A pediatric orthopedic dentist specializes in dental prosthetics for the youngest patients. Pediatric orthopedics is not the most common branch of dentistry, and therefore finding a real professional in this matter can also be difficult. A good doctor must not only thoroughly study the structure of the jaw apparatus in children, he must perfectly master prosthetics and dental restoration in children. In any clinical situation, the doctor must do everything possible to restore dental elements rather than give preference to installing a denture. The activities of a pediatric orthopedic dentist will be discussed in more detail below.
What does a doctor do?
In short, it is approximately the same as an adult prosthetist - he is engaged in the restoration and prosthetics of dental elements, but only in children. Despite the fact that these are the main tasks of a dentist, they still need to be distinguished.
The thing is that dental restoration and prosthetics in children are two radically different procedures. This applies not only to the indications for the procedure, but also to the process itself.
IMPORTANT! An experienced orthopedic dentist will never perform artificial prosthetics if there is at least a minimal chance of saving the tooth. This is especially important in pediatric orthopedics, since the child’s jaw apparatus is just beginning to form, and hasty prosthetics can result in a number of adverse consequences.
Restoration of dental elements
This procedure is carried out if the root of the dental unit remains intact. This technique is always resorted to when there is at least a small chance of saving the tooth and returning it to its original healthy appearance.
During reconstruction or restoration, an orthopedic dentist will create a crown based on individual measurements (in fact, it will imitate a regular tooth without being a prosthesis, because the root remains healthy). Next, the crown will be installed at the site of the damage.
Prosthetics
This procedure is resorted to if the tooth root has been damaged too much (or is completely missing). Naturally, with such a deviation, it will no longer be possible to restore the tooth, so the orthopedic dentist will create a modern and comfortable prosthesis that will replace the damaged or missing dental unit.
IMPORTANT! Prosthetics involves not only the complete restoration of the appearance of the damaged tooth, but also the preservation of all the basic functions of the element.
The prosthetic procedure involves the installation of various structures:
- Fixed elements (pins, crowns, inlays) . With this method, installed fixators and prostheses are not removed by either the patient or the doctor.
- Conditionally removable elements (prosthesis for one dental unit). Such structures can only be removed by an orthopedic dentist, but not by the patient.
- Removable structures (inserted dentures). Such elements can be completely removed by the patient; they are rarely used in pediatric orthopedics, almost never.
In addition, a pediatric orthopedic dentist deals with the elimination of disorders that were caused by dental injuries, as well as the treatment of the following problems:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- cheilitis;
- periodontitis;
- dental erosion;
- persistent pain that occurs after filling a dental unit.
How to transfer from a children's clinic to an adult clinic?
The compulsory medical insurance policy gives the right to children under the age of 18 to be served in children's clinics, after which they need to be transferred to an adult medical institution. Tells how this happens.
AlfaStrakhovanie-OMS reminds that the transfer of an insured person from a children's clinic to an adult clinic and the preparation of the necessary documents are regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated May 5, 1999 No. 154 “On improving medical care for adolescent children.”
To transfer to an adult clinic, healthy teenagers do not need to come to a medical institution; the transfer takes place in absentia. Those who have serious illnesses and are registered with a dispensary are accepted by a commission that includes adult and pediatric doctors.
Find out the conditions
For all adolescents, immediately before reaching the age of 18, the doctor at the children's clinic draws up a translated epicrisis, a list of updated diagnoses, fills out information about vaccinations received and enters the data into the computer. This data is transmitted to the adult clinic. The transfer itself is formalized by a bilateral act.
There are lists of those who will be transferred in the near future in both adult and children's clinics. When the insured person comes to the adult clinic, his card will already be prepared by the district nurse and transferred to the registry.
The insured person can undergo the first medical examination in an adult clinic at the age of 21 and then every three years (at 24, 27, 30 years, etc.). At the age of 18, medical examination, as a rule, has already been completed in a children's clinic, before the citizen finishes being observed there and is subject to further observation in an adult.
“The transfer of an insured person from a children’s clinic to an adult clinic is regulated by an order of the Ministry of Health and for relatively healthy patients occurs automatically. If you are asked to come to a children's medical institution and pick up documents or an extract “about absenteeism,” then medical workers do not comply with the required standards. In these cases, an insurance representative will come to your aid,
– says Svetlana Babarykina, director of regional management of AlfaStrakhovanie-OMS LLC.
– If a teenager or his parents (legal representatives) have a desire to be assigned to a specific clinic, in this case they must come there and write an application.
Also, do not forget that at the age of 14, after the child receives a passport, it is necessary to come to the insurance company and enter the data into the register.” You can contact an insurance representative with any questions about the transition from a children's clinic to an adult clinic by calling the 24-hour free hotline "AlfaStrakhovanie-OMS" 8-800-555-10-01, through the website www.alfastrahoms.ru, as well as during a personal visit to any company office in the territory of 13 constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
How can the doctor help?
Modern dental equipment allows not only to eliminate the violation of the integrity of dental elements in a small patient, but also to restore their original aesthetic appearance. However, all this can only be done by an experienced orthopedic dentist.
If you are looking for an experienced doctor who can restore your child’s beautiful smile, then contact our dental clinic. We employ real professionals who:
- will be able to give the child a new dazzling smile;
- in case of loss of a baby tooth, they will retain sufficient space for the formation of a molar (permanent) dental element;
- return the jaw apparatus to its full function so that the child does not experience discomfort when chewing food;
- will restore the tooth to its original condition, if the root was not damaged.
If a child needs dentures, the doctor will select the most comfortable and attractive option that your child will wear with pleasure. All prostheses and retainers are made of lightweight and hypoallergenic materials, so you don’t have to worry about the safety of your child.
Therapeutic manipulations
Children 3 years of age should be treated exclusively in the presence of adults, with only a few exceptions when sterile conditions are required.
In the dental chair, the baby is in the arms of his mother or father.
Treatment of children over 3 years of age takes place in the presence of parents, but with its own characteristics: if we are talking about a surgical operation, then the mother may be present in the office, but be at a distance. For some surgeries and conditions, parental presence in the office is prohibited.
- Mother in a chair with a child: the dentist can give this type of treatment based on the baby’s age, characteristics of his behavior or physical condition. One of the parents acts as a guarantor of adequate behavior of the child in the chair, and, if necessary, will hinder the child’s movements. When treating children diagnosed with autism, Down syndrome, mental retardation, cerebral palsy and other movement disorders, treatment takes place with the mandatory presence of the mother.
- Mother next to the child: children after 5-6 years old can sit in the dentist’s chair independently, and the mother plays the role of a dental assistant. The close presence of parents in the office gives children a feeling of security and safety. The specific position of the mother and her role are determined by the dentist; the main thing is not to interfere with the treatment.
- The mother is in the office, but out of sight of the baby. Dentists may ask the mother to leave the baby's field of vision if his behavior is capricious. In the absence of “spectators,” the hysteria stops.
Treating young children is very complex. This is explained not only by physiological characteristics, but rather by behavioral ones. Parents should help the doctor and respond adequately to requests and comments.
In what cases is it worth going to a specialist?
You should contact a professional if you have the following deviations:
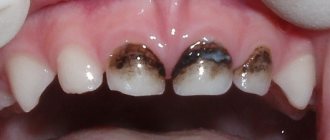
- The dental unit can no longer be restored. If neither fillings nor other treatments help, then you should at least consult an orthopedic dentist. This situation occurs especially often when the baby has severe caries.
- Fluorosis. If there is too much fluoride in a child's body, tooth damage cannot be avoided. So if you don’t want inflammation to occur, have the damaged area removed by an orthopedic dentist.
- The child has consequences of dental trauma. For example, a child knocks out or severely damages a tooth. In this case, the doctor will help restore the damaged tooth element.
- Too early loss of baby teeth. With this problem, the molars may not have enough space to erupt and secure. The doctor will help you choose a retainer for the child that will preserve space for the formation of the radical elements.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of caries of permanent teeth in adolescents.
To maintain the health of your teeth for a long time, you need to start carefully monitoring their health as soon as they erupt.
To do this, just follow a few simple rules.
- Provide quality hygiene, including professional dental hygiene for the child.
- Try to regularly attend preventive dental examinations at your clinic every 6 months, because... The development of caries in children in mixed dentition occurs very quickly.
- As a preventive measure at this age, it is recommended to do fissure sealing - this is “sealing” the recesses on the chewing surfaces of the lateral teeth
special filling material containing fluoride. This procedure mechanically closes the “weak” spots of the tooth and, at the same time, strengthens its enamel, releasing fluoride into the tissue.
- Teenagers often develop whitish spots on their teeth. It is necessary to find out what type of lesion such a defect belongs to - carious or not. This can be done by undergoing caries diagnostics with the Diagnocam apparatus in our clinic - this type of examination is digital and does not expose the child to radiation, therefore it is suitable for regular use. If a carious lesion is detected at an early stage, it can be cured without resorting to preparation using the modern ICON infiltration method
- If a child has crooked teeth and crowded teeth prevent them from being properly cleaned, then it is necessary to consult a pediatric orthodontist and begin orthodontic treatment.
- Treat caries in a timely manner in the early stages of the disease - this will allow you to save permanent teeth as much as possible from preparation, because the earlier caries is detected, the less affected tooth tissue the dentist will have to remove.
This approach to the child’s dental health, if not eliminates it, will significantly reduce the risk of serious carious lesions. If time was lost at the first symptoms of the disease, then a complication of caries – pulpitis – will have to be treated.
Why do you need a pediatric dentist?
Pediatric dentistry has its own specific features related to the anatomical structure and physiology of the child’s jaw. Only a person with a certificate in pediatric dentistry knows these fundamental nuances at an ideal level.
He has knowledge of therapy, pediatrics, pharmacology, and understands the pathogenetic principles of the appearance of dental pathologies depending on the age of the child. A children's doctor, in addition to professional skills, must have communication skills to communicate with children, be a good psychologist, and take into account the emotional and behavioral characteristics of his patients.
Why does a child need a pediatric dentist?
- The oral cavity in children is characterized by morphological differences from the adult jaw.
- Children's dental diseases have a specific course, on which treatment tactics depend.
- The technology for treating inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis) in children is fundamentally different from adults.
- Traumatic injuries to the teeth and jaw have their own characteristics.
- Anesthesia for pediatric patients is different from that for adult patients.
- Children need an individual psychological approach.
What are the responsibilities of a pediatric dentist?
A dentist in a children's office examines the supragingival and subgingival structures of the teeth, oral mucosa, periodontal tissue, bones, jaw joints, salivary glands, tongue, and submandibular lymph nodes. The competence of a pediatric dentist includes:
- taking anamnesis;
examination of the oral cavity using dental mirrors;- identification of defects in crowns, rows, and dental anomalies;
- referral for x-ray examination;
- drawing up a treatment program;
- carrying out planned sanitation (treatment, filling, cleaning, etc.);
- fissure sealing;
- exercises control over the formation of permanent teeth and bite;
- administration of drugs, anesthetics;
- provision of emergency dental care;
- carrying out clinical examination of children with dental and periodontal pathologies;
- referring children (if necessary) to an orthodontist and other specialists;
- interaction with doctors of other specialties, providing them with advisory assistance;
- prescribing therapeutic treatment at home.
The pediatric dentist will teach the child the rules and methods of personal oral hygiene, and explain to the child the need to perform it twice a day.