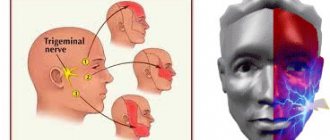
Causes of inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve
Factors contributing to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve are:
- surgical interventions on the jaw bones;
- fractures of the base of the skull, lower and upper jaws;
- tumors;
- complex tooth extraction;
- hypothermia;
- surgery on the maxillary sinus;
- improperly administered anesthesia;
- incorrectly performed dental prosthetics;
- metabolic disorders;
- the presence of foreign bodies that irritate the nerve trunk or injure nerve endings;
- bacterial or viral infection;
- various types of intoxication of the body;
- hypovitaminosis;
- weakening of the immune system.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is done using:
- Palpation of the area. Initially, the doctor feels the area of nerve endings.
- MRI. Usually, if inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve is suspected, the specialist will prescribe magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Angiography. Another diagnostic method is magnetic resonance angiography. It will allow you to see whether the anterior inferior cerebellar artery is dilated. It can put pressure on and irritate the trigeminal nerve.
- X-ray of the skull and paranasal sinuses. Abnormalities may be detected, such as narrowing of the channels through which the nerve passes.
It is important to remember that if the first symptoms are detected, you must immediately contact a specialized medical institution and not resort to treatment with folk remedies. Otherwise, the initial inflammatory process may develop into a chronic disease.
Treatment options for trigeminal neuralgia
Classical therapy requires hospital conditions. Therefore, the patient is hospitalized in the hospital, where he remains until the end of treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. The patient can be discharged after severe pain has been eliminated and muscle spasm has been relieved. The doctor can transfer the patient to a day hospital or to home treatment.
Drug treatment involves pain relief - novocaine-alcohol blockade, sometimes a stronger painkiller is used and a reduction in local edema. To relieve swelling, doctors prescribe antispasmodics, glucocorticoids (prednisolone) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Glycerin injections show good results in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve.
To relieve the pathological process, medications are prescribed that stimulate the renewal and nutrition of nerve fibers. The main thing to remember is that medications in each case should be recommended by the attending physician.
If therapeutic treatment does not help, then it is replaced by surgical intervention. Today there are several invasive ways to combat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- radiosurgery. This is a method using ionizing radiation. You will not need pain medication during radiosurgery. Moreover, after the operation you will not have any scars;
- decompression. During surgery, the surgeon will remove or displace the vessels that are compressing the trigeminal nerve. It is indicated for those who have congenital anomalies. However, the method is fraught with possible side effects such as stroke or hearing loss and sensitivity.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia using MDM therapy
This is a modern physiotherapeutic method based on electrical stimulation effects on the structures of the midbrain.
In the early stages of the disease, electrical stimulation eliminates pain in 1-2-3 sessions. During another 4-7 sessions, the inflammation goes away completely. MDM therapy will also help cope with chronic inflammation. If a disease of the trigeminal nerve occurs as a complication of the underlying disease, then more than one course may be needed for a complete cure.
Advantages of the technique
Treatment of chronic diseases. The MDM therapy method will help to significantly boost immunity and increase the body's resistance in stressful situations.
Analgesic effect. After the first procedure, MDM therapy allows you to reduce the intake of analgesics, and then completely abandon them.
Rapid restoration of nerve fibers and tissues. The method can be successfully combined with invasive treatment methods. It accelerates regeneration processes. In addition, MDM therapy has a positive effect on neurogenesis.
Increasing the effect of drug treatment. If you have a chronic form of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, then MDM therapy can increase the effectiveness of the drugs.
You can undergo a course of such treatment only in some medical institutions in the capital. The Happy Family clinic is one of them.
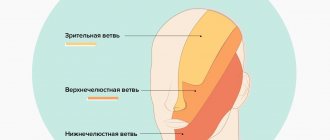
Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis
The maxillary trigeminal nerve consists of three types of nerve fibers:
- vegetative;
- motor;
- sensitive.
The symptomatic picture of neuritis may vary depending on which fibers were affected by the inflammatory process.
Damage to sensory fibers
In particular, with inflammation of the sensory fibers, the patient may complain of a tingling sensation, numbness, and weakened sensitivity in the area innervated by the trigeminal nerve.
Damage to motor fibers
When motor fibers are damaged, there is a partial or complete decrease in strength in the innervated muscles, their atrophy and deterioration of tendon reflexes.
Damage to vegetative fibers
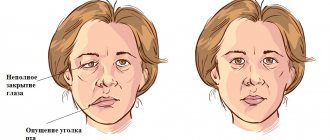
When the vegetative fibers are inflamed, the patient experiences cyanosis and swelling of the skin, dryness and thinning of the skin, and the potential risk of developing a trophic ulcer increases.
Possible complications
If a person does not pay attention to the symptoms and simply takes analgesics to relieve attacks of pain, the condition may worsen.
Untreated inflammation can cause:
- loosening of teeth (molars and wisdom teeth);
- atrophy of the muscles with which chewing occurs;
- earlier appearance of wrinkles;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organs of vision or cornea due to a failure in the production of moisturizing fluid;
- deterioration in the appearance of the skin due to lack of normal nutrition;
- madarosis, that is, loss of eyelashes and eyebrow hair.
In order not to encounter unpleasant complications, you need to take preventive measures, and if there are initial signs, do not postpone a visit to the doctor.
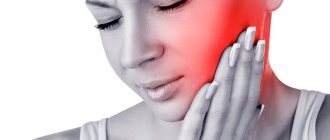
Pain due to inflammation
In addition, a disease such as inflammation or neuritis of the facial trigeminal nerve makes itself felt with attacks of pain of a very diverse nature:
- cutting,
- burning,
- pricking,
- tearing
- shooting, etc.
In this case, the area of pain does not always correspond to the area of innervation and can spread to the lower jaw, cheeks and chin.
Pain may be accompanied by:
- muscle spasms (facial, chewing),
- the appearance of nasal discharge,
- development of hypersalivation,
- increased lacrimation.
Lack of sensation in the tongue, lips and chin
With inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve, not only the entire nerve can be damaged, but also its individual branches. This is why numbness and pain can occur in various areas of the face. For example, when the lingual branch of the nerve is inflamed, patients complain of pain and sensitivity disturbances in the anterior part of the tongue, and when the mental branch is damaged, in the area of the lips and chin.
Pain when laughing, chewing, brushing teeth and shaving
Pain due to neuritis of the maxillary trigeminal nerve can intensify with touching, chewing, laughing and with changes in temperature. That is why patients, trying to prevent the recurrence of painful attacks, avoid excessive mobility and prolonged conversations, and refuse brushing their teeth and shaving.
Activities for making a diagnosis
If necessary, the specialist can refer the patient to see a dentist, surgeon or ENT doctor.
In some cases, complaints about characteristic symptoms are sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. In difficult situations, a set of measures is prescribed for a thorough examination:
- CBC and blood test for biochemistry;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the head;
- computed tomography of the head;
- electroneurography;
- X-ray of the half of the face where the pain is localized.
After conducting an external examination and establishing the cause of the patient’s complaints, the doctor selects a treatment regimen, which includes medications, physical therapy or surgery.
Treatment of neuritis of the maxillary trigeminal nerve
Therapy
The treatment program for trigeminal neuritis is drawn up taking into account the causes of the disease and its clinical signs. The main goals of treatment are:
- achieving a sensitizing effect;
- fight against bacterial and viral infection;
- increasing the body's immune forces;
- elimination of swelling of the nerve trunk;
- restoration of natural adaptive and compensatory reactions;
- normalization of the patency of nerve impulses.
Healing procedures
The set of procedures aimed at blocking the inflammatory process and eliminating all manifestations of neuritis includes:
- antibacterial therapy;
- antiviral therapy;
- elimination of factors contributing to the occurrence of intoxication;
- removal of tumor-like neoplasms or dissection of adhesions compressing the nerve;
- prescribing vitamin and mineral complexes to the patient;
- stimulation of nerves and muscles;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, UHF, ultrasound, paraffin therapy).
People suffering from trigeminal neuritis are advised to regularly visit dental clinics and have their oral cavity sanitized.
Possible causes of inflammation
- Hypothermia. The disease can be caused by prolonged exposure to the cold.
- Presence of facial injuries. The inflammatory process can occur as a result of bruises and blows. A special risk group includes people who have suffered traumatic brain injuries.
- Presence of head pathologies. This could be oncology, benign tumors or vascular aneurysm.
- Viral and infectious diseases. These include pulpitis, meningitis, herpes zoster, periodontitis, chronic caries and others. The cause of inflammation can also be a progressive herpes virus.
- Mental disorders, endocrine diseases, immune problems and chronic allergies.
Alternative Treatment
Alternative therapy is mainly represented by acupuncture. In case of TN neuritis, you should protect yourself from wind, cold, and provide as much heat as possible, especially to the affected area (face, temples, jaw). Warm him up using infrared radiation, an electric blanket, or gel pads.
Elderberry liqueur
Folk remedies include black elderberry juice prepared with alcohol - a liqueur.
You need:
- 2.5 liters of elderberries;
- 1 liter of water;
- 1 vanilla sugar;
- 1 kg sugar;
- 6 tbsp. strong coffee (brewed);
- ½ l rum.
Boil the berries in water for 15 minutes. Then squeeze, add sugar, coffee, vanilla sugar, cook until everything dissolves (about 3 minutes). The next day, add rum, stir, pour into bottles. Shelf life: minimum 2 years.
Herbs and teas
It is also recommended to take Robert's geranium. St. John's wort tea helps. Infusions of anti-inflammatory herbs have a good effect, including:
- calendula;
- common agrimony;
- chamomile;
- jasmine;
- sage;
- elm.
1 tsp dried herb, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for about 15 minutes, strain. Drink 1 glass per day. You can use herbs in combination - prepare a mixture of equal parts of plants, brew and drink as described above. St. John's wort oil or ointments containing calendula and lavender extracts help.
Carry out a 14-day sedative therapeutic course, using a herbal mixture of lemon balm, Leuzea safflower, Scutellaria Baikal, hops, St. John's wort. Perform reflex therapy on the feet - massage the big toe and sole of the foot.
As part of home treatment, it is recommended to additionally take vitamin B1, found in yeast, fish, nuts, and sunflower seeds. If you have problems with TN, you should avoid coffee and strong black tea, which inhibit the effect of vitamin B1.
Effective decoctions
Medicinal decoctions and infusions help well in the fight against arthritis. Medicinal herbs are used for their preparation.
Effective ways to treat arthritis:
- Multicomponent infusion. To prepare the medicine you need parsley root, willow bark - 50 g, nettle leaves - 7 pcs., elderberry inflorescences - 50 g. Grind all components thoroughly, you can use a coffee grinder for this. The resulting mixture is poured with hot water, 1 tbsp. l. 200 g of water. The medicine is infused for 10 minutes and filtered. The infusion should be taken twice a day, it helps to quickly relieve inflammation.
- Horse chestnut. The infusion is prepared from horse chestnut inflorescences (30 pcs.) and vodka (0.6 l). Chestnut flowers are poured with vodka and left for 2 weeks. The medicine can be taken orally three times a day in portions of 2 tbsp. l., can be used for rubbing.
- Linden decoction. This remedy helps relieve swelling in the affected joint. The medicine is prepared from linden and black elderberry inflorescences in equal proportions (3 tablespoons each). Mix the ingredients thoroughly, 2 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the resulting mixture and leave for 15 minutes. The infusion needs to be strained and cooled. Use the product three times a day, taking 70 g orally.
- Sunflower. You should take one small sunflower and chop it. The resulting mass is poured with vodka (500 ml), finely grated soap (15 g) is added. The mixture is thoroughly mixed and left for 2 weeks in a dry and dark place. The finished product is rubbed into the affected area twice a day. After applying the medicine, the sore spot should be wrapped well.
- A decoction based on cyclamen. You will need tubers of this plant (20 pcs.), they should be placed on the bottom of the pan and filled with water (10 l). Place the container on fire and boil. To rub it into the joints, it is enough to pour 2 liters of medicine. The rest of the broth can be used for steaming. After warming up in the bathroom, the solution is applied to the affected area and wrapped with a warm cloth.
Application diagram
Migraine triptan selection chart
So, in order to treat migraine using a triptan, it is necessary to follow the following principles of therapy:
- Treatment should begin with taking analgesics (they can be supplemented with anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs).
- If after this the desired effect is not obtained, then after 45 minutes you can take a triptan.
- If the drug taken does not help and the pain remains, then after a while you can take another drug from the presented group.
It should be borne in mind that a triptan is still a powerful drug. You should not take it yourself without consulting a doctor. In addition, there are some features of its interaction with other medications. For example, a triptan should not be used in combination with antidepressants, antifungals and antibacterial agents.
You should also be careful when combining triptans with anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the presented medicine does not give the desired result, then the doctor can combine it with other substances: beta blockers, anticonvulsants. These include: Topiramate, Penbutolol, Metoprolol, Topamax.