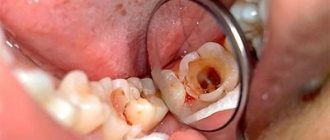
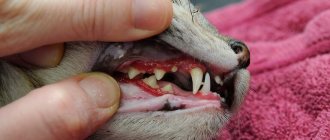
Problem: a woman came to the Family Dentistry for dental prosthetics. In addition to the main reason for the visit, the patient complained of pain in the lower jaw on the left, but could not indicate the exact location. Diagnostics showed that the wisdom tooth was destroyed by caries, and there was inflammation inside the tooth - pulpitis. The woman did not want to have the tooth removed.
Solution: pulpitis of the wisdom tooth (eighth tooth) was treated with a microscope, the tooth was restored with a composite.
What is special about wisdom teeth?
The maximum set of molars for an adult is 32. In this case, it is considered normal to have 28 teeth, since four teeth are the so-called eighth molars or wisdom teeth. For some, they do not erupt at all, for others, when “eights” appear, complications and pathologies arise, but in other cases, wisdom teeth occupy the correct position in the dentition and do not bother their owner. “Eights” usually appear between the ages of 17 and 27, that is, during the period when a person has already formed an attitude towards hygiene and his own dental health. Why is it important? Due to the remote position of wisdom teeth, it is quite difficult to carry out high-quality cleaning, so only very good hygiene can reduce the risk of dental damage. In reality, it is the third molars that are in the top in terms of the number of cases of caries and its common complication - pulpitis.
How to prevent the development of dental caries?
Good dental hygiene helps prevent the development of dental caries, and regular dental examinations detect caries at the very beginning and prevent complications. The distant teeth - wisdom teeth - can be difficult to access for self-cleaning. Maintaining a good level of hygiene requires professional teeth cleaning. Plaque removal using the Air Flow method cleans the most difficult to reach areas. Visiting a hygienist twice a year is a reliable prevention of caries and gum inflammation. Read more about caries prevention measures and dental hygiene here.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: symptoms and treatment
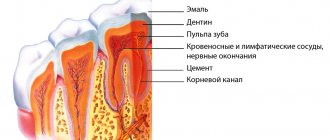
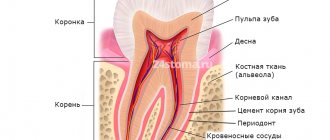
Pulpitis affects the connective tissue of the tooth - the pulp. It has a crown and a root part: depending on the shape and degree of the disease, one or both parts may be affected. The symptoms of wisdom tooth pulpitis are exactly the same as in the case of other teeth.
- Painful sensations.
In acute pulpitis, the pain is acute and paroxysmal, and can be felt in the temples, ears and other parts of the jaw. The pain intensifies at night and when exposed to irritants (temperature, chemical or mechanical). With chronic pulpitis, the pain is dull and less pronounced, which makes it difficult to diagnose the disease, given the location of the wisdom tooth;
- Bleeding.
It appears only in chronic hypertrophic pulpitis, when granulation tissue grows;
- Change in tooth color.
Observed in the case of tissue necrosis with gangrenous pulpitis.
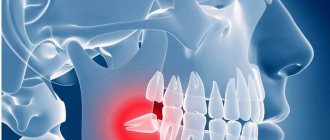
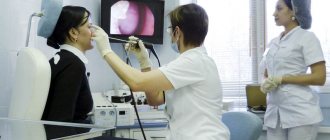
When a wisdom tooth hurts, pulpitis is just one of the options that could be the cause. To diagnose pulpitis, a visual examination, x-ray or EDI (electrodynamic diagnostics) is required. Of course, such procedures are carried out only by professionals, so if you suspect pulpitis, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor. Most patients who face a similar problem have two questions: is wisdom tooth pulpitis treated and is it worth treating wisdom tooth pulpitis. The answer to the first question is yes, but to answer the second, you need to consider each clinical case separately.
Complications of pulpitis
If you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner, pulpitis can develop into a more serious disease - periodontitis, cyst or granuloma, periostitis. That is, the inflammation will go deeper and go beyond the tooth root. Such complications can lead to tooth extraction, after which neighboring teeth will begin to shift, leading to malocclusion. Since the disease causes some discomfort while chewing food, the patient may face serious gastrointestinal problems.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: treat or remove?
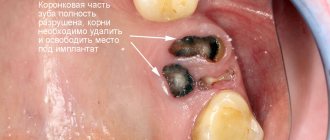
In most cases, a wisdom tooth with pulpitis is removed. The main indications for removing a diseased “eight” are developmental pathologies, as well as being outside the bite (in this case, the tooth has no function). We are talking, first of all, about retention and dystopia. An impacted wisdom tooth is completely or partially hidden in the jaw, and a dystopic wisdom tooth has an incorrect position relative to the rest of the dentition. These pathologies in themselves are a good reason for removing the “eight”, however, if pulpitis occurs due to the impossibility of full treatment, such teeth are definitely removed.
Reasons for the development of the disease
- untreated caries or poor quality of filling, when an inflammatory process has developed again under the installed filling,
- preservation of the nerve under the crown - in this case (if the tightness of the prosthesis is broken, there is inflammation underneath) there is a high risk of pulp inflammation,
- tooth injury – inflammation penetrates from the outside, i.e. through cracks and chips that are located on the root or in close proximity to it,
- exposure to aggressive stimuli - temperature and chemical, for example, during previous canal treatment, naturally, with an incorrectly selected dosage of the drug.
Treatment of wisdom tooth pulpitis
Treatment of wisdom tooth pulpitis is carried out in the same way as on other teeth. In 90% of cases, the doctor performs complete removal of the pulp: only in the initial stages of chronic fibrous pulpitis is it possible to save part of the pulp. However, even if the wisdom tooth is positioned correctly and has completely erupted, very often the doctor suggests extraction rather than treatment. This is due to some features of wisdom teeth that reduce the likelihood of a successful treatment outcome.
- Location of position. Wisdom teeth are difficult to reach, and treatment of pulpitis requires almost pinpoint precision.
- Wisdom teeth have curved roots, which sometimes makes the depulpation procedure extremely difficult.
Despite the difficulty of treatment, sometimes preserving wisdom teeth is advisable. First of all, this applies to situations where, of all the molars, only “eights” remain (in the future, a prosthesis can be attached to them), as well as in the initial stages of the disease, when the chances of a successful and predictable result are higher.
Treatment methods
Treatment of pulpitis is carried out in a complex: as a rule, the nerve is removed (only in rare cases, when there is slight inflammation, it can be treated with medication and thereby kept alive for some time). After this, the canals are filled and the coronal part is restored if it is destroyed. Diagnosis and treatment monitoring are necessarily carried out using an x-ray - a targeted image of one tooth.
Dental canal treatment The dental canals are cleaned using special instruments and medications. The treatment takes 2 visits - during the first, the nerve is removed and the cavity is thoroughly cleaned. In the second, the quality of the treatment is assessed, the temporary filling is removed and a permanent one is placed.
Price:
from 4,500 rubles more details about the solution
Installation of a core tab After cleaning the dental canals, if the crown is almost completely destroyed, i.e. under the root, it is necessary to restore the tooth. An inexpensive option is to install a pin, but a more rational option is to make a stump tab that completely replicates the structure of the root system. This way the load is distributed more evenly, so the tooth will last longer. Next, you can install a crown or line the top of the inlay with a composite material.
Price:
from 5,000 rubles more details about the solution
Installing a crown Installing a crown after treatment of pulpitis may be necessary if the apex of the tooth is destroyed by more than half. For the lateral teeth, the best option would be to use metal-ceramics, for the front teeth - pure ceramics. In both cases, a crown made of zirconium dioxide is suitable, since it is characterized by increased strength and at the same time has a snow-white tint. A single prosthesis can be attached to the tooth itself (if there is something left of it), or to a pin or core tab.
Price:
from 11,000 rubles more about the solution
Symptoms that may indicate the development of pulpitis
Knowing the symptoms characteristic of pulpitis will help you promptly suspect the development of this disease and seek treatment for it. The following symptoms will be common to any form of pulpitis:
- Hypersensitivity of the diseased tooth to temperature stimuli;
- Changing the color of the natural enamel coating of the tooth;
- Redness, inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity near the diseased dental unit;
- The appearance of putrid odor from the mouth.
But the main symptom of pulp inflammation will be excruciating pain, which patients describe as shooting, rolling in attacks. The attacks become most intense at night; unpleasant sensations during the initial phases of development are localized in the area of the diseased tooth, and later begin to radiate to different parts of the face, head and even neck. USEFUL TO KNOW: in some cases, pulpitis develops in the tooth without any external manifestations. Moreover, it can at any time turn into periodontitis and periostitis - diseases in which the risk of losing a tooth increases significantly. For timely diagnosis of latent pulpitis and the beginning of its treatment, you should regularly visit the dentist and undergo a preventive examination.
First visit:
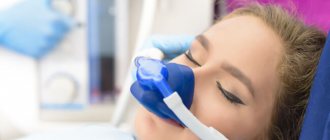
Anesthesia or is it painful to remove a nerve from a tooth?
How painful is it to treat pulpitis: It is definitely very painful if you decide to do it without anesthesia. Fortunately, modern anesthetics can completely solve this problem. If you still feel pain after anesthesia, this may be due to the anesthetic not being strong enough or the anesthesia technique being used incorrectly. The latter usually happens when the doctor tries to anesthetize large molars in the lower jaw (mandibular anesthesia, which is complex in technique, is performed there).
An example of anesthesia (video) –
Drilling out all carious tissues with a drill -
Firstly, at this stage all carious tissue is removed. Secondly, healthy tooth tissues are also partially removed, namely all tooth tissues above the pulp chamber and the mouths of the root canals. This is necessary to ensure visualization of the root canal orifices and ease of their processing with instruments. In Fig. 6-7 you can see the boundaries of excision of hard tooth tissues in the treatment of pulpitis. Figure 8 shows a view of the root canal mouths after they have drilled into the required amount of tooth tissue.
Tooth isolation from saliva –
This is done using a rubber dam. Isolation is necessary to prevent infection from the oral cavity from getting into the root canals along with saliva. This is standard international practice, but in Russia a rubber dam can often be seen only when a doctor fills a tooth. Normally, any work with root canals should be carried out using a rubber dam.
Removal of pulp from the tooth crown and root canals –
It is carried out with special tools designed to work in canals.
In Fig. 9 you can see tooth pulp wound around such a tool. By the way, video 1, which we posted above, shows the process of pulp removal. The video below clearly shows the moment when the tooth pulp is removed from the root canal (time – 1 minute 5 seconds). Treatment of pulpitis: video of nerve removal from a tooth
Measuring the length of root canals in a tooth –
This is one of the most important stages, because... if the length of each channel is determined incorrectly, it will cause -
- or underfilling of the canals, which will lead to complications after the end of treatment,
- or refilling the canals, which can lead to long-term pain and injury to the mandibular nerve.
Measuring the length of the canals is ideally carried out using a combination of the x-ray method and the use of an “apex locator”. In this case, first, special K-file instruments are introduced into each root canal in turn (Fig. 10), which are connected to the apex locator using a thin electrode (Fig. 12). The K-files are gradually advanced deeper into the root canal until there is a signal on the apex locator screen that the tip of the instrument has reached the apex of the tooth root.
It is necessary to measure each channel in turn, because The length of each channel is unique and there are no exact standards. After the measurements are completed and the data are recorded, K-files are simultaneously inserted into all channels (each to its own depth), and a control x-ray is taken (Fig. 11). The apex locator sometimes makes mistakes, so the x-ray will show how accurately the length of the canal was measured and whether adjustments are needed.
Mechanical processing of channels –
A budget option for mechanical treatment of root canals involves the use of manual files (K-files or reamers) - in Fig. 13 you can see a K-file in the root canal. The dentist rotates this instrument by the handle with his fingertips, and the cutting edges of the instrument excise chips from the walls of the canal, expanding it. The purpose of mechanical treatment is to widen the canal so that later it can be properly filled.
A better and more expensive processing option involves the use of an endodontic micromotor and special nickel-titanium files with shape memory. Mechanical processing of each channel is carried out to the depth determined at the previous stage. This is necessary to ensure that each root canal is filled exactly to the root apex. During the expansion process, it is very important to constantly rinse the canals with antiseptics, which is necessary for disinfection, but first of all, to wash out the shavings from the canal (24stoma.ru).
Mechanical treatment of root canals:
In video 1, you can see in detail how the expansion of root canals is carried out with ordinary hand instruments (for this, hand-held K-files of different diameters are used - from smaller to larger). In video 2, the dentist processes root canals using an endodontic micromotor and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium profiles.
Placing a temporary filling –
After the canals are washed and dried to remove excess moisture, turundas soaked in antiseptic are left in them, and a temporary filling is applied to the tooth. The cost of treatment is calculated based on the number of root canals in the tooth.
Causes of inflammation of the dental nerve
Infection in the pulp.
Most often this happens as a result of complications of untreated caries. The carious cavity expands, bacteria penetrate into the pulp and infect it. The infection can also enter the pulp through the apex of the tooth root from deep periodontal pockets with gum disease or through blood from other foci of infection.
Tooth trauma with damage to the pulp chamber, bruxism.
Even a small crack in the tooth enamel can allow bacteria from the oral cavity to penetrate into the pulp and cause inflammation. Therefore, any, even minor, tooth injury requires consultation with a dentist and subsequent observation if there is a suspicion of opening of the pulp chamber. If there is an open pulp, the tooth requires urgent endodontic treatment.
Doctor's mistakes.
Incorrect actions by the dentist can also damage the pulp and provoke inflammation. This may happen if:
- the tooth was treated with too aggressive alcohol or alkaline solutions during treatment,
- the pulp was overheated during the preparation of tooth tissue without sufficient cooling,
- the pulp chamber was damaged due to negligence during the treatment of caries,
- a filling material was used that caused an allergic reaction in the patient.