean the affected area and then restore the surface using high-quality, reflective filling compounds. Installing fillings makes teeth straight, white and neat, and also reduces the rate of spread of the lesion and reduces the risk of complications.
Prosthetics
Installation of full crowns on affected permanent teeth or production of veneers. For children, prosthetic options are selected by the doctor according to the indications and the current clinical situation.
Plaksina Margarita
Unfortunately, children with hypoplasia are sometimes brought to the appointment too late. It is not always possible to save a tooth; it has to be removed. In the case of a primary malocclusion, the child is given an orthodontic ring to maintain space for the permanent unit. This is necessary so that neighboring teeth do not take up free space and spoil the bite.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptoms of the pathology include a change in the color of the enamel: white spots appear on the outer surface. Such changes do not cause unpleasant feelings. In addition, the surface of the teeth in the affected areas is smooth and non-pigmented.
More severe forms of hypoplasia are characterized by the presence of pronounced depressions. At the initial stages, the lesions have a natural shade, but over time they become pigmented. Sometimes on such teeth you can notice deep grooves located horizontally or vertically. Despite the hyperpigmentation of certain areas, the integrity of the enamel is not compromised.
Aplasia (complete absence of enamel) is characterized by pain upon contact with any irritant. In addition, aplasia is associated with underdevelopment of dentin. This leads to the fact that the teeth gradually begin to change shape.
Hypoplasia of dental enamel in children without treatment
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia in primary teeth is required, since in the absence of timely intervention, the root units will suffer. Among the likely consequences:
- development of caries, pulpitis;
- violation of permanent occlusion due to tooth displacement;
- increased abrasion of tooth enamel;
- painful reaction to cold, heat, sour, sweet;
- tendency to form fistulas;
- absence of rudiments of permanent units;
- loosening, destruction and loss of teeth.
Why does tooth sensitivity (dentin hypersensitivity) occur?
When the root of a tooth becomes exposed, it does not have a layer of enamel like the crowns of your teeth. The roots have a very vulnerable coating - cementum, which, after the loss of the top layer, leaves the dentin exposed. Excessive brushing with highly abrasive dental paste causes abrasion of the surface of the tooth enamel and exposes dentin. A very acidic diet with lots of acidic fruits and pickles can also cause tooth decay and dissolve the surface of the tooth, exposing dentin. It is important to visit your Doctor periodically if you have any symptoms of sensitivity so that he can examine your mouth and identify any symptoms associated with dentin sensitivity and suggest you the best treatment plan. When teeth react painfully, brushing them can be painful, and if you don't brush your teeth because of pain, it can lead to the destruction of enamel and gum disease. Reactions to heat, cold, sugar, sour and salty foods and drinks are also a clear sign of tooth decay, or a sign of a broken tooth, in which case your dentist will treat you comprehensively. Some of the most common causes of sensitivity are:
- Gum recession due to age or improper brushing of teeth
- Acidic drinks (such as soda), which cause enamel erosion and dentin attack
- Brushing with very low quality toothpaste, improper brushing, and brushing more than three times a day will result in loss of enamel.
- Gum disease that can lead to gum recession
- A broken or fractured tooth can expose dentin
Additionally, some dental procedures may cause sensitivity. Procedures such as teeth whitening, professional teeth cleaning, braces or fillings are known to cause sensitivity during or after the procedure.