From this article you will learn:
- what do white spots on gums mean?
- why does a white coating appear on the mucous membrane,
- what to do if your gums turn white.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
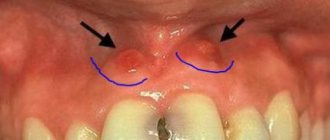
A white spot on the gum is a symptom of diseases of the oral mucosa, which is most often characteristic of a disease such as leukoplakia. And this is not such a harmless disease (as it may seem at first glance), but it has its consequences and requires certain therapy. According to the International Classification of Diseases, leukoplakia is classified as a precancerous disease of the oral cavity, i.e. in some cases, mucosal lesions can become malignant.
But there is a similar variant of damage to the oral mucosa, in which a white coating may appear on the gums, tongue, mucous membrane of the cheeks and palate. In some cases it can be easily scraped off, but in later stages of the disease it is usually firmly attached to the mucosal surface. The appearance of such white plaque on the gums, tongue and other parts of the oral mucosa indicates the development of oral candidiasis.
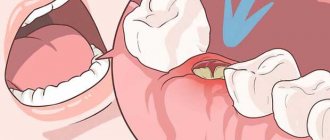
Abscess on the gum and its symptoms
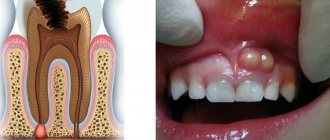
An abscess is a painful process of suppuration in a place where an infection occurs. Most often, inflammation occurs in the area of the diseased tooth. The compaction with pus is a protective mechanism that prevents the infection from spreading throughout the body. If you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner, the abscess can destroy the jaw bone, as well as the periodontal structure, which sometimes leads to tooth extraction.
The first signs of infection in the gums are pain and discomfort while eating. Symptoms of an abscess on the gum:
- continuous throbbing pain;
- pain when pressing on a tooth;
- discomfort when eating hot/cold foods;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- swelling and redness of the face;
- bleeding from the gums;
- mobility and change in the natural color of the tooth;
- lump on the gum and swelling of the face;
Diseases in which a lump on the gum does not hurt
There are diseases in which the resulting compaction does not bother the patient with pain. It is because of this that people are in no hurry to see a doctor, which can subsequently complicate treatment. In what diseases does a lump that appears on dental tissue not hurt?
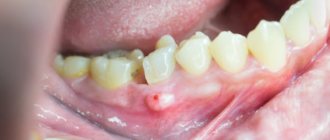
Fistula
If a lump with pus appears in the gum, for the flow of which there is a hole in the gum, we are talking about a fistula. The formation is a growth 3-5 mm in size with a white tip. When the outlet is not blocked by compacted exudate and pus flows freely, such compaction, as a rule, does not hurt. The reason for the formation of a fistula is a complication of periodontitis, in which the tissue grows and becomes infected by accumulated bacteria. Despite the fact that pus periodically flows out and does not accumulate in large quantities, if left untreated, an acute fistula becomes chronic. If the fistula is not treated, there is a risk of infection spreading through the periodontium and tooth loss.
Exostosis
Exostosis is a type of jaw abnormality when the bone protrudes slightly to the surface. Such a lump is hard and painless to the touch, since it is, in fact, a bone or osteocartilaginous growth of a benign nature. The causes of occurrence are hereditary predisposition, congenital pathology or consequences of injury. With such an anomaly, prosthetics are difficult or even impossible: the prosthesis will rub the skin on the bone growth, which can cause injury and infection.
Important! Exostosis is determined by x-rays. The decision to remove is made by the patient, but it is worth considering that such growths can become malignant over time.
Epulis
If a lump appears above the gum, shaped like a mushroom on a stalk, pale pink or red in color, we are talking about epulis - a pathological formation, common mainly in women, and also occurs in children when their first teeth erupt. The reasons for the appearance of epulis are often post-traumatic in nature (large filling, tartar, chips), however, a pathological growth can also appear due to malocclusion, hormonal disorders or wearing low-quality dentures. The symptoms of epulis are similar to those of gingivitis, so for an accurate diagnosis, the doctor uses radiography or a histological test.
Periodontitis
You should think about periodontitis if a lump has formed on the gum - hard to the touch, up to 10 mm in diameter. The causes of inflammation of the periodontal tissues are usually unsealed dental canals and their infection. An abscess forms at the root apex. A characteristic sign of the disease is that when you press vertically on a tooth, pain appears. If the pus has already drained, there may be no pain, but the disease cannot be ignored, as it can lead to tooth loss and further spread of infection.
Attention!
If a seal appears on the gum, under no circumstances should you apply a warm compress or hot rinses: this can aggravate the course of the disease!
Hematoma
A soft-to-touch swelling with watery contents – a hematoma – is formed as a result of tissue injury during tooth extraction. This bump, as a rule, does not require special treatment, dissolving a few days after its appearance.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Types of dental abscess
- Desnevoy
- Periodontal
- Periapical
- Pericoronal
- Combined (periodontal-endodontic)
Desnevoy
A superficial formation on the soft tissues in the area of the gingival papillae between the teeth. Inflammation is associated with the ingress of food, foreign objects, or trauma to the gums with a toothbrush or floss. A gum abscess is relatively easy to correct, but if not treated early, complications can arise.
Periodontal
This is an internal inflammation of the soft tissues of the gums, often caused by periodontitis. In this case, the infection is localized between the outer wall of the alveolar ridge and the gum when the dental pulp is healthy. A purulent exudate forms in the affected gum, which forms a lump in the periodontal pocket. There is no place in the gum for fluid with infection to escape, so the soft and bone tissues near the site of suppuration are gradually affected.
Periapical
The most common type of abscess, the cause of which is complicated caries or untreated periodontitis. The infection affects the root system of the tooth, resulting in pus accumulating at the apex of the root. When the immune defense is weakened, the inflammatory process affects the periosteum of the tooth, spreads to the soft tissue of the mucosa and leads to the formation of a fistulous tract and a purulent lump on the gum.
Pericoronal
Inflammation occurs in the soft tissues above the erupting tooth when food debris and bacteria get there. Pericoronitis can cause swelling of the neck, jaw, and also lead to angina pectoris (impaired respiratory function).
Combined (periodontal-endodontic)
Damage to the gums in the pulp and soft tissues, which causes periodontitis on adjacent teeth.
Consultation, image and treatment plan free of charge
Enter your phone number, we will call you back and select a convenient appointment time for you. Or call us yourself - +7
Already received your application
We will contact you from 9 to 10 am and advise you on all your questions.
Diseases in which a lump on the gum is accompanied by pain
But the situation is much more complicated when the appearance of periodontal compaction is accompanied by severe pain. In such cases, we are talking about more serious diseases. If a tooth hurts and a lump appears on the gum: what could be the reason?
Periostitis
If periodontitis is not treated on time, the pus, instead of coming out through the fistulous tract, can go into the bone, causing its inflammation - periostitis (popularly known as gumboil). This disease has a more severe course: the temperature rises, swelling of the oral mucosa spreads to the soft tissues of the cheeks and lips, the lymph nodes become inflamed, and the person experiences acute, twitching pain. Such a lump can also form as a result of tooth extraction.
Attention!
Flux is a dangerous purulent disease, which, if delayed, can lead to inflammation of the jaw bone, phlegmon and sepsis. At the first signs characteristic of periostitis, you need to urgently contact a dental clinic!
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a rapidly developing gum disease that leads to the destruction of the tissues that support the tooth. The reasons are the formation of tartar, lack of vitamins in the food consumed, and improper load on the teeth when chewing. The gums begin to bleed, itching appears, the teeth become loose, and gaps form between them. Then, in advanced cases, periodontal pockets appear between the tooth and the tissue, bad breath due to the release of purulent exudate, the necks of the teeth become exposed, and pain occurs when eating cold, hot, sour and salty foods. Due to the accumulation of pus in the pockets, the gums become covered with light-colored small bumps - a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. The appearance of such symptoms is a good reason to urgently contact a dental clinic: delay will lead to tooth loss.
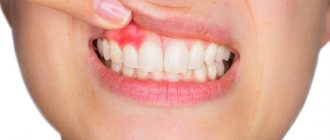
Gingivitis
If bright red bumps appear on the gums, small in diameter, the gums bleed and are slightly hyperemic, we may be talking about hypertrophic gingivitis - the initial form of the inflammatory process of periodontal tissues. The disease occurs due to poor quality oral care and, in the absence of timely treatment, leads to serious complications, including periodontitis.
Important! Any pathology associated with the oral cavity can lead to serious health consequences. You should visit a dentist not only for treatment, but also for disease prevention!
Treatment of gum suppuration
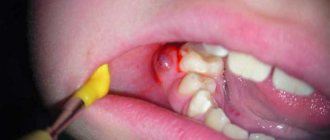
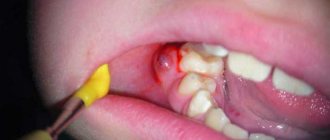
Minor or severe pain requires the help of a dentist. The choice of methods to eliminate suppuration remains with the doctor. Treatment begins after a survey, external examination, and X-ray diagnosis of the patient. The specialist’s main goal is to remove accumulated pus as a source of infection. Depending on the severity, surgical treatment may be required.
Surgery
Treatment methods depending on the type of inflammation:
- With a gingival abscess, the pocket with pus is opened, and then cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
- In cases of periodontal inflammation, it may be necessary to cut the boil to gain access and eliminate the infection. The pus is removed through auxiliary dental canals so that the infection does not spread further through the blood vessels. After eliminating the purulent process and residual infection, curettage of the periodontal pocket and other procedures for the treatment of periodontitis are performed.
- Patients with a periapical abscess are most often prescribed cleaning and refilling of the root canals according to the periodontitis treatment regimen, as well as removal of pus by opening and draining the flux.
- To eliminate a pericoronal abscess, it is necessary to remove the tissue that is preventing the tooth from erupting.
Don't forget antibiotics!
After surgery, the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial therapy: anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, as well as a course of home antiseptic rinses.
Read more about surgical and conservative methods of treating abscess.
Treating an abscess at home
At home, it is impossible to completely cure gum suppuration, but you can significantly reduce the pain.
Before visiting the dentist, you can use the following home remedies:
- a decoction of chamomile and oak bark for rinsing the mouth;
- rinsing with a solution of salt, soda or chlorhexidine;
- local application of ointments and internal administration of analgesics.
Types of dental abscess
- Osteomyelitis
- Phlegmon
- Tooth loss
Osteomyelitis
When pus remains in the soft tissues, complications arise. Dense formations with pus form in the bone tissues, and swelling of the lymph nodes also occurs.
Phlegmon
A life-threatening complication occurs when the infection spreads into the soft tissues of the gums. The growth of pus leads to chronic pathologies.
Tooth loss
If the infected fluid spreads to the base of the tooth, painful swelling appears, which may lead to tooth extraction.
White plaque on the gums (candidiasis) –
If your gums turn white, then you can suspect not only leukoplakia, but also oral candidiasis, in which a white coating may appear on the gums, tongue, mucous membranes of the cheeks and palate. Candidiasis is caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Most often it occurs against the background of reduced immunity, endocrine diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, anemia, hypovitaminosis, diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, chronic hepatitis, and smoking.
Long-term use of antibiotics and mouth rinses containing antibiotics and antiseptics can also lead to candidiasis. The presence of untreated carious teeth, inflammation of the gums, and poor oral hygiene also plays a big role in the occurrence of candidiasis.
White plaque on gums: photo