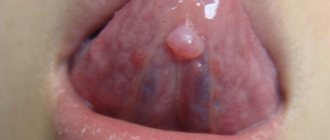
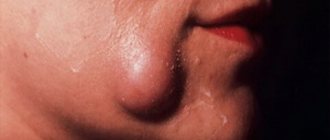
An oral mucosal cyst (also called a mucocele or mucocele) is a small capsule filled with fluid. According to dentists, such cysts are generally harmless and painless, but they can cause discomfort because they feel like a foreign object.
Mucoceles usually occur on the inner surface of the lips, but can also appear on the tongue, palate, buccal mucosa, and floor of the mouth. These cysts also form around tongue or lip piercings. A cyst on the bottom of the mouth is called a ranula, and on the gum - an epulis. Mucous cysts are bluish in color and filled with clear fluid. The dentist usually recognizes them at first sight.
Content:
- Why does a cyst grow in the oral cavity?
- Types of oral cysts
- Signs of a cyst
- Examination of patients who have a cyst in their mouth
- How to treat
- Treatment of cystic formation at home
- How to reduce the likelihood of developing education
Sometimes, when visiting a dentist, a patient hears a strange diagnosis - mucocele.
More simply, it sounds like an oral cyst. Underneath this disease lies a cavity tumor neoplasm containing mucous contents. It is benign and develops due to obstructed outflow of secretions produced by parenchyma cells. The peculiarity of mucocele is that it does not have a strong epithelial membrane. Usually localized on the mucous membrane of the lower lip or under the tongue. It can also form in the chewing area. Neoplasms of the submandibular zone are very rarely encountered in dental practice.
Conducted studies demonstrate that most often young people under the age of thirty experience mucocele. The disease also occurs in adolescent children.
Retention cyst on the lip: treatment
A lump on the inside of the lip is treated in the same way as a lump under the tongue.
There is only one treatment option - surgery, which involves removing the entire cyst (there are no other treatment options). The surgery is very simple and usually does not take more than 15 minutes of the dental surgeon's time. It is performed under local anesthesia with lidocaine solution, and you will not feel any pain at all. It looks like this: a small incision is made on the surface of the mucous membrane next to the cyst, through which the entire cyst is removed, along with its contents. After this, 2-4 sutures are placed on the edges of the mucous membrane, which will need to be removed after about 7 days.
Removal of a retention cyst: video of the operation
During the operation, it is very important not to damage the cyst membrane, because if the walls of the cyst collapse, it is immediately lost in the tissues, and it is almost impossible to remove it entirely after this. If you leave a small fragment of the cyst shell in the tissues, the retention cyst on the lip will appear again.
Why does a cyst grow in the oral cavity?
Most often, doctors are unable to determine the exact cause of the disease. It is believed that its development can be caused by:
- repetitive trauma to the mouth;
- inflammatory pathologies of the oral mucosa;
- congenital obstruction of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands.
Some doctors are inclined to believe that frequently appearing cysts of the sublingual salivary gland indicate a non-standard structure of the latter. There is also a dysembryogenetic version of the origin of tumors. But dentists give the main importance to the traumatic factor. Thus, blisters on the inside of the lower lip often form due to the habit of constantly biting it.
The pathogenesis of the disease can be described as follows:
- The excretory duct of the salivary gland becomes blocked for a certain reason.
- Internal hydrostatic pressure increases. The mucus accumulates and cannot come out.
- Throughout the day, the mucous secretion permeates the surrounding tissues.
- Swelling forms and the blood vessels are compressed. Tissue permeability is impaired.
- A capsule consisting of connective tissue is formed. She is gradually growing.
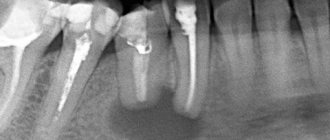
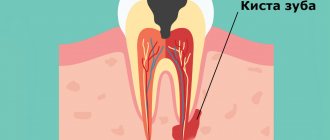
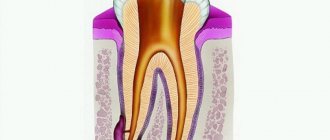
What is a dental cyst (root cyst)
A cyst on the root of a tooth is a tumor-like formation surrounded by a dense fibrous membrane consisting of stratified mucous epithelium. The internal space of the sac is filled with serous or purulent fluid. The size of the cavity can vary widely: from 0.1 to 3 cm. Cysts less than 5 mm are called granulomas.
The most common location of dislocation is the area of the apex of the tooth root. Therefore, such cavities are called radicular (“radix” - root). They can be located near the entrance to the root canal, between the roots, or at the top under the crown. Other localization areas:
- near the alveoli of the frontal segments;
- under the third molars (wisdom teeth);
- inside the maxillary sinus.
A cyst in a tooth can have different origins. According to this feature, the following types of formations are distinguished:
| Variety | Description |
| Radicular | Found in the area of the apex of the roots of any tooth. The main reason is the destruction of osteocytes due to advanced caries and pulpitis. |
| Follicular (pericoronal) | Benign tumor of non-inflammatory origin. Occurs in the area of transition between enamel and cement. Formed from the tooth germ due to disruption of eruption. |
| Periodontal | A congenital dental cyst formed from remnants of the epithelium of the dental plate. Most often localized in the premolar area. |
| Retromolar | Formed as a result of carious inflammation or abnormal eruption of the eighth segment |
| Residual | Appears due to incorrect extraction of the dental unit and poor revision of the alveoli. |
| Primordial (keratocyst) | Develops from epithelial cells of the enamel organ. Capable of keratinization. Localized in the corner of the lower jaw, near the lower premolars. |
Types of oral cysts
Based on their origin, mucoceles are:
- true;
- extravasal.
The first ones lack their own membrane and are covered with a gland capsule. They occur due to blockage of the duct and accumulation of mucus. The second are post-traumatic. They are formed when the tightness of certain structures is broken and the mucous secretion enters the surrounding tissues.
According to the localization criterion, the neoplasm is classified into:
- Sublingual. It is located in the hyoid-maxillary muscles or submandibular region. During rapid growth, it grows very quickly and then causes serious discomfort.
- Submandibular. Located in the lower submandibular region. It feels like a dense ball to the touch. Promotes disruption of the natural mechanism of salivary fluid secretion.
- Parotid. Rarely encountered in dental practice. It can be very painful when you open your mouth wide. It is formed due to impacts, injuries, after which the inflammatory process caused the closure of the salivary ducts.
- Extravasal. Most often found on the inner surface of the lip. Occurs due to mechanical damage. The inside is filled with granulation tissue.
Causes of retention cysts
The reasons for the formation of cysts are varied, but more often than others, factors such as:
- chronic inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx with periodic exacerbations - tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- autoimmune diseases accompanied by the production of a large number of lymphocytes;
- smoking, especially tobacco with a high tar content;
- injuries, including the habit of swallowing small bones;
- hormonal imbalance;
- occupational hazards, inhalation of aggressive aerosols;
- decreased immunity, especially local.
The formation of a cyst is caused by impaired drainage of the mucous lacunae of the tonsils against the background of the inflammatory process.
Signs of a cyst
Among the main symptoms of the disease:
- The appearance of an unusual protrusion on the soft tissues of the mouth. It may resemble an abscess. It usually has a bluish color with a burgundy border, but it can also match the tone of healthy gums. The “older” the mucocele, the thinner its walls become. The “bubble” is movable; it is not fused to the surrounding tissues.
- Discomfortable sensations while chewing food. There is a feeling as if there is a foreign object in the mouth that is constantly in the way.
- An unpleasant feeling of constriction of the mucous membrane. In this case, pain does not occur.
The cyst may burst if there is a lot of pressure on it. Spontaneous opening sometimes occurs while eating. The difficulty is that afterwards it forms again - through the passage in the mucous membrane, the cleared cavity is refilled with liquid contents.
What happens if you don't treat a dental cyst?
The formation does not manifest itself clinically for a long time. The progression of the disease leads to discomfort in the pathological area (especially when chewing food). Over time, a tubercle forms on the surface of the gum near the root area, which gradually increases. The mucous membrane changes color and swelling appears.
When the process suppurates, a person experiences symptoms of inflammation and intoxication: hyperthermia, headache, toothache, chills, tachycardia. A fistula may form in the middle of the protrusion, from which the contents of the cavity are released.
If you do not start treating cystic formation in a timely manner, serious complications may develop:
- phlegmon;
- lymphadenitis of nearby lymph nodes;
- inflammation of the maxillary sinuses;
- periostitis (spread of infection to the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis;
- abscess;
- deformation of the dentition;
- blood poisoning.
Examination of patients who have a cyst in their mouth
Diagnosis of the described disease is simple.
The doctor examines and palpates the abnormal lesion and studies the symmetry of the face. If the mucocele has reached a diameter of more than one and a half centimeters, then its color is blue. When the lesion is opened, viscous yellow contents are released. If the resulting biological material is submitted for analysis, a large amount of salivary proteins and amylase will be found in it. If necessary, the Trommer reaction is performed to confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
During ultrasound diagnostics of the salivary gland, the doctor observes an anechoic formation of a round shape. Its borders are smooth. The fact that the patient has a mucocele is said:
- presence of granulation lining;
- absence of epithelial membrane;
- the presence of mucin and protective blood cells.
If there is doubt about the benignity of the tumor, the patient is referred to an oncologist.
Treatment methods
Conservative treatment:
- washing the tonsils;
- inhalation;
- rinsing;
- ultrasonic influence;
- laser therapy.
These procedures cleanse the tonsils, increase blood circulation, have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, which has a positive effect on the recovery process of the tonsils and their proper functioning.
If conservative methods do not produce results, then surgical treatment is resorted to.
How to treat
It is very dangerous if a person tries to remove a cystic formation on his own and, to do this, puts pressure on it or bites it. Any mechanical influences have a negative effect on the course of the disease. Due to external pressure, the liquid inside the bubble begins to flow beyond its boundaries. Afterwards it accumulates again in the inflamed area. But at the same time, the risk of infection of damaged tissues increases significantly.
Doctors most often treat mucocele surgically. If the “bubble” is localized on the lower lip, two semilunar incisions are made in its projection, after which the internal neoplasm is isolated along with all its contents. Finally, stitches and a sterile pressure bandage are applied.
If the problem concerns the sublingual area, the following can be done:
- cystectomy;
- cystsialadenectomy.
In the first case, only the cyst itself is removed. It is cleaned and cut out. In the second type of surgery, the gland is also removed.
If there is a formation in the parotid zone, a parotidectomy is performed - complete or partial. It involves excision of the cyst and part of the parenchyma. Lesions located in the submandibular area are always removed along with the gland.
If we are talking about treating a child or a weakened elderly person, the dental surgeon may decide to excise only the dome (upper part) of the abnormal structure.
Signs, diagnosis and treatment
Manifestations of the disease depend on the location of the cyst. Most often, these are rounded formations that slowly increase in size, elastic and soft to the touch. They do not cause pain at first, rarely exceeding 1 cm in diameter. But in the absence of treatment, cysts begin to seriously interfere not only with eating, but also during conversation. The formation may disappear if, due to an accidental breakthrough, the contents come out. However, over time, the cyst forms again; if its size becomes very large, it acquires a characteristic bluish tint.
For diagnosis, methods such as visual inspection, palpation, and a number of hardware studies are used. Ultrasound, sialography to determine the problem with contrast, MRI and CT are more often performed. Additional examination methods may also be prescribed, for example, cystography of the bladder, probing of the salivary ducts, histology. If the diagnosis is questionable, a biopsy and puncture of samples are performed.
Conservative therapy does not bring any effect; when diagnosing a cyst of this type, surgical intervention is recommended. For this, local anesthesia is used, after which the formation is removed along with the affected gland and membrane to prevent relapses. If surgical intervention is refused, the formation often develops into phlegmon, and a tissue abscess develops.
The conservative method provides only temporary results. To do this, the membrane is punctured and the contents of the cyst are sucked out. But in all cases, the formation appears again, that is, this method of therapy is not recommended, as it is ineffective.
Surgery includes the following steps:
- inspection and surface preparation are carried out;
- local anesthesia methods are used for pain relief;
- the area with the cyst shrinks, which reduces blood flow and ensures stability of the tissue position;
- two oval-shaped incisions are made near the formation, after which the contents are husked;
- the affected lobes of the gland are removed, which helps to avoid complications or relapses in the future;
- the wound is sutured, thin sutures are applied, and self-absorbing sutures are often used.
The contents of the capsule are sent for additional research. This helps to eliminate serious risks, especially if the development of malignant processes is suspected. In case of serious intervention, plastic cystotomy is recommended. Typically, this situation occurs when removing a maxillary-hyoid formation.
Treatment of cystic formation at home
Home therapy for oral cysts only makes sense if for some reason you cannot get to a dental surgeon in the next few days. It consists of rinsing with herbal solutions and antiseptics. You can also make compresses with anti-inflammatory herbal medicines.
If the hearth breaks through, it’s too early to rejoice. Most likely, it will soon reappear in its original place. This is how cysts work - their contents expire, but the outer layer remains.
Under no circumstances should you treat a bulge on the gum or mucous membrane as a regular pimple. Any attempts to open it mechanically will not lead to anything good. But the resulting wound can become infected. Then the inflammation will spread to deeper layers in a fairly short time, and it will be much more difficult to cure.
Prevention of palatal cysts
It is important to understand that a cyst is usually formed as a result of a long-term inflammatory process. Carrying a bag of pus in the throat is extremely harmful; it is a source of chronic infection. Microbes have access to the bloodstream; if the body is weakened, this can lead to diseases of the heart, joints and kidneys.
ENT doctors at CELT have extensive practical experience in treating tonsil cysts. Specialists are ready to help people of all ages, including children, as well as those who have unsuccessfully tried treatment in other clinics. The main thing is to cooperate with your doctor to complete treatment until complete recovery. You can safely contact our clinic with this problem.
How to reduce the likelihood of developing education
To minimize the risk of mucocele formation, you need to follow the rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, quit smoking;
- carefully observe oral hygiene;
- rinse your mouth after every meal;
- eat a balanced diet;
- do not put foreign objects in your mouth;
- get rid of the habit of biting your lip;
- correct malocclusion;
- undergo oral hygiene every year;
- avoid trauma and chemical burns to the lips;
- promptly replace dentures;
- Follow the rules for wearing braces and caring for them.
People who follow preventive measures are much less likely to need treatment for oral cysts. If a lesion has appeared and is growing in size, there is no need to expect it to disappear on its own. This happens very rarely. It will either “deflate” or be filled again with contents and ultimately may grow to such a size that it will not be possible to do without emergency surgical intervention.
Symptoms of tonsil cyst
The clinical manifestations of this pathology depend on the size of this formation. For symptoms to appear, the retention cyst must exceed five millimeters. Before this, her discovery during examination was accidental. The location of the cyst also influences the clinic.
The patient is concerned about the following:
- sore throat; constant sensation of a foreign body; difficulty breathing; pain when swallowing saliva; there is a tingling sensation at the location of the cyst; have difficulty swallowing food and drinks; food entering the nasopharynx; change in voice timbre (hoarseness, hoarseness); sensation of unpleasant taste; constant coughing; bad breath.
If blood appears, it is necessary to suspect malignant degeneration of the tumor. When the cyst suppurates, the temperature rises, the throat turns red, and swelling of the tonsils is noted. The disease is differentiated from purulent tonsillitis.
The main differences between granuloma and cyst
Indicators and signs for comparative analysis Granuloma Cyst External signs, structure Solid formation covered with connective tissue. Reddish color Cavity with liquid or pus, covered with stretched skin, transparent, dirty-white in color Overall dimensions, diameter of the abscess 40 – 80 mm 90 –300 mm Result of X-ray studies There are no contours of the tumor The image shows a clear border of the round capsule Clinical course of the disease Tooth stable and stands motionless in its place The tooth becomes mobile The condition of the gums and other periodontal soft tissues, lymph nodes Swelling appears in the oral cavity, and redness of the mucous membrane occurs. The effect on bone tissue is insignificant. The cyst develops locally, the inflammation is not transmitted to the mucous membrane. The tumor causes a negative effect by reducing the development of bone tissue, “corroding” it, so the picture shows the process when hard bone tissue decreases