Root cysts or gingival granulomas are a common problem today. Neglect of regular examinations, hygiene rules, the development of caries or periodontitis contribute to the development of cystic formations. The disease affects all segments of the population, regardless of gender and age. In fact, it does not matter on which jaw a radicular cyst occurs, because the process of appearance, treatment, and consequences develop according to the same scenario. To eliminate pathology, there are a number of new techniques that can completely eliminate the disease with a guarantee of no relapses.
Content:
- Classification of pathology
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic measures
- How to treat
- What will happen if left untreated?
- What can you do to avoid getting sick?
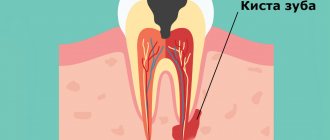
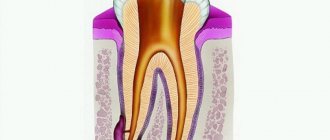
A jaw cyst is a hollow benign formation localized in the jaw bone.
There is liquid content inside it. Very often, the structure develops unnoticed by a person for a long time and is accidentally discovered during an X-ray diagnosis for another reason. If a cyst in the jaw becomes inflamed, the patient immediately feels it. Suppuration can provoke the occurrence of periostitis, sinusitis, osteomyelitis, and fistula.
Unfortunately, most often the formation has to be removed surgically. The doctor performs a resection of the apex of the tooth root and at the same time fills the cavity cleared of exudate with a special biological composite composition.
Etiology and provoking factors
The appearance of a cystic component is the body’s response to the inflammatory process in the tooth. Cysts form in patients with a long course of carious destruction, when the lesion reaches the root part of the tooth. But there are other diseases or conditions that can serve as a trigger for the formation of cavity formations:
chronic periodontitis; severe pulpitis; trauma to the tooth and gums: previous illness of an infectious nature; chronic stomatitis; inflammation of the maxillary sinuses; abnormal bite; catarrhal otitis; diseases with a pronounced decrease in immunity; complication during the eruption of wisdom teeth.
A radicular cyst of the maxillary bone is most often formed under the influence of a long-term untreated carious tooth. Sometimes the cause of the appearance of a radicular cyst in the upper jaw is unprofessional treatment of caries, violation of canal filling technology, or lack of competence of a specialist in the treatment of chronic forms of periodontitis. Lack of treatment for a radicular cyst can lead to serious complications not only from the maxillofacial anatomical zone, but also from all organs and systems of the body as a whole.
Classification of pathology
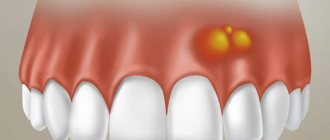
Cysts localized in the tissues of the upper or lower row of teeth are very common. With their development, a cavity appears, the walls of which are covered with fibrous tissue, and the inner surface consists of an epithelial layer. The capsule holds clear or cloudy liquid.
Doctors distinguish the following types of pathology:
- Primordial. This is a cyst of the lower jaw. It appears in the area of the third molar. She has very thin fibrous walls. The inside of the capsule is lined with flat epithelium. According to its structure, the tumor may contain one or several small chambers.
- Follicular. Formed before tooth eruption. It can grow in the area of the alveolar margin. Includes cells that intensively produce viscous mucus. Because of this, the internal contents of the anomalous structure are quite viscous. A follicular formation is formed from the enamel organs of the unerupted unit. One or several teeth are found inside it. These may be formed crowns or tooth buds.
- Radicular. It occurs more often than others - in eighty percent of cases. Usually grows above the upper teeth. The diameter reaches from half to two centimeters. Often inflamed. Then the cells begin to hyperplasia, network-like processes are formed that extend into the thickness of the walls. The liquid contents of the radicular structures are rich in neutrophilic leukocytes. Often with this type of pathology, the patient develops sinusitis. This is due to the peculiarities of the localization of the inflammatory site.
- Retromolar. It is formed due to a long-term inflammatory process occurring in the thickness of the soft tissues. It is a consequence of complicated teething.
- Nasoalveolar. It occurs near the nasopalatine canal (the border between the upper row and the wing of the nose).
- Aneurysmal. Very rare in dental practice. Appears only on the lower jaw. This type of neoplasm is still poorly studied. It is known that there is blood or a red-pink liquid inside it. Many scientists agree that the symptoms of an aneurysmal cavity are a consequence of hormonal imbalance.
- Traumatic. Occurs due to recent facial trauma.
- Residual. The result of mistakes made by the doctor during tooth extraction, or the consequence of the patient ignoring the surgeon’s instructions.
The doctor decides how to treat a dental cyst, taking into account the cause of its development. It is very important to understand why the tumor occurred. If the root cause is not identified, the likelihood of relapse will remain high.
What treatment methods for jaw cysts exist?
The choice of treatment method for an odontogenic cyst directly depends on the symptoms it causes, as well as the results obtained during instrumental and laboratory diagnostics.
If surgical treatment is chosen (cystotomy or cystectomy), the maxillofacial surgeon performs complete removal of the cyst. In some cases, it is necessary to remove the cyst along with the affected parts of the tooth root. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
If the choice falls on therapeutic treatment, the doctor will carry out procedures aimed at reducing inflammation. This is a long process, taking at least six months.
The first step is to drain the contents of the cyst using a special drainage tube, which is inserted into a small incision in the tumor. As the contents drain out and the tumor shrinks, the size of the tube is adjusted downward.
After removing the contents of the cyst, the dentist cleans the root canals and administers medications that destroy the tumor tissue. At the end of all procedures, the doctor uses a special solution aimed at accelerating healing.
Treatment is monitored radiographically.
Both after surgical and therapeutic treatment, the patient requires preventive measures that will help avoid the re-formation of an odontogenic cyst.
Causes of the disease
Already based on the classification, it becomes clear that tumors appear in the tissues of the oral cavity for a variety of reasons. Among the main provoking factors:
- Damage to hard dental tissues. Untreated caries, periodontitis, pulpitis are all diseases in which pathogenic agents penetrate the periodontium through unsealed root canals.
- Inflammation of the area adjacent to the area where the cyst is located. Quite often it turns out that a benign tumor formed after sinusitis or inflammation of the gums. This happens because the infection penetrates through the bloodstream into the bone tissue from the maxillary and nasal sinuses.
- Injuries, bruises, blows. The first time after them, a person may not notice anything. But later a nagging pain appears, indicating a problem.
Very rarely do doctors have to treat congenital cysts. It has not been established why they occur.
What is the difference between a cyst and a granuloma?
There are other diseases in the oral cavity that are symptomatically similar to a cyst. Specifically, a granuloma is an outwardly swollen round projection in the root zone of a tooth. The doctor must correctly diagnose the disease, since the sequence of exposure, removal techniques, and pharmacology have significant differences. Granuloma is eliminated with the help of medications, as well as accompanying mouth rinsing with phytocomponents. The cyst has deeper roots and does not go away without surgery.
Symptoms of the disease
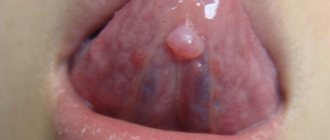
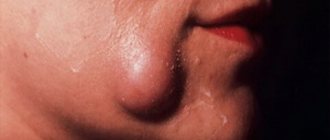
In the first days of development of the pathology, there are no subjective symptoms. But the larger the cyst becomes, the stronger and more vividly it declares itself. Then a kind of gumboil may form in the gum area. At first, the protrusion does not hurt during palpation and hardly bothers the patient.
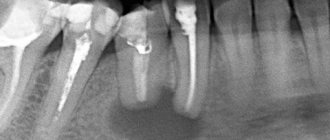
On an orthopantomogram, the doctor observes a spherical cavity with clearly defined contours. On an x-ray, you can see the root of the affected tooth with inflamed periodontium.
In advanced cases, when a large amount of purulent mass accumulates inside the cavity, the patient experiences the same symptoms as with osteomyelitis. Then the tumor volume increases. The gums swell and become very painful. Periodically, a small hole appears in its wall through which pus is released.
How to treat
In most cases, cysts cannot be treated without surgery. Only in unadvanced cases is it possible to get rid of the tumor by opening it and draining it.
The operations performed for the disease are called cystectomy and cystotomy. They both involve removing the formation. But in the first case, it is removed completely, and in the second, only the front wall is excised.
The main goal of a dental surgeon is to preserve the tooth growing in the area where the tumor is located. Unfortunately, this is not always possible. So, if the tooth root is immersed in the cyst cavity by more than 60% of its length, emergency removal is indicated. Such a unit can no longer be functional. Soon after excision of the tumor, it will still become loose and fall out.
Therefore, it is very important not to start the disease. Considering that it may not manifest itself for a long time, it is important to undergo a specialized examination at the dental office every year. This will increase the chances of successful early diagnosis.
Clinical picture
The development of the cystic component can develop for about several years and does not manifest itself symptomatically. If unexpressed but unpleasant signs of a cyst appear, treatment should be carried out immediately, since treatment of the tumor after its significant growth will be quite difficult. As the cyst grows, it puts strong pressure on the surrounding connective tissue, so its growth is rapid. In the photographs, the cyst looks like a small spherical formation. The main manifestations are:
the appearance of severe throbbing pain; swelling and redness of the gums in the affected area; feeling of tooth mobility; feeling of fullness in the apical space; bad breath: prolonged persistence of low-grade body temperature.
An early cyst can be diagnosed by X-ray examination, and later stages of development are detected by visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity. Usually the suspicion of the presence of a cystic cavity is justified.
What will happen if left untreated?
Despite the fact that most patients do not have acute symptoms with the diagnosis described, the growth of the cavity can lead to very unpleasant and even dangerous consequences for health. This means:
- sepsis;
- phlegmon;
- premature loosening and loss of one or more teeth;
- inflammatory damage to the tissues of the periosteum;
- the formation of a malignant tumor due to cell degeneration;
- osteomyelitis;
- frequent occurrence of fistulas;
- high risk of fracture.
All these consequences are not harmless, which is why it is so important to detect pathology at the very beginning of its development.
What can you do to avoid getting sick?
You can reduce the likelihood of developing the disease by following simple rules:
- Brush your teeth twice a day. Use a high-quality brush and paste during hygiene procedures. Don't forget about the role of dental rinses and dental floss.
- Once a year, remove tartar in the dental office using an ultrasonic scaler. Professional hygiene is the best prevention of most dental ailments.
- Eat a balanced and healthy diet. Eat less sweets. Eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Check your dental health once a year. You need to visit a doctor, even if nothing bothers you.
- Always follow your dentist's instructions.
- Avoid traumatic injuries to the face. When engaging in potentially dangerous sports, always wear special protective equipment.
A jaw cyst is a dangerous tumor. Initially it is benign, but under certain conditions it can become malignant. Fortunately, this happens extremely rarely.
If the tumor grows very quickly, even a jaw fracture is possible. It shouldn't come to this. Treatment must be timely and competent.
Laser technique
The most modern way to remove a cyst is a laser, which is inserted through the canals. This method has a number of advantages over classical surgical treatment methods, namely:
- painlessness;
- sterility;
- possibility of complete preservation of the tooth;
- quick and easy recovery period.
When using the laser technique, after opening the tooth and removing the fillings, a laser is introduced into the dental canals, which removes the tumor and disinfects the cavity. The liquid and remaining tissue fragments are then removed using vacuum suction.
The only drawback of this technique at the moment is the relatively high cost.