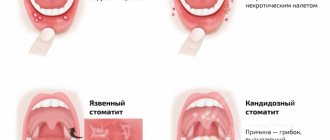
Ulcers with stomatitis
Stomatitis is a fairly common oral disease. He's pretty nasty. It begins with inflammation of the oral cavity. Sores appear, eating and drinking becomes much more difficult. Sometimes it even hurts to open your mouth.
Often the disease develops from an incorrect diagnosis. It is important to note that if stomatitis is not treated correctly, it can lead to chronic forms of the disease. What to do if a child’s gums bleed due to stomatitis or other unpleasant symptoms occur?
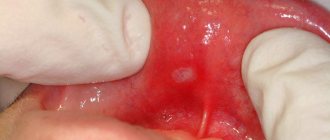
What does aphthous stomatitis look like?
Aphthae occur on the inside of the cheeks or lips, under the tongue, at the base of the gums, or on the soft palate.
https://img.medscapestatic.com/pi/meds/ckb/75/43075.jpg
They can be confused with manifestations of herpetic infection , but the latter usually appears at the red border of the lips, rarely in the oral cavity - usually on the gums or hard palate.
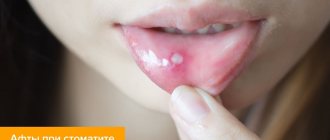
Aphthae first look like red bumps (papules), which then quickly turn into ulcers, surrounded by a red rim and covered with a gray-yellow coating (exudate). 1-2 days before the appearance of aphtha, there may be a local burning sensation of the mucous membrane.
Sometimes the child or family members notice what often triggers the appearance of aphthae. Journaling can help with this.
According to American data, about 20% of the population suffered from recurrent aphthous stomatitis at one time or another in their lives.
Most often children suffer and usually these are minor canker sores.
The peak incidence of aphthae is 1-19 years.
How does the treatment work?
If a child has stomatitis or bleeding gums, you should immediately consult a doctor. You should not contact your pediatrician. They cannot always determine the form of stomatitis.
The further success of the treatment process depends on a correct diagnosis. It is important to strictly follow all doctor's instructions. Incorrect treatment can cause complications.
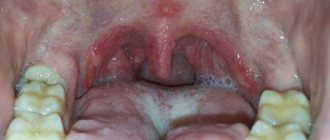
Pediatric herpetic stomatitis
There are different types of stomatitis, so it can be difficult to make a diagnosis on your own. Some symptoms can only be seen by a professional.
Depending on the type of stomatitis, the doctor prescribes different medications. Their price depends on the type of treatment and the degree of the disease. To avoid significant expenses on medications, you need to diagnose the disease as early as possible.
Mild forms of stomatitis can be treated quickly and rarely lead to complications. For more information, you can watch the video in this article.
Types of aft.
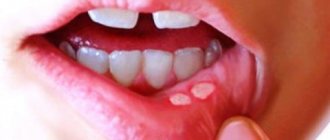
Small aphthae is the most common type of aphthae (80-85%). Their size ranges from 1 to 10 mm. Ulcers can appear singly or several at a time (up to five).
Usually heal in 7-10 days.
Large aphthae (10-15%) - more than 10 mm in diameter, can even be up to 3 cm, deeper, take longer to heal (10-30 days).
They may leave scars behind. Very rare in children.
Herpetiform aphthae (5-10%) are small, from 1 to 3 mm, located in groups like herpetic vesicles. They heal quickly, within 10 days. They are not typical for children; they usually occur in the elderly.
The rest of the oral cavity looks normal - there is no inflammation of the gums, redness of the tonsils and pharynx, enlarged and painful cervical lymph nodes.
There is no fever or other general manifestations.
Aphthae in children is manifested primarily by refusal to eat and drink due to pain in the mouth.
The reasons for the recurrence of aphthae are not completely clear; the most popular theory is related to errors in the immune system.
Doctors most often do not find a specific cause of the failure; most likely it is a combination of several factors.
But doctors still have assumptions about some factors.
What are the different forms of stomatitis?
Stomatitis can manifest itself in mild, moderate and severe forms:
- With a mild form, a slight temperature occurs, approximately 37ºC. You can detect rashes, the oral cavity turns red.
- The average form provokes other unpleasant symptoms. This may be a headache, general weakness, nausea. The temperature reaches 39ºС. When a child has such stomatitis, the gums bleed and a rash appears near the mouth.
- In severe cases , the temperature rises to 40ºС. Weakness, muscle pain, nosebleeds, and vomiting appear. The lymph nodes in the neck and near the jaw become enlarged. Stomatitis occurs in children on the gums, tongue and cheeks. A rash may also appear near the mouth and may spread to the fingers, earlobes, and even eyelids.
A characteristic symptom for all types of stomatitis is bad breath. Salivation increases.
What predisposes to recurrent oral aphthae?
Perhaps the microflora of the oral cavity, herpes group viruses, and maybe Helicobacter pylori, a microorganism that causes stomach and duodenal ulcers, play some role.
Also influence:
- injuries to the oral mucosa
- stress
- deficiency of vitamins B12, B1
- vitamin D deficiency
- zinc deficiency
- poor oral hygiene
- nitrates in drinking water
- Sodium lauryl sulfate is a very popular surfactant in the industry, which is often added to toothpastes for better cleaning and foaming effect.
- food allergies (eg, cow's milk protein) or food hypersensitivity (cinnamon, coffee, chocolate, cheese, figs, pineapple, citrus fruits, some spices)
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
It is very important to understand: recurrent aphthae is an independent disease (most often this happens) or a manifestation of some systemic disease.
The latter option is rare, but the doctor should always keep in mind the possibility of this situation.
Nutrition and other factors
Child nutrition becomes a big problem. This process is accompanied by unpleasant and painful sensations. These can be reduced by using painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
As for the food itself, you can give your child dairy products. They should be low-fat. This is due to the fact that fat may not be absorbed and cause digestive problems. You can give your child soft-boiled eggs, omelettes, and liquid porridge. Decoctions of vegetables and fruits are also good.
It will be useful to include various soups and purees in your diet. If fish and meat are present in the diet, they should be well boiled and ground.
What should be excluded?
It is also important not to give your child very cold or hot food. It should be warm to reduce discomfort. It is imperative to remove salty and sour foods. Spicy foods are also excluded.
You also need to reduce the amount of sweets. This will speed up the healing process and help the medications work properly. You should not feed your baby more than four times a day. Eating in between is excluded.
Stomatitis in a baby
The general recommendation would be to structure the diet in such a way as to reduce the impact on the oral mucosa and not injure it further. Honey is also excluded.
Doctors say that it can provoke the appearance of a fungus, which leads to the onset of the disease. It’s also a good idea to give your child juices and rosehip infusion.
It is important to note that citrus juices can negatively affect the healing process. Therefore, the best solution would be carrot juice. Decoctions of sage, chamomile, oak bark, calendula and eucalyptus will be useful. It is also important to drink plenty of water. It should be warm. Rinsing your mouth also helps.
How else can you speed up the healing process?
To prevent the disease from progressing, the child must remain at home. Therefore, parents need to make sure that he does not go to school or kindergarten.
You need to provide him with a separate towel and dishes. The room in which the child is located must be frequently ventilated and wet cleaned.
If a child has stomatitis on the gum, then the teeth should be brushed with a synthetic brush. This will reduce the traumatic effect on the gums and oral cavity in general. Under no circumstances should this be done with someone else’s brush, because the likelihood of spreading the disease is high.
Stomatitis on a child's gum
What systemic diseases can manifest as aphthae?
- Reiter's syndrome
- Behçet's disease
- AIDS
- cyclic neutropenia
- PFAPA syndrome
The gastroenterologist is especially interested in the connection between recurrent ulcers and specialized systemic diseases.
Celiac disease is found in 5% , and for a long time canker sores may be the only manifestation of a reaction to gluten.
Let me remind you that the estimated prevalence of celiac disease in the general population is about 1%.
Enamel defects and aphthous stomatitis in celiac and healthy subjects: Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies
Other important conditions that manifest as canker sores are inflammatory bowel diseases: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Extraintestinal Manifestations of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Prevalence, Presentation, and Anti-TNF Treatment
Treatment of gingivitis in children in the dental clinic
If your child exhibits characteristic signs of gingivitis, make an appointment for your child at the specialized dental clinic “Aesthetics”. High-level children's specialists with extensive professional experience work here.
The center is equipped with modern equipment that allows high-precision diagnostics and painless treatment of any diseases of the teeth and gums. When treating gingivitis in children and adults, qualified dentists use only high-quality medications from reliable global suppliers.
The center has a flexible pricing policy. All patients who leave their reviews on the Aesthetics website are guaranteed a 3% discount on all dental services.
What can help in finding the cause of aphthae?
A conversation sometimes helps to find out whether relatives have important diseases with a family predisposition - celiac disease, Crohn's disease, lupus erythematosus.
During the examination, the doctor can evaluate the general manifestations of the disease (not typical with ordinary recurrent aphthous stomatitis) and check for the presence of ulcers outside the oral cavity.
The simplest laboratory examination is carried out - this is most often enough.
A general blood test may show anemia due to deficiency of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12.
The level of neutrophils is also assessed - their decrease may be a sign of the rare systemic disease cyclic neutropenia
A high ESR may be a sign of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Serum iron levels may be reduced in up to 20% of recurrent canker sores.
Preventive actions
The best prevention of inflammation of the mucous membrane is daily and high-quality hygiene from an early age and proper nutrition.
Hygiene
The concept of “quality hygiene” includes brushing your teeth at least twice: in the morning and in the evening, in conjunction with cleaning the palate and tongue.
Parents should take a very responsible approach to hygiene from the day the first tooth appears. And after he grows up a little, learn the rules of brushing his teeth: regularly and efficiently. The toothbrush and toothpaste should be selected according to the age of the small patient.
Nutrition
In addition to hygiene, parents need to approach the diet wisely: it should be balanced and include vitamins and minerals. Sweets and carbonated drinks should be consumed by the child in limited quantities. In addition, after finishing eating sweets, the baby should rinse his mouth with water and, if possible, brush his teeth. Note that a diet that promotes the proper development of a growing body includes nutritious and timely meals. Snacking and disordered eating should be kept to a minimum.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis.
There is no radical and quick treatment.
The main task of the doctor is to fight the pain caused by aphthae. This is especially important for young children, who may refuse to eat or drink due to pain and become easily dehydrated.
For this purpose, local painkillers and drugs are used that form protective films on the aphthae.
The second goal is to speed up healing.
The most popular drugs for healing are anti-inflammatory corticosteroids for aphthae, in rare, especially severe situations - even orally for a short course (prednisolone tablets).
The third task is to avoid or at least reduce the frequency of recurrent aphthae.
For some people, regular intake of vitamins (especially B12), zinc, and iron helps.
Avoiding oral hygiene products containing lauryl sulfate may be helpful.
Together with your dental hygienist, you can consider ways to improve your oral hygiene.
A gluten-free diet will help with celiac disease.
Main symptoms of stomatitis
Stomatitis often appears in young children; more serious forms of the disease can occur in adulthood. There can be many causes of stomatitis. This includes poor nutrition, a complication from other diseases, metabolic disorders, and it can also be infectious. It often occurs against a background of reduced immunity.
Stomatitis can manifest itself in different ways. For example, a child changes his behavior. Irritated and capricious, seemingly for no reason. Parents need to be attentive to their child’s complaints. As a rule, with stomatitis, it is painful for children to eat, and sleep is often disturbed. Body temperature rises. Photos of the external manifestations of stomatitis can be viewed in this article.
Stomach upsets, such as bloating and diarrhea, also occur. This is a clear sign that you need to pay attention to the child's health. If stomatitis occurs not for the first time, then parents should be wary.
Typically, this occurs due to the child's weak immune system. Vitamin deficiency also affects the recurrence of the disease. In this case, you need to carefully monitor your diet and take appropriate measures for treatment.
Conclusions:
Aphthae in the mouth recur at some point in life in almost 20% of all people, most often in the second decade of life.
It is difficult to establish a clear and unambiguous reason.
If recurrent aphthae occurs, the pediatrician, physician, or dentist should consider the possibility that rare aphthae are a manifestation of a serious systemic disease.
In such situations, the gastroenterologist must exclude celiac disease, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
4, total, today
What causes bleeding?
Bleeding is often considered the main symptom of periodontitis and stomatitis. The disease occurs when brushing teeth, intensive chewing, or intense pressure on the jaw. But it can also happen during sleep. Along with this, with stomatitis, bleeding occurs due to infection of the mouth by bacteria and viruses. It appears in conjunction with the following diseases:
- For Vincent's stomatitis (ulcerative-necrotic)
- Herpetic stomatitis
- Aphthous stomatitis
Dentists say that stomatitis, which has progressed to the stage of gingivostomatitis and is characterized by the presence of ulcers, aphthae, and necrotic tissue, provokes severe bleeding. In addition, it is necessary to take into account traumatic stomatitis. This is explained by the fact that the factor affects the mucous membrane and can injure the gums. This also provokes bleeding and the occurrence of gingivitis.
This is interesting: Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes: causes and treatment
Causes
Often a child gets sick for the first time during teething. It prevents you from brushing the area where the tooth is erupting. As a result, infection accumulates in this place and inflammation of the gum tissue occurs, which gradually spreads. It is aggravated by frequent allergic reactions to introduced complementary foods.
In older children, pathology is provoked by the following reasons:
- mechanical microtraumas - damage to gum tissue occurs when brushing teeth with hard brushes or hard food when biting it;
- the introduction of herpes is provoked by other viral or infectious lesions of the oral cavity;
- the presence of polyps in the nasal cavity and breathing problems contribute to the penetration of an infectious agent into the gum tissue;
- an incorrect bite in a child leads to constant trauma to the mucous membrane and the development of inflammation;
- lack of nutrients, vitamins and microelements in the baby’s diet reduces local immunity;
- the manifestation of a viral infection is provoked by burns in the mouth;
- Dental diseases (caries, pulpitis) contribute to the development of the virus in the gum tissue, weakening local immunity.
The infection spreads to other tissues quite quickly, and isolated gum damage spreads to periodontal structures.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of herpes gingivitis is quite easy for a child to make, since the disease has characteristic clinical manifestations. The diagnosis is made by the dentist based on an examination of the baby’s oral cavity and data on the course of the disease. Characteristic formations on the mucous membrane and manifestations of inflammation in the mouth clearly indicate that this is a specific lesion. To clarify the nature of the lesion, the doctor prescribes general blood and urine tests. If the disease is severe, it is necessary to clearly identify the type of pathogen. In this case, specific laboratory research methods are used.
These include:
- virological study;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- immunofluorescence method;
- HSV test for the determination of immunospot G-specific glycoprotein;
- serological test with immunoglobulin M.
These methods determine with a high degree of accuracy the type of pathogen in the blood and discharge from ulcers. But they are very expensive and labor-intensive, so they are used quite rarely.