Anesthesia or local anesthesia in dentistry allows you to treat teeth without pain, which provides comfort for the patient and ease of work for the dentist.
Local anesthesia only acts on a limited area and is usually administered by the dentist himself.
Currently, dental treatment without anesthesia is nonsense. Modern medical standards require not only high-quality, but also the most comfortable and painless treatment for the patient. The dentist individually decides how and with what drugs to treat pain, taking into account the amount of work, area, depth and individual characteristics of the patient.
Many of us often delay visiting the dentist because... They have been afraid of them since childhood, but “advanced” caries can cause serious complications that may even require surgical intervention. The smaller the destruction and the earlier the patient consulted a doctor, the better, faster and less painful the treatment can be.
Dentists strongly recommend not to delay your visit. Tooth decay is more dangerous than you think. Possible consequences:
- pulpitis and periodontitis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system and joints, because caries is a source of infection;
- chronic allergic reactions;
- if the tooth is completely destroyed, this will affect the quality of chewing food and, as a result, may lead to gastrointestinal diseases
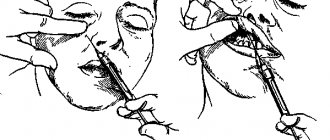
Indications for local injection anesthesia
Most dental treatment is performed under local anesthesia.
It is mandatory to use:
- Removing a nerve from a tooth
- Gum operations – gum plastic surgery, deep periodontal cleaning – curettage and others.
- Installation of orthopedic structures on living teeth.
- Removal of any teeth and roots, as well as oral surgery
During minor interventions, such as the treatment of superficial caries, some patients can easily do without any anesthesia at all.
There are also types of treatments in dentistry for which anesthesia is not usually given, but there are people with increased sensitivity and a low pain threshold who may need it.
- Teeth cleaning by a hygienist
- Artistic restoration without preparation
- Making removable dentures - at the stage of taking impressions, anesthesia is sometimes given to people with an increased gag reflex
In pediatric dentistry, there is no need to rush with anesthesia - the sensitivity of the internal tooth tissue - dentin - is less pronounced in children than in adults. Therefore, first you need to try to prepare the tooth without an injection - and give anesthesia only at the request of the child. After all, many children are afraid of an injection more than anything else, and after it they may simply refuse to open their mouth again.
Coming time
Intrapulpal and intraligamentary anesthesia begins to take effect within a few seconds. Application, infiltration, intraosseous - after 1-5 minutes. Conduction anesthesia is the most variable - from instant pain relief at the same second (if the needle hits the nerve) to half an hour. Sometimes patients, rising from the dental chair after completion of treatment, claim that “only now the freezing has really taken hold.”
Soft tissues are anesthetized before teeth. If the lip or tongue is already “frozen,” the teeth may still remain sensitive, and their premature preparation will be painful.
Contraindications to local injection anesthesia
- Allergic reactions to anesthetic
- Severe fear of dental treatment
- Mental disorders
- The child’s age is too young (usually under 3 years old)
- Lack of effect from drug administration
Validity
The duration of anesthesia also depends on the anesthetic, the concentration of the vasoconstrictor, the type of anesthesia, the dose of the drug, the qualifications of the dentist and the individual response of the patient. Conduction anesthesia lasts up to 2-3 hours or more. Some patients note that the anesthesia wears off completely only in the evening (if the treatment was carried out in the morning). But this is with a strong anesthetic, a high concentration of adrenaline, a significant dosage, and close contact with the nerve trunk. In other situations, conduction anesthesia may not last even one hour. Infiltration anesthesia lasts 1 hour or less. Other types are even smaller.
Types of local anesthesia
- Application anesthesia
Typically, topical anesthesia is used as the first stage - its essence is that a lidocaine-based gel or liquid is applied to the mucous membrane, which penetrates well through the surface layers and causes numbness. Most often, thanks to it, they achieve dulling of sensitivity for a more painless injection.
Sometimes it can be used as an independent method of pain relief - for example, to remove a baby tooth that is supported only by a thin strip of gum.
Preparations for topical anesthesia are made with a pleasant smell and taste - this makes it easier for patients to accept the treatment.
- Infiltration anesthesia
Infiltration anesthesia is a type of local anesthesia that spreads to 2-3 adjacent teeth and is currently the most popular method of anesthesia.
During the injection, our doctor creates an anesthetic depot in the projection of the root of the tooth that is going to be treated. The anesthetic penetrates into the bone within a couple of minutes and blocks the transmission of nerve impulses in the injection area. If a single-rooted tooth is being treated, then one injection is given from the side of the cheek, but if the tooth is multi-rooted, an injection is often added from the palatal side.
This is why infiltration anesthesia is more effective on the upper jaw than on the lower jaw - the bone of the upper jaw is more spongy and allows the solution to pass through more easily.
This method of anesthesia is not recommended for purulent foci of inflammation - it is not effective enough in this environment and at the same time brings more pain. When treating purulent inflammations, it is better to use conduction anesthesia.
- Conduction anesthesia
Conduction anesthesia in dentistry is one of the most effective methods of anesthesia. With this option, it is not small nerve endings that are blocked, but larger nerve trunks. Due to this, it is not the area of 2-3 adjacent teeth that becomes numb, but half of the jaw and adjacent tissues.
Types of conduction anesthesia: palatal anesthesia, tuberal anesthesia, infraorbital anesthesia, incisive anesthesia - these are subtypes for the upper jaw.
For the lower jaw, conduction anesthesia is divided into: mental anesthesia, mandibular anesthesia and torus anesthesia.
- Intraosseous
It is most often used during extraction and involves administering an anesthetic under pressure directly into the bone tissue between the roots of the teeth. The effect of intraosseous anesthesia does not last long, since a very small amount of the drug is injected. But the action comes almost instantly.
- Intraligamentary
With this type of anesthesia, the drug is injected into the space between the tooth and the bone. Since there is little space there, a very small amount of anesthetic is injected, and the numbness will last up to half an hour. Thanks to this, you can treat several teeth at once in one visit.
- Intracanal anesthesia
When a nerve is removed, there is often residual pain even after intraligamentary anesthesia. Then our doctor injects the anesthetic directly into the nerve cavity - in this case, numbness occurs immediately and lasts quite a long time.
If you are planning a visit to the doctor, we advise you to observe a number of points:
- do not drink alcohol the day before, this may worsen the effect of the anesthetic;
- if you have a cold, cough, or runny nose, it is better to postpone your visit until you have fully recovered;
- Women and girls are not recommended to visit the dentist during menstruation, because... during this period, blood clotting worsens (by the way, do not be surprised if the anesthesiologist asks you this question before surgery; operations are not performed during menstruation.
- choose your clinic carefully! Now their choice is very large, but very few comply with important requirements and all antiseptic requirements!
Instruments for local anesthesia
At the moment, a carpule syringe is used to inject the anesthetic - this is a metal syringe, it can be used many times, it is sterilized in the same way as other dental instruments. A carpule with an anesthetic is inserted into the carpule syringe - a special glass cartridge, factory-made.
Currently, the Trilogy Medical and Dental Center uses carpule syringes for injection anesthesia - they are much more convenient and more sophisticated than conventional disposable syringes.
The thickness of the carpule syringe needle is only from 0.3 to 0.5 mm - thanks to this, the injection is much more painless than when using a conventional disposable syringe.
The needle is also very flexible and not brittle - thanks to this, the doctor can bend it at an angle convenient for himself and perform anesthesia even more accurately and conveniently for the patient.
Dosage
The volume of one carpule is 1.7-1.8 ml. This amount is enough for most manipulations within one or two teeth. When treating a larger number of teeth (especially if they are located far from each other), several carpules and injections into different parts of the oral cavity are required.
A second injection of anesthetic into the same place is carried out if the first one is unsuccessful or after some time, when long-term treatment has not yet been completed and the anesthesia begins to wear off. The introduction of the same drug can help if conduction anesthesia is ineffective the first time. With other types of anesthesia, it is necessary to change the anesthetic itself to a more powerful one. It is impossible to increase the volume of the injected solution indefinitely - in case of an overdose, a toxic reaction occurs. For articaine with adrenaline and lidocaine with adrenaline, the maximum dose is 7 mg/kg body weight. One carpule (1.7-1.8 ml) contains 34-36 mg of 2% lidocaine or 68-72 mg of 4% articaine. Therefore, for a person weighing 70 kg, the maximum number of carpules at one time is: 14 for 2% lidocaine and 7 for 4% articaine.
Medications to relieve fear and anxiety before visiting the dentist
There are many sedatives that reduce anxiety, one of which is Afobazole. This drug does not have a hypnotic effect, however, for positive results, you should start drinking it a week before the expected visit to the dentist.
Cheaper drugs (Corvalol, valerian extract, etc.) should be started three days before visiting the doctor, but these drugs in high doses can lead to weakness, drowsiness and decreased performance.
Also, in many clinics you can be given premedication - the administration of sedatives intramuscularly half an hour before dental procedures. Such drugs are classified as tranquilizers and are available by prescription (Seduxen, Relanium, etc.).
What drugs are used for pain relief
Based on the experience of visiting dentists, many people ask the question: why is it painful to be treated in one clinic, but not in another? The patient's sensations may depend on many factors, but the most important is the painkiller itself.
At the beginning of the last century, novocaine was actively used, and from the middle of the century they began to use a more powerful anesthetic - lidocaine. This was considered a breakthrough in medicine, but the pain could not be completely eliminated.
Modern dental clinics use painkillers based on articaine. Let's look at the most popular of them:
Ultracaine
The most commonly used anesthesia, since the drug contains a small proportion of epinephrine (adrenaline) and almost no preservatives. Available in three forms: with an adrenaline concentration of 1:100000, 1:200000 and without it at all. The analgesic effect is achieved after 10 minutes and lasts for 2-3 hours. It is used even in the presence of allergic reactions, suitable for patients with heart disease and pregnant women. Its effectiveness is very high, while it is instantly eliminated from the body and does absolutely no harm.
Ubistezin
The drug is produced in Germany. Contains adrenaline, due to which it has a vasoconstrictor effect at the injection site. The drug has 2 release forms with an adrenaline concentration of 1:200000 and 1:100000. The analgesic effect occurs after a few minutes, and the duration of action is at least 1.5 hours.
Septanest
It has been used in dentistry for quite a long time. Available in 2 forms: with an adrenaline content of 1:100000 and 1:200000. It is used in complex cases and in the absence of contraindications. Allowed for pregnant women and children over 4 years old. A distinctive feature is good tissue tolerance and moderate vasoconstrictor effect. The duration of exposure is at least 45 minutes.
Scandonest
This drug does not contain adrenaline or preservatives. Used for adrenaline intolerance. It is not used for bronchial asthma, but is suitable for patients with diabetes, thyroid diseases, allergies and the elderly. Provides fast and strong pain relief. One drawback is the short validity period. Requires repeated administration during prolonged manipulations.
Does it happen that the anesthesia does not work?
In fact, such situations are very rare. Less than 1% of all patients are sensitive to a certain type of drug, so you just need to find the right one. Here, most often the reason lies in the incorrect administration of anesthesia or incorrectly selected anesthesia.
And in conclusion, I would like to emphasize once again: do not be afraid of dentists. Today, anesthesia allows treatment to be carried out as comfortably and painlessly as possible. And the anesthetics used for pain relief are not only effective, but also safe.