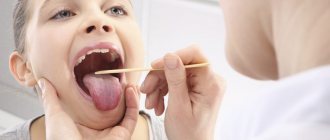
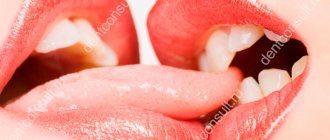
Most often, a sore throat is associated with viral inflammation, which is accompanied by fever, cough, runny nose and minor difficulty swallowing. But, unfortunately, in some situations these diseases can be complicated by the development of purulent-inflammatory complications, for example, peritonsillar abscess, and the task of the ENT doctor at the present stage is the correct diagnosis of this complication and timely treatment, because this complication does not tolerate deposits and is fraught with more significant spread of infection into the deep tissues of the neck. At the GMS Hospital Otolaryngology Center, a comprehensive approach is used to treat peritonsillar abscesses, combining conservative and surgical techniques.
More about the disease
Peritonsillitis is an acute condition secondary to tonsillitis or tonsillopharyngitis, which results in the penetration of an infectious agent (bacteria) into the loose peritonsillar tissue (peritonsillar space). The process is always one-sided, as a result of which it has certain symptoms:
- pain or increased pain on one side;
- severe difficulty swallowing;
- swelling and bulging on the neck on one side;
- asymmetry and bulging of pharynx tissues.
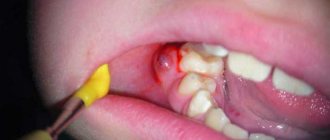
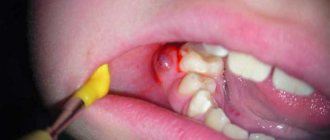
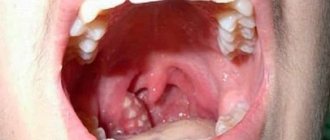
A peritonsillar abscess occurs when a cavity filled with pus forms, located in the peritonsillar (peritonsillar) tissues.
It can form several days after the development of a sore throat or an exacerbation of tonsillitis. Less commonly, due to traumatic injury to the oropharynx or penetration of a foreign body into the tissue around the tonsils. In people with a weak immune system, an abscess can form within a day. It is more often unilateral, but cases with bilateral paratonsillar abscess have been reported in the literature. This pathology is one of the most severe purulent lesions of the oropharynx. With further spread, the infection moves into the deep tissues of the neck (parapharyngeal space), which can lead to a life-threatening condition. Depending on their location, there are several forms of peritonsillar abscess, but all of them require surgical treatment.
The Surgical Otolaryngology Center at GMS Hospital provides proper treatment and diagnosis of paratonsilitis and paratonsillar abscess of any form. Treatment tactics are selected by specialists individually, depending on the stage of the disease, the presence of complications and concomitant pathologies.
General information
Peritonsillar abscess (synonyms - paratonsillitis , phlegmonous tonsillitis ) is one of the nosological forms of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the pharynx, which differs from other forms (parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal abscess) in the prevalence of the pathological process and anatomical and topographic localization.
A peritonsillar abscess is an acute inflammatory and purulent manifestation in the area of the peritonsillar tissue. ICD-10 code for paratonsillar abscess: J 36. In most cases, tonsillar abscess is secondary, that is, a complication of chronic tonsillitis/acute catarrhal, lacunar or follicular tonsillitis . Much less often, it can be an independent disease (primary), developing as a result of an odontogenic process, trauma to the pharynx by a foreign body, or with chronic obstruction of the nasal cavities (adenoiditis).
Pathogenic microflora penetrates into the paratonsillar tissue mainly by contact from the enlarged, altered and branching lacunae of the tonsils through damaged (melted/necrotic) capsule tissue. That is, a purulent abscess in the throat (peritonsillar abscess/peritonsillitis) is a consequence of the transition of an acute infectious-inflammatory process from the palatine tonsils directly to the peritonsillar tissue and adjacent tissues, which is characterized by unilateral/bilateral inflammatory infiltration. The infectious-inflammatory process in loose connective tissue involves the buccal-pharyngeal fascia, as well as the upper pharyngeal constrictor with fascia. In most cases, there is a unilateral abscess; bilateral lesions occur only in 7-10% of cases.
Peritonsillar abscesses are the most common and severe disease among all purulent processes of the pharynx. It occurs in people of all ages, but people aged 15-40 years are more likely to get sick. No gender differences were found. The development of the disease is characterized by seasonality: it is more often observed in the off-season/cold season. Acute paratonsillitis occurs less frequently in the summer, mainly in cases of sudden local hypothermia - ice cream, cold drinks, swimming in cold water, etc.
Why is it necessary to open and drain a peritonsillar abscess?
Peritonsillar abscess is an urgent condition in otolaryngology. The proximity of vital structures (windpipe, large vessels of the head and neck) requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. In the initial stages, when an abscess has not yet formed, the pathology responds well to drug therapy. A course of antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory and painkillers is prescribed. If conservative treatment is ineffective, the abscess is opened surgically.
Peritonsillar abscess is dangerous due to its complications, fraught with the development of phlegmon, mediastinitis and even sepsis. The Otolaryngology Department at the GMS Clinic has everything you need to accurately diagnose and treat peritonsillar abscesses.
The opening of the abscess is carried out using modern surgical equipment. During the operation, the potential of laser and radio wave surgery is actively used, which allows the procedure to be performed in the most gentle manner, eliminating the development of surgical complications. Opening abscesses in children is performed under anesthesia, which significantly increases the comfort of the intervention.
Cost of treating peritonsillar abscess
The prices indicated in the price list may differ from the actual prices. Please check the current cost by calling +7 495 104 8605 (24 hours a day) or at the GMS Hospital clinic at the address: Moscow, st. Kalanchevskaya, 45.
| Name | Price |
| Opening of the epiglottis abscess | RUB 54,999 |
| Opening abscesses, phlegmon of the laryngopharynx | RUB 64,995 |
| Opening a paratonsillar or retropharyngeal abscess | RUB 46,998 |
| Drainage of peritonsillar abscess | RUB 24,997 |
| Tonsillectomy + removal of peritonsillar abscess (According to Quinzey) | RUB 189,994 |
Dear Clients! Each case is individual and the final cost of your treatment can only be found out after an in-person visit to a GMS Hospital doctor. Prices for the most popular services are indicated with a 30% discount, which is valid when paying in cash or by credit card. You can be served under a VHI policy, pay separately for each visit, sign an agreement for an annual medical program, or make a deposit and receive services at a discount. On weekends and holidays, the clinic reserves the right to charge additional payments according to the current price list. Services are provided on the basis of a concluded contract.
Plastic cards MasterCard, VISA, Maestro, MIR are accepted for payment. Contactless payment with Apple Pay, Google Pay and Android Pay cards is also available.
Western standards of treatment (evidence-based medicine)
Continuous staff development
Regular interaction with leading Russian and foreign medical institutions
Modern medical equipment and advanced diagnostic and treatment methods
Unified standard of service
We work around the clock 24/7/365
Make an appointment We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Oksana
Signs and symptoms of paratonsillitis
The disease has an abrupt onset. An abscess forms a few days after an exacerbation of tonsillitis or the onset of a sore throat and is accompanied by vivid symptoms:
- acute pain in the throat, radiating to the jaw or ear;
- sensation of a “lump” in the throat;
- fever (temperature 39-40°C);
- submandibular lymph nodes are greatly enlarged;
- difficulty swallowing (even drinks);
- the appearance of a repulsive odor from the mouth;
- neck pain that gets worse with exercise;
- general weakness;
- inability to fully open the mouth;
- headache;
- speech impairment (voice as if there is a hot potato in the mouth);
- difficulty breathing (with large ulcers).
Spontaneous breakthrough of suppuration into the throat cavity is accompanied by an improvement in well-being and the appearance of an admixture of pus in the saliva.
The spread of the abscess contents into the peripharyngeal space significantly worsens the condition, so there is no need to delay operations to open the abscess. If you have even one of the symptoms listed above, schedule a consultation with an otolaryngologist today. Doctors at the Center for Operative Otolaryngology at GMS Hospital use gentle microsurgical techniques, which contributes to a speedy recovery and the absence of relapses of the disease.
What is an abscess and how does it develop with sore throat?
An abscess with tonsillitis begins with inflammation that affects the tissue around the tonsils of the palate and lymph nodes, during which suppuration occurs. Its formation is due to the presence of several bacterial pathogens, consisting of streptococcal, staphylococcal, fungal or anaerobic and aerobic pathogens of phlegmous sore throat, which can lead to the development of pyogenic microorganisms. After the incubation period, the catarrhal process turns purulent and an extensive paranthosillar abscess begins. In addition, the disease often progresses due to the presence of chronic sinusitis, rhinitis or otitis in the body.
Abscesses can form not only around the tonsils, but also in the tongue, tubal tonsils or nasopharyngeal system.
They often arise as a result of dangerous hypothermia during an illness or frequent relapses, when the tissue of the tonsils is still fragile and inflamed. In rare cases, suppuration can begin after diseases such as influenza, scarlet fever, ARVI, measles, periostitis, neck injuries or purulent inflammation of the teeth and salivary glands.
The pathology occurs due to the structural features of the tissues of the tonsils, when an excess amount of blood enters the capillaries and swelling begins, and the crypts of the tonsils are filled with purulent discharge, most often in the upper part of the palate. There are several varieties, each of which has an individual development pattern.
- Lower - affects the fiber located between the tonsils of the tongue and palate, behind the lower third of the palatine arch. With an odontogenic cause, the development remains a rare type of abscess.
- Posterior - complicated by edema of the pharyngeal system and breathing problems, manifests itself mediocrely in patients of different ages in a ratio of 1:10.
- Supratonsillar - pus spreads to the tonsils and surrounding tissue, accumulating due to poor outflow, and is the most common type of suppuration.
- Lateral is the most severe form of the disease, due to the likelihood of microflora spreading to the pharyngeal area. Formed after mechanical damage or as a result of infection.
- Peri-almond is a complication due to tonsillitis with the participation of various bacterial microorganisms that greatly aggravate the pathology due to decreased immunity and scarring on the surface of the tonsils.
- External - pathology affects the surface of the tonsils and is very rare in medical practice.
People suffering from diseases such as immunodeficiency, anemia, diabetes mellitus or people with a predisposition to oncology are in the primary risk group for the development of severe pathological conditions of tonsillitis. There are no anatomical reasons for the development of an abscess, so the therapist, when treating, always focuses on the accompanying symptoms.
Diagnostics
For the differential diagnosis of paratonsillitis, the following research methods are used:
- examination by an otolaryngologist;
- laryngoscopy;
- pharyngoscopy;
- laboratory tests (blood tests, culture for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics, etc.).
In some cases, to clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are performed - ultrasound, CT scan of the soft tissues of the head and neck.
A comprehensive examination allows you to assess the condition of the abscess and tonsil, determine treatment tactics and the scope of intervention. You can complete all the required tests at the GMS clinic in a day.
Treatment methods
The treatment tactics for paratonsillitis depend on the extent of the spread of the purulent process and the presence of complications. Peritonsillitis in the initial stage is treated conservatively, with antibiotics, decongestants, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If drug treatment is ineffective or an abscess forms, the abscess is surgically opened and its cavity is drained. The opening of the paratonsillar abscess is carried out under local anesthesia. The otolaryngologist dissects the wall of the abscess, removes the purulent contents, and rinses the cavity with an antiseptic. An improvement in the condition is observed immediately after opening and draining the abscess.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
Classification
The classification is based on several characteristics. According to the localization of the pathological process, anterior-superior, posterior, posterior-superior, anterior, lateral (external), inferior and bilateral peritonsillar abscess .
According to clinical and morphological manifestations, they are distinguished: edematous , exudative-infiltrative and abscess forms , which, in fact, are stages of development of the pathological process in the peritonsillar tissue that transform into one another. It is the first two forms that are combined with the term “acute paratonsillitis.” The abscess formation stage, with timely and adequate therapy, may not occur.
Prevention of paratonsillitis
The following simple preventive measures will help prevent the development of peritonsillar abscess:
- strengthening the immune system;
- healthy lifestyle;
- timely treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, adenoids, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.), caries;
- rejection of bad habits.
In the presence of recurrent abscesses, elective tonsillectomy is recommended.
Opening a peritonsillar abscess at the GMS clinic is a simple and safe surgical procedure that is performed in an outpatient or inpatient setting. Recovery takes 10-14 days, after which you will return to your normal life. You can make an appointment with an otolaryngologist at GMS Hospital by phone or using an online application.
Causes
The main cause of a peritonsillar abscess is usually a bacterial infection. Namely: the penetration of infection from the crypts (folds) of the tonsil into the surrounding peri-tonsil tissue. In the vast majority of cases, the cause of abscess formation is pyogenic streptococcus. Less commonly - Staphylococcus aureus and other microorganisms.
Often, inflammation develops as a complication of tonsillitis or chronic tonsillitis in the absence of timely correct treatment. A risk factor is weakened immunity associated with inflammatory diseases, diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency, poor nutrition, smoking, and alcohol abuse. Less commonly, the disease develops against the background of caries and injury to the tissues of the pharynx.