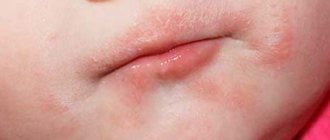
Quite often, parents may notice a soft bump that appears on their child’s gum when pressed. What could be the reasons for this phenomenon?
- inflammation of the roots (both baby teeth and molars, permanent ones);
- the beginning of tooth eruption.
Why does an abscess occur?
There can be many reasons for the formation of a lump (fistula, swelling), but the most common of them is undetected or ignored caries. Not all children maintain oral hygiene and eat properly, and not all parents carefully control this, which causes caries to appear on one or several teeth at once.
If caries is not treated, it will develop into pulpitis, extending beyond the tooth area and affecting the upper part of the root. As a rule, a lump appears just near the tooth whose root is inflamed. Typically, a lump can be noticed near a tooth with caries or with a filling that was placed long ago or poorly; Another common reason for its appearance is an injury received from a strong blow or an accidental fall, which can trigger the onset of the inflammatory process.
Stages of development of an abscess:
- As a result of caries, the infection penetrates into the pulp, affecting the root tip.
- Pus begins to form near the top of the root.
- Purulent formations fall under the mucous membrane of the gums.
- A cyst appears, looking like a small lump from the outside.
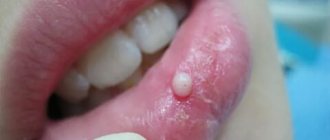
The most important symptom of an abscess is a soft and painful swelling, even with slight pressure.
Sometimes, due to an excess of pus, the lump may burst under pressure, and then a fistula appears - a small hole in the gum, which is connected with the source of inflammation located in the upper region of the root. A feature of the fistula is the constant release of purulent formations.
If inflammation decreases for some reason, the fistula may close on its own. However, when the child’s immunity decreases and the inflammatory process begins again, accompanied by pus formation, the appearance of a fistula will not be long in coming.
Why does an abscess form?
Among the reasons for the appearance of ulcers may be poor oral hygiene, weak immunity, mechanical and thermal injuries, and gum disease.
Baby teeth are more often exposed to various infections, and caries spreads much faster in them. In just a few months, a cavity can form that reaches the nerve. If this is not treated, the bacteria enter the dental nerve and then affect the bone. Here they multiply, dissolve the bone and thus form pus, which can be released into the oral cavity.
Otherwise, it accumulates and appears under the gum, which swells and takes on the appearance of a lump. Sometimes it bursts, but then appears again. The danger of this process is that in any case there is an infection in the body, and the pus can damage the growing permanent tooth.
Also, the formation of an abscess can occur due to the following factors:
- periodontonitis is an inflammation of the connective tissue that is located between the cementum of the tooth and the alveolus. The process can begin due to a virus, bacteria, hypothermia or injury;
- single-gene osteomyelitis - damage to the bone and surrounding tissues due to infection in the dental canal. This is possible due to poor quality dental treatment;
- dental cyst is a formation in the bone tissue of the jaw that is filled with fluid. In this case, an abscess is formed if the cyst becomes inflamed with the formation of pus, which begins to come out;
- odontogenic sinusitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. Infection can occur due to untimely dental treatment or dental errors.
It is also important to treat caries in the early stages to prevent the development of pulpitis - inflammation of the pulp, which consists of various vessels and nerves that provide important functions of the tooth.
How to treat an abscess on the gum?
If an abscess or fistula appears, then you should not expect that the situation will resolve on its own: you need to make an appointment with a dentist. Treatment of an abscess on a baby tooth and a molar one will be different.
The appearance of an abscess on a baby tooth indicates periodontal inflammation. Such teeth must be removed, since the inflammatory process in the upper part of the root, accompanied by the formation of pus, may well spoil the molar, which will soon erupt in place of the milk tooth. This happens because the roots of temporary teeth are located next to the rudiments of molars. Bad bacteria and infection can also enter the lymph nodes under the jaw, causing them to become inflamed. The occurrence of a fistula means that pus will constantly seep into the mouth, which can cause the development of tonsillitis, since the tonsils will become infected. Various colds in a child are a direct consequence of an abscess on a tooth. Also, do not forget that toxins formed in the area of inflammation will definitely enter the bloodstream: this can result in allergic reactions, asthma and other serious general somatic diseases.
If we are talking about an abscess on a molar, then ordinary treatment is required for adults (provided that the tooth is not fundamentally damaged and can still be saved from removal).
Having discovered an abscess in a child, you should not try to cure it on your own. You can easily find a lot of advice on the Internet on how to relieve inflammation, but no amount of rinsing or even taking powerful antibiotics can eliminate the inflammatory focus located at the root of the tooth. Moreover, it is useless to hope that the tooth ache will stop. A bursting lump (this often happens) indicates only a short respite, during which, meanwhile, bacteria will still continue to enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This situation can turn into a serious problem if the child has diseases of the respiratory system, heart and other internal organs.
Often, dentists suggest leaving teeth near which the inflammatory process is occurring, persuading the parents of a young patient to carry out the silvering procedure. The arguments for refusing removal can be very compelling: possible problems with diction and pain during the removal operation. However, such dentists neglect the information contained in every textbook on dentistry, which clearly states that a baby tooth with a purulent focus must be removed. Silvering will only complicate the situation, and an unresolved inflammatory process can lead to asthma, tonsillitis and even diabetes: in comparison with these diseases, temporary problems with diction will seem like sheer nonsense.
But the formation of an abscess can be prevented, and this is not difficult to do - just teach the child to maintain oral hygiene. At an early age, a child cannot be adequately responsible for his actions, including those related to the care of the oral cavity, teeth and gums, so responsibility for the procedure lies entirely with his parents, who must control how and when the child brushes his gums and teeth . It is the parents who should buy the most effective baby toothpaste that guarantees maximum protection against caries.
Treatment of inflammation
Removal of a lump with pus on a child’s gum should be started immediately. Only a dentist can help the baby.
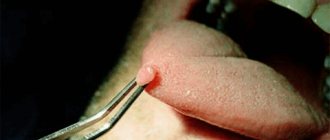
IMPORTANT! Self-medication, as well as piercing and squeezing are strictly prohibited! Such an intervention will lead to serious complications.
When an abscess forms over a baby's baby tooth, the doctor most often removes it. Such measures are necessary to exclude the possibility of destruction of the rudiments of the root. If a child has a lump on his gum next to a permanent tooth, treatment begins with a thorough examination. Sometimes the dentist will send you for an x-ray to assess the extent of the damage. Removal of a permanent tooth is carried out in extreme cases.
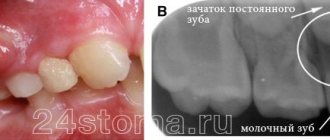
A lump on an area of the gum where there is no tooth yet: what to do in this case?
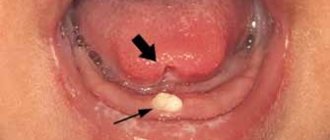
A couple of weeks before the tooth erupts, a cyst may appear on the gum, looking like a lump filled with a clear or bluish liquid. Such bumps are by no means common: dentists do not consider such formations to be a pathology requiring treatment. In addition, such formations on the gums in no way indicate an inflammatory process.
According to statistics, a small percentage of children are affected by the appearance of such a cyst. The child may not even suspect that he has a lump in his mouth, because if he touches it, there is no pain. However, a dental examination is still necessary, because the inflammatory process may still begin, in which case intervention will be required. The presence of inflammation is indicated by such signs as increased body temperature, pain when touching the lump, and swelling of the mucous membrane.
Most parents do not like the fact that their child has a lump in his mouth: in this case, you can ask the dentist to make an incision under anesthesia, as a result of which the fluid inside the cyst will come out. As a rule, when part of the cyst is removed, the crown of the tooth about to erupt is visible.
Symptoms
Symptoms can be divided into general (malaise, fever) and local (pain in the tooth area and when eating, redness and swelling of the gums, development of an abscess).
At the initial stages there are no external manifestations. Then the gums become red, swollen and painful when touched. The next stage is an increase in swelling, which forms due to the fact that pus begins to accumulate between the surface of the bone and the periosteum. After which it gets under the mucous membrane and a lump is formed.
As the abscess matures, it becomes white and the pain can spread to the entire jaw. The body temperature often rises, the child refuses to eat and is capricious.
Children may not always complain of discomfort, especially if they are still very young, so parents should regularly examine the oral cavity themselves.
How to help a child at home with suppuration?
If suppuration and the formation of a lump on the gum appear, it is recommended to contact a dentist as soon as possible, but, unfortunately, for various reasons this is not always possible.
If an adult can endure pain (although, of course, situations are different), then it is much more difficult for a child to endure painful sensations, and it is not easy for parents to watch their child suffer. There are ways to alleviate the baby's condition. Naturally, they will not replace full-fledged treatment, so you can resort to them only in situations where going to the doctor is impossible right now.
These include:
- take as much warm liquid as possible, which reduces intoxication of the body;
- eat liquid food (moderately warm, but not hot!), as it injures already damaged gums;
- If the pain becomes severe, you can use painkillers. For example, Nurofen or Paracetamol - the exact dosage depends on the age of the child, so before use you should carefully read the instructions for the drug;
- to reduce swelling, you can resort to cold - any frozen product from the freezer compartment of the refrigerator is wrapped in a soft cloth and applied to the cheek;
- use rinsing solutions that temporarily relieve pain - chamomile decoction or the drug chlorhexidine, which reduces irritation.
Preventive measures to prevent the formation of lumps on the gums
To reduce the likelihood of an abscess to a minimum, a child from childhood should be taught to carefully observe oral hygiene.
The list of the most effective measures includes:
- Brushing your child's teeth twice a day. First, parents should brush their child’s teeth themselves, showing how to do it correctly, gradually giving the child more independence in this matter;
- rinsing your mouth after every meal;
- minimizing sweets in the diet - it is important to ensure that the child keeps caramel and candies in his mouth as little as possible;
- Do not introduce your child to chewing gum (the product is especially harmful if it contains sugar).
Principles of treatment of childhood stomatitis
Doctors do not recommend treating childhood stomatitis at home, since in this case there is an extremely high probability of causing serious harm to the child’s health with drugs that are not intended for the treatment of children, especially for an unconfirmed diagnosis. At the clinic, the child will be examined by a dentist, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Treatment is often based on stages such as:
- isolation of a sick child from other children;
- disinfection of objects with which he came into contact;
- drawing up a suitable daily diet (it is important to minimize the amount of carbohydrates);
- ensuring oral hygiene to prevent secondary infections.
Features of treatment of different types of childhood stomatitis
There are several types of childhood stomatitis. Most often, specialists encounter the following:
- vesicular (viral) - appears due to the influence of bacteria; transparent bubbles form on the larynx, lips, cheeks, tongue;
- herpetic - the herpes virus enters the child’s mouth;
- aphthous - occurs due to allergic effects;
- candidiasis - appears due to the proliferation of Candida fungi in the mouth.
Any type of stomatitis should be treated under the supervision of a doctor. The treatment process for each type of disease has its own characteristics.
If it is important for you that the treatment of stomatitis has a positive effect, then you can contact the Moscow Region clinic. For your child, our specialists will develop the most effective treatment plan and select the most appropriate medications. You can find a complete list of the cost of services in the pediatric dentistry department. We are always happy to be useful to each member of your family!