Have questions?
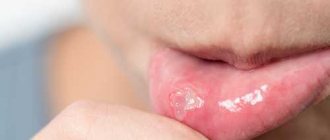
Stomatitis is a disease in which the oral mucosa becomes inflamed.
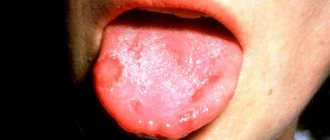
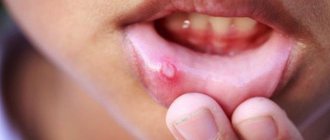
Stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of painful ulcers and wounds in the mouth, which cause significant discomfort to the patient. They are localized on the gums, tonsils, inner lips, cheeks, and under the tongue. The disease is most often bacterial or viral in nature and occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene or microtrauma of the oral cavity, through which microorganisms enter the soft tissues. It may also have an allergic or fungal origin. It mainly affects children, but often occurs in adults.
Types of stomatitis and the main reasons for its occurrence
There are many types of stomatitis. Based on the causative agent of the disease, a specific type of treatment is selected. A white sore may appear in single or multiple quantities on the tonsil for the following reasons:
- taking certain medications (usually antibiotics, which provokes a fungal form of pathology); herpetic lesions (aphthous stomatitis); trauma to the mucous membrane (rough food, foreign objects, hot food, chemicals); viral lesions (vesicular stomatitis, transmitted by airborne droplets); bacterial diseases (catarrhal stomatitis) and so on.
In everyday life, the disease most often occurs due to injury or due to the constant presence of infection (caries, runny nose, adenoiditis). In children, stomatitis can occur due to the constant presence of foreign objects in the mouth during teething.
Causes of stomatitis in the throat
Stomatitis is a disease whose mechanism of occurrence is that the human immune system reacts to irritants in an atypical way, resulting in ulcers in the mouth and throat. This reaction of the immune system can be triggered by bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms. Therefore, stomatitis in the throat is often a concomitant disease that occurs against the background of another infection.
Based on this, we will name the following causes of stomatitis ulcers in the throat:
- Bacterial infection of the oral mucosa
. Most often, the causative agents of infection are various strains of microorganisms such as streptococci or staphylococci. If a person neglects oral hygiene, or if, for example, he gets a bacterial sore throat, this can trigger the development of stomatitis in the throat. - Viral infections.
In most cases, the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the mouth is provoked by the herpes virus, which penetrates the human body and develops as a separate infection. In this case, small bubbles appear in the throat, which are located in groups. The occurrence of herpetic ulcers is accompanied by itching, pain and redness. - Fungal infection of the oral mucosa.
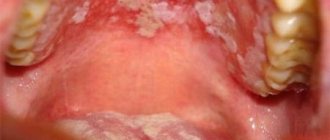
A fungus of the genus Candida most often develops in the human mouth. Normally, it is always present on the mucous membrane, but weakened immunity, stress, long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs can provoke its growth. As a result, a white coating appears in the throat, palate or tongue of a person, which indicates a fungal infection. The development of stomatitis against the background of a fungal infection is also quite common.
Weakening of the human immune system. The immune system of an adult is weakened by stress and somatic diseases. The child’s immunity is weakened in principle, since it is not yet fully formed and is just learning to fight infections. Stomatitis in this case either occurs as a separate disease or becomes a consequence of some current illness. Avitaminosis. A lack of various vitamins and microelements in the human body can also provoke the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the throat.
Allergic reaction. Allergies to certain foods (chocolate, citrus fruits, peanuts) or the substances they contain (for example, gluten, which is rich in cereals) provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in the throat and on the oral mucosa of a person.
Diagnosis of pathology
A doctor can assess why stomatitis appears on the tonsil and make the correct diagnosis during a routine examination. No additional manipulations or analyzes are usually required.
For each type of disease, appropriate therapy is used. If you want to get rid of the pathology quickly and correctly, you should consult a doctor. When diagnosing the disease, the following factors are taken into account:
- age and lifestyle of the patient; presence of additional stimulants of the disease; localization and area of rashes; additional symptoms in the form of fever, runny nose, enlarged tonsils, chronic diseases.
What to do if you suddenly notice a white ulcer on your tonsil? Many patients will suspect a sore throat.
But they will not always be right. Treatment of stomatitis and tonsillitis differs significantly. This is why it is so important to make a correct diagnosis.
Therapy of the disease consists of the use of symptomatic remedies that alleviate the patient’s discomfort and the use of medications that affect the cause of the disease. Folk recipes and grandmother’s methods of treating stomatitis are also very popular. Let's look at effective options in more detail.
Classification and forms of the disease
According to the nature of the disease, stomatitis can be:
- Spicy . The appearance of painful ulcers in the mouth is accompanied by fever. The disease lasts 2–3 weeks;
- Chronic . The disease progresses in waves, with periods of long lulls and rare exacerbations. Lasts up to 2–3 years.
According to the type of pathogen, stomatitis is:
- Viral . Its causative agent is the herpes virus. It causes bubbles of clear liquid to appear. After the bubbles burst, aphthae remain in their place.
- Radial . If the mucous membrane is irradiated by ionizing radiation, compactions and erosions may occur.
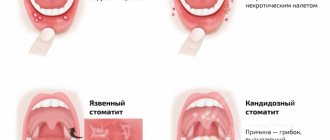
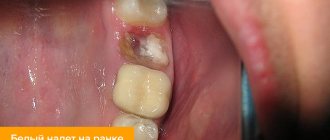
- Fungal . Occurs when immunity decreases or a shock dose of antibiotics. A powdery coating forms on the seals of the mucous membrane, and when you try to remove it, the aphthae is exposed.
- Bacterial . Caused by streptococci and staphylococci. The whole process goes quickly - ulcers are actively formed, aphthae quickly stop hurting and heal.
- Chemical . This is the result of burns to the mouth from acids or alkalis. In this case, deep ulcers are formed and the tissue is deformed.
Depending on the type of pathogen, several forms of acute stomatitis are distinguished:
- Fibrinous. In the initial stage, rashes appear no more than 1–3 times a year during exacerbations of systemic diseases or microtraumas of the mouth. Small blisters covered with fibrous plaque are located on the inner surface of the lips, tongue, and cheeks. They scar after 1–2 weeks. If the cause of the disease is not treated, aphthae form more and more often and cover large areas.
- Necrotic. Typical for patients suffering from severe chronic pathologies. In this case, aphthae become a consequence of the death of the epithelium. In the initial stage, aphthae are painless, but then develop into ulcers that do not close within a period of several weeks to a month.
- Gradular . It develops when the salivary glands are damaged, and aphthae develop next to them. The ulcers are painful and take 1 to 3 weeks to heal, after which the ulcers reopen.
- Scarring. Aphthae cover the mucous membrane of the mouth near the salivary glands, pharynx and palate. At first they are small in size, but quickly unite into deep painful ulcers with a diameter of up to 1 centimeter. They heal slowly (up to 3 months) and form scars.
- Deforming. The most severe form of aphthous dermatitis. Aphthae grow deeply into the mucous membrane and, when healing, form rough scars that deform the oral cavity. Deforming stomatitis is the most difficult to treat; recovery will take at least 2 months.
- Herpetic . Consequence of infection by the herpes virus. Up to 30 small ulcers simultaneously form on the mucous membrane, the tissues become inflamed and turn bright red. It is more common in infants who become infected with the virus in utero or during childbirth.
- Recurrent . Aphthae do not heal for a long time, merge with each other and form a large painful ulcer. The lesions become covered with a white coating, make it difficult to eat, and the person suffers from pain and burning. This form of stomatitis occurs only in adults.
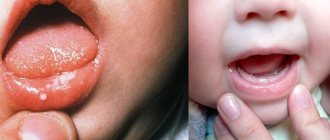
In children, 2 forms are most often observed:
- Spicy . Children under 3 years old are ill, usually against the background of other infectious diseases - whooping cough, diphtheria, measles. In acute stomatitis, a lot of saliva is released, the smell from the mouth is unpleasant, putrefactive.
- Mixed. They appear in children over 4 years of age and cause frequent relapses. In this case, the disease affects an increasingly larger area each time.
Use of painkillers and antipyretics
Very often, stomatitis on the tonsil is accompanied by high body temperature and terrible pain.
A person cannot eat normally, it is even difficult to drink. But drinking plenty of fluids and eating nutritious food is an important condition for a quick recovery. A variety of over-the-counter antipyretics can be used to reduce fever:
- based on ibuprofen (Nurofen, Burana, Advil) - these drugs are the most popular today, they can be used in infants, but only in the form of syrups and suppositories; products with paracetamol (Panadol, " Efferalgan") - have been known for a long time, act quickly, but negatively affect the functioning of the liver (people with diseases of this organ are not recommended to use); medications with nimesulide ("Nise", "Nimulid", "Nimesil") - effectively and permanently eliminate fever, but they have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract, so they should be taken only after meals.
All of the drugs mentioned have an analgesic effect to a greater or lesser extent.
But practice shows that medications based on diclofenac and ketorolac (“Ketorol”, “Ketanov”, “Diclovit”) are most effective in eliminating this symptom. These medications should be taken no more than 3-5 days in a row. Medicines have a symptomatic effect, but do not affect the cause of the disease in any way.
Antiseptics and their names
If stomatitis appears on the tonsils, then doctors almost always prescribe antiseptic drugs. Such medications prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and eliminate existing viruses, fungi and bacteria. The following remedies can be used at home:
- “Miramistin” or “Chlorhexidine” (the latter must be diluted before use) - the drugs eliminate the growth of bacteria, viruses and fungi, so you can’t go wrong with this medicine. Zelenka is an outdated, but proven remedy for the treatment of stomatitis, treatment of ulcers is done pointwise. Lugol - one of the most effective means for treating tonsils, treatment is carried out with a sterile cotton swab soaked in a solution. “Fukortsin” - has an antimicrobial and antifungal effect, promotes rapid tightening of aphthae and improvement of well-being. “Hexoral” - effective if stomatitis on the tonsil is caused by a herpetic infection, it is applied using a spray and has a pleasant taste. “Tantum Verde” is a spray that has an antiseptic and analgesic effect, suitable for use even in pregnant women.
All antiseptics must be used carefully. Many of the drugs described have a drying effect, which can be harmful if used excessively.
Literature
- Aphthous stomatitis // Nurse/ No. 5. – 2015. – P. 21.
- Bulkina N.V. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis: features of the clinical course and complex treatment // Saratov Medical Scientific Journal / Volume 7. - No. 1. - P. 281-282.
- Strakhova S. Yu., Drobotko L. N. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis (lecture) // Regular issues of “RMZh” / No. 29. - dated December 27, 2006. — P. 2096.
- Volkov E. A., Butova V. G., Pozdnyakova T. I., Dzugaeva I. I. Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) for chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Russian Dental Journal / No. 5. – 2014. – P. 35-49.
- Galizina O. A. Main aspects of the occurrence, clinical manifestations, treatment and prevention of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Russian Dental Journal / No. 18(6). – 2014. – P. 39-42.
- Chemicosova T. S. On the prevention of exacerbations of recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Kazan Medical Journal / volume 84. - No. 4. - 2003. - P. 267-269.
- Association of General Practitioners (Family Doctors) of the Russian Federation Clinical recommendations for general practitioners Stomatitis // 2014.
- N. N. Bazhanov Dentistry // ed. Moscow GEOTAR-MED / 2002. – P. 99-100.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol // Reg. number P N014010/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution // Reg. number P N014010/02 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS // Reg. number LSR-002626/07 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC // Reg. number P N015976/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA // Reg. number LSR-004122/09 //
Rinse treatment
Stomatitis on the tonsil can be eliminated quickly enough if you rinse regularly. For this purpose, solutions are selected that have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, regenerating and analgesic effects. If you choose the right product, improvements will be noticeable within 1-3 days.
Decoctions of plants, herbs and rhizomes. Chamomile, plantain, sage or a collection of several types of plants will help cope with the problem.
The decoction is prepared simply: pour a tablespoon of dry herb with a glass of boiling water. It is necessary to gargle after each meal, but at least 4-6 times a day. Hydrogen peroxide has an antimicrobial, healing and decongestant effect. It will do its job perfectly for candidiasis, aphthous and herpetic stomatitis localized on the tonsils.
It is important to be careful not to swallow the solution while rinsing. Furacilin is an antimicrobial agent. The medicine is available in tablets, from which you need to prepare a solution. For 100 ml of warm water you will need one tablet.
Wait for it to completely dissolve, then rinse the tonsils 3-4 times a day. “Rotokan” is a solution that has a hemostatic and anti-inflammatory effect. The medication is effective in the treatment of autozous stomatitis. Rinse with a solution diluted in water for 5-7 days.
After rinsing, refrain from eating or drinking for 30-60 minutes.
Prices
| Name of service | Price, rub.) * |
| Initial consultation with a dentist-therapist | 1,500 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a dentist-therapist | 800 rub. |
| Treatment of caries (imaging, anesthesia, isolation of the oral cavity, installation of an insulating lining and filling made of composite light-curing imported material) | from 4,350 rub. |
| Comprehensive oral hygiene (OptraGate oral cavity isolation, AirFlow removal of colored plaque, ultrasonic removal of dental plaque, polishing with paste, preventive fluoridation of teeth) | 7,000 rub. |
We accept VISA, MASTERCARD, MAESTRO bank cards for payment.
Would you like us to call you back?
Home medicine
If stomatitis appears on the tonsils, how can it be treated without a doctor? Therapy can be carried out using folk remedies and well-known methods. Some of them turn out to be very effective, so they are used from generation to generation:
- rinsing with soda - disinfects, relieves inflammation and promotes healing; lubrication with aloe juice - inhibits the growth of microorganisms, creates a protective film; spot compresses from crushed garlic - a natural antibiotic; rinsing the mouth with cabbage and carrot juice - increases immunity and promotes the healing of ulcers.
If stomatitis appears on the tonsils in children (photos of ulcers are provided for your visual reference), then you should not resort to self-medication. Be sure to show your child to the doctor.
Stomatitis on the tonsils in a child: what to do?
Often this disease appears in children. What drugs do doctors recommend using in these cases?
"Vitaon" is an oil product based on plant components.
It has a softening, anti-inflammatory, healing effect. “Viniline” is a thick solution that forms a film on the treated surface. Protects ulcers from irritation by food and drinks. "Cholisal" is an anesthetic and antiseptic gel that retains its effect for 6-8 hours. "Lizobakt" is an antiseptic and antimicrobial agent, available for use in children over three years of age and pregnant women. Oxolinic ointment - used to provide an antiviral effect. The drug also prevents further spread of infection along the mucous surface.
If your baby has stomatitis on the tonsils (you have already seen the photo), then you should definitely reconsider the child’s diet. Food should be soft, without salt and spices. Eliminate fruits and raw vegetables, and offer your baby more to drink.
How to treat stomatitis in adults and children?
The question of how to treat stomatitis in the throat worries people who have had to deal with this disease in the first place. Because the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in the mouth is accompanied by severe unpleasant symptoms, and you want to get rid of them as soon as possible.
Only an experienced doctor - dentist or therapist - can draw up a competent treatment regimen for stomatitis in a patient’s throat. You can seek help from specialists from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics to solve problems associated with the occurrence of stomatitis ulcers.
The method of treating stomatitis in the human throat involves an integrated approach and the use of local and general therapy. In addition, there are prescriptions for the patient’s diet and lifestyle.
The treatment regimen for stomatitis in the human throat includes:
- Gargling with antiseptic solutions or infusions of medicinal herbs.
- Taking antipyretic and painkillers to relieve symptoms of stomatitis.
- Internal administration of antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antihistamine or other drugs. Such medications are prescribed by a doctor who first diagnoses the causes of the disease. In accordance with the reason, the choice of drug against stomatitis that occurs in the human oral cavity occurs.
- Taking immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin complexes. It is necessary to support the body, help a person cope with infection, and restore strength. If the causes of stomatitis lie in vitamin deficiency and a weakened immune system, then this is the best way to cope with this disease.
- Compliance with dietary recommendations. In order not to injure the inflamed mucous membrane and ulcers on it, only soft food should be taken, preferably pureed. In this case, puree soups are ideal for a sick person.
- It is necessary to temporarily give up bad habits, such as drinking alcohol and smoking, as this causes an exacerbation of the symptoms of stomatitis localized in the person’s throat.
A timely visit to a doctor, accurate diagnosis and a competent treatment regimen will help save you and your loved ones from oral stomatitis in 7-14 days. The rehabilitation period depends on the severity of the disease and on the reasons that provoked the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in a person’s throat.
The choice of clinic and specialist is of great importance in this situation. As mentioned above, treatment of stomatitis in the mouth is carried out either by a dentist or a therapist. In order to diagnose the disease, you need to come to an appointment with one of these specialists. The doors of the LeaderStom clinic are always open to new patients of any age. Our doctors have been successfully treating oral stomatitis for many years and are happy to offer you their help in solving your health problems.