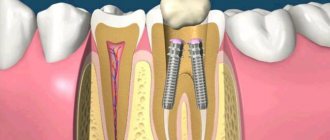
What is an abscess
People who do not pay attention to oral hygiene and proper gum care will sooner or later find out what a tooth abscess is. This is an acute inflammatory dental disease, which is often a complication of other pathologies.
There is an accumulation of pus under the tooth in the gum or hole left after extraction. A dense rounded bulge is formed. This is a fistula - a channel through which pus comes out of the tooth. Sometimes it opens and the contents leak out. But this does not mean that the pathology has passed, because its cause has not been eliminated. If bacteria continue to multiply, pus will again accumulate in the dental canal.
Without timely treatment, it is dangerous to health. An extensive abscess of the jaw may appear, the infection will penetrate into the bone or spread through the blood throughout the body. This threatens the development of osteomyelitis, inflammation of the bone marrow, and sepsis.
Cyst and granuloma of the tooth
Previously, it was generally accepted that if a neoplasm on the root of a tooth measures up to five millimeters, it is a granuloma, and if it is more than ten millimeters, then it is a dental cyst. Some dentists also distinguish a certain transitional stage - cystogranuloma, but practice shows that there are granulomas reaching even twelve millimeters, so an accurate diagnosis cannot be made only by the size of the formation and its shape. In addition to X-rays, histological examination of tissues is necessary.
The question often arises of how a granuloma differs from a dental cyst. The fact is that a cyst is a bladder filled with fluid or pus, with a shell formed by connective tissue and lined on the inside with endometrium. Secretory fluid is produced by the membrane, and due to this the cyst increases in size. Granuloma grows due to the growth of tissues containing infected cells.
Types and forms of abscess
Depending on where the pus accumulates, there are three types of pathology:
- gum abscess or gumboil affects only the gums;
- periodontal develops in the periodontal pocket;
- periapical appears with severe destruction of the pulp and other dental tissues.
This pathology often occurs in an acute form and requires immediate dental treatment. But sometimes the fistula opens on its own. The pus comes out and the patient feels relief. If complex therapy is not carried out, the pathology can become chronic.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Cause
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, and periodontitis is a more severe form of the disease when not only the gums, but also the jaw bone are involved in the inflammatory process. Both diseases are often chronic and do not cause the patient much discomfort, but during periods of exacerbation more severe symptoms appear and the patient consults a doctor.
There are many causes of gum inflammation:
- hard and soft dental deposits;
- sharp edges of crowns and fillings, which constantly injure the mucous membrane;
- improperly restored contact points between teeth (due to which food accumulates in the gap, puts pressure on the gums and is an excellent place for microorganisms to settle);
- malocclusion (crowding of teeth, incorrect position in the arch);
- general diseases (diabetes, vascular problems, infectious diseases and others) can cause gum inflammation;
- changes in hormonal levels (during pregnancy, for example).
These are not all possible causes of gum disease, but most patient visits have one (or several) of these factors predisposing to inflammation in the gums.
Constant trauma (from food, the edge of a crown, tartar), microbial toxins, and impaired blood flow in the gums lead to the development of an inflammatory process. Usually, pus as such is not visible, but during periods of exacerbation, noticeable suppuration often occurs from periodontal pockets or its accumulation in the thickness of the mucosa (this formation is called a periodontal abscess).
Symptoms of gingivitis (periodontitis) in the acute stage
Patients with this diagnosis complain of:
- pain in the gums near a group of teeth;
- redness of the gums, swelling, pain when touched;
- it hurts to brush your teeth and eat;
- pus (sometimes with bloody veins) is released from the periodontal pocket or from the fistula tract (a fistula can form if the pockets are very deep);
- with gingivitis, the teeth usually do not suffer, but with periodontitis, tooth mobility, exposure of roots, pain from cold and sweet foods may be observed (since the root is more sensitive to irritants than the crown part of the tooth);
- Sometimes there is a deterioration in general health: fever, weakness, headache.
Exacerbations most often occur against the background of a general decrease in immunity (with acute respiratory infections or other diseases). In addition, periodontitis is characterized by seasonality (in spring and autumn, exacerbations occur more often).
Diagnostics
How to distinguish periodontitis from periodontitis? Outwardly, both cases may look the same: swollen gums, redness, a fistulous tract from which pus is released. In both cases, it hurts to bite on the teeth. In addition, one disease does not exclude another (there are cases when a tooth is surrounded by inflamed bone on all sides and it is almost impossible to say with certainty what is primary: periodontitis or periodontitis).
An x-ray is required to make a correct diagnosis and choose treatment tactics. In the image with gingivitis, we will not see any changes at all, but with periodontitis, areas where there is no bone tissue will be visible, while the teeth will be either healthy or well treated.
Treatment
It must be said right away that gingivitis is a reversible process, and periodontitis cannot be completely cured in most cases (it can be stopped, put into remission, but growing back the height of the bone is very problematic, and in many cases it is completely impossible).
If in the case of periodontitis we were dealing with microbes inside the root canal, then here we also have a microbial infection, only it is localized in the gums and bone. Treatment should be aimed at combating the cause, so the following measures can be taken:
- mandatory professional hygiene – removal of soft and hard dental plaque, polishing the surface of teeth, removal of granulations from periodontal pockets;
- correction of fillings and orthopedic structures, creation of normal contact points between teeth;
- if there is mobility of the teeth, they need to be splinted (limit movement);
- active anti-inflammatory therapy (rinses, dressings, ointments with antimicrobial action, in severe cases - antibiotics);
- general therapy (at the doctor’s discretion and depending on the severity of the process, antihistamines, painkillers, immunostimulants, vitamins, etc. can be added).
Usually this is enough to stop suppuration and relieve the acute process. To prevent exacerbations in the future, it is imperative to maintain hygiene (remove tartar at least once every six months), restore the dentition (if some teeth are missing), correct the bite (if there are problems with this) and maintain general health (if the cause of periodontitis is some common diseases).
Symptoms
The main symptom of a tooth abscess is pain. It is localized in one place and intensifies when pressed or chewed. The tooth becomes sensitive to cold, hot or sour foods. If the tumor appears in the upper jaw, pain spreads along the trigeminal nerve.
The following manifestations of pathology are also common:
- malaise, weakness, headache;
- temperature increase;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- the appearance of greenish discharge;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- if there is pus in the mouth, an unpleasant odor and bitter taste appear.
Abscess on the gum with periodontitis -
Gum suppuration can look completely different, but in any case, the formation of an abscess on the gum always occurs in the projection of the causative tooth. If the cause of suppuration is an infection in the root canals, then you will always see an old filling or crown on the causative tooth, or the tooth will be partially destroyed. In this case, infection in the root canals gradually leads to the development of a focus of chronic inflammation at the apex of the tooth root.
In dentistry, such inflammation of the tooth is called chronic periodontitis. From time to time, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation may occur, and in this case, pus begins to form at the apex of the tooth root, which comes out through the bone tissue and penetrates under the gum, forming an abscess there. Therefore, please note that with periodontitis, an abscess on the gum most often forms not at the gingival edge, but closer to the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth.
Abscess on the gum with periodontitis: photo
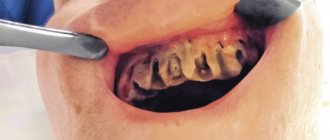
Symptoms - an abscess with periodontitis may look like a slight swelling of the gums in the area of 1 tooth or in the area of several teeth, if a significant purulent abscess has formed - flux (Fig. 4). Typically, the appearance of gum swelling is preceded by pain when biting one of the teeth. The pain can be acute, but sometimes purulent inflammation can occur without pain. Sometimes, in the projection of gum suppuration, swelling of the soft tissues of the face appears.
The abscess formed under the mucous membrane of the gums can burst with the formation of a fistula opening (Fig. 7-8). The fistula opening is connected through a fistulous tract to the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Therefore, gradual discharge of pus may be observed from the fistula openings. As soon as the acute inflammation at the root apex subsides and the process of pus formation stops, the fistula openings can close, but only until the process worsens again.
X-ray diagnostics - if you have a fistula or a purulent sac on your gum, treatment is only possible at the dentist. Before starting treatment, you need to take an x-ray to confirm the presence of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (24stoma.ru). The image will also show the quality of root canal filling, if it was performed previously. It’s sad, but according to official statistics, dentists fill root canals poorly in as many as 60-70% of cases.
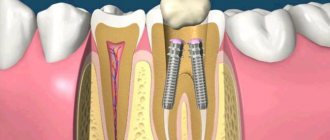
The most common mistake dentists make is not filling root canals up to the apex of the tooth root, as a result of which infection begins to multiply in the part of the root canal that is not filled with filling material. As a result, a focus of chronic inflammation develops at the apex of the tooth root, for example, in the form of a cyst or granuloma. Below you can see what cysts and granulomas look like on a diagram, an x-ray, and also on the apex of the root of an extracted tooth.
Treatment of gum suppuration during periodontitis -
If, against the background of an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, an abscess appears on the gum, then what to do will depend on the results of examining the tooth and analyzing the x-ray. In some cases, it may turn out that the tooth can no longer be treated, and then you will be referred to a surgeon for removal. However, in most cases, it is possible to cure such a tooth, and then the doctor’s algorithm for further actions will depend on whether root canal filling was previously performed in this tooth.
1) If the root canals are not filled –
This greatly facilitates the doctor’s work, because... in this case, the dentist will not have to go through the trouble of unsealing poorly filled root canals. In this case, a standard method of treating periodontitis is used, which includes mechanical treatment of the root canals + treatment of the inflammation at the root apex. On your first visit, the dentist will remove your old filling or crown, drill out tooth tissues destroyed by caries, and perform a mechanical expansion of the root canals to allow pus to drain out through them.
After this, the dentist will prescribe you antibiotics, antiseptic rinses, and will most likely send you to a surgeon to make an incision in the gums, which is necessary to create a good outflow of pus. After 3-4 days, the dentist will make an appointment for you again to complete the mechanical treatment of the root canals and seal them. If the lesion is small at the apex of the tooth root, the doctor can immediately perform a permanent filling of the root canals with gutta-percha. But usually, the canals first have to be filled with temporary medicinal paste for a period of 1-2 months, and only after that permanent filling with gutta-percha is carried out.
How the gum incision is made - the incision is usually completely painless and is performed under local anesthesia. If the abscess is small, the size of the incision usually does not exceed 5-7 mm, but if a large purulent abscess develops (as in the video below), the incision is made up to 1.5 cm. After opening, pus comes out of the gum, then the wound is washed with antiseptics and into it a small rubber drain is inserted. The latter prevents the edges of the wound from sticking together, which is necessary so that the inflammatory purulent exudate does not accumulate, but continues to separate from the wound. The drainage is usually left for several days.
2) If the canals in the tooth are sealed poorly -
If the dentist sees on an x-ray that the cause of suppuration lies in poor-quality root canal filling performed earlier, then there are 2 possible treatment options. This is either a standard treatment of periodontitis with preliminary filling of the root canals, or a minor surgical operation (resection of the root apex)…
- Standard therapeutic treatment - on the first visit, the dentist drills out the old filling, removes the crown and tries to unfill poorly filled root canals.
Next, the canals are washed with antiseptics, the tooth is left open for several days + antibiotics are prescribed. If necessary, the patient is also sent to a surgeon for a gum incision. Thus, unlike the previous treatment option, only 1 point has been added here - unsealing the root canals. When the inflammation subsides after a few days, first, either temporary filling of the canals with medicinal paste, or immediate permanent filling with gutta-percha can be carried out. The medicinal paste is left in the canals for a period of 1 to 3 months. During this period, an x-ray will be taken to record a decrease in the size of the focus of chronic inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. When the lesion disappears or becomes small, the canals will be sealed with gutta-percha and a permanent filling or crown will be placed. - Resection of the root apex (Fig. 13) –
This method allows you not to re-treat root canals or remove the crown from the tooth.
It consists of making a small incision in the projection of the apex of the tooth root on the gum, through which the doctor uses a drill to cut off the apex of the root with the unfilled part of the root canal from the tooth. Also, a cyst or granuloma is scraped out of the wound. However, the operation can only be performed on those patients whose root canal is poorly filled only at the very apex of the root. Root resection is a very simple operation and usually takes only 25-35 minutes. It is easiest to carry out on the front teeth, much more difficult on the side teeth. Low cost of the operation + no need to spend money on replacing the crown and re-treating the tooth. The operation is performed after the acute inflammation has been relieved, which may require an incision and antibiotic therapy.
→ Root apex resection operation
Causes of abscess
The main cause of tooth abscess is the penetration of bacteria. This can happen if hygiene rules are not followed, enamel or gums are injured. Pus often accumulates in the tooth in the presence of large carious cavities, pulpitis, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
Sometimes a tooth abscess develops after it is removed. The reason may be failure to follow the extraction technique or the use of poorly sterilized instruments. If removal is difficult, a fragment or piece of root may remain in the hole. But even if the dentist did everything correctly, a gum abscess may develop if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed.
Less commonly, the cause is common infectious diseases. It could be otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia. The infection is carried into the gums through the bloodstream. At risk are people who eat a lot of sweets, people with diabetes, and people with reduced immunity.
Treatment of dental granuloma with antibiotics and physiotherapy
Dentists often suggest treating dental granuloma with antibiotics. As a rule, this is only a temporary solution to the problem, since it does not eliminate the source of inflammation, and after some time the disease will return. Dentists successfully use physiotherapeutic treatment methods. For example, depophoresis works great for curved or complex tooth canals. Its action consists in the effect of a weak electric current on a suspension with copper hydroxide, which relieves inflammation, penetrating into all corners of the tooth.
Treatment methods
Pathology sometimes does not cause pain at the initial stage, so not everyone goes to the doctor on time. But usually the inflammatory process develops quickly, and within a day a noticeable tumor forms. You definitely need to see a dentist. Only a doctor after an examination can determine how to treat a tooth abscess.
Home remedies such as rinsing the mouth with saline solution or herbal decoctions, as well as taking painkillers, may provide temporary relief, but will not eliminate the cause of the pathology. They can be used if it is not possible to immediately get to the dentist.
Treatment prescribed by a doctor must be comprehensive. Its purpose is to remove pus and destroy infection. The following methods can be used for this:
- drainage of pus;
- cleaning dental canals or sockets after extraction;
- treatment of caries, pulpitis and filling;
- use of local antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Opening a tooth abscess is often performed surgically. Some clinics use low-intensity laser. It allows you to painlessly clean the cavity from pus and disinfect it.
If inflammation has developed on a healthy tooth, it can be saved if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Removal is a last resort; doctors resort to it only in advanced cases. But this is the main method of treatment if an abscess has developed in a baby tooth or wisdom tooth in an adult, as well as in cases where the dental tissue is severely destroyed.
Treatment of dental granuloma: what to do?
Today, therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma is successfully carried out; in some cases, dental granuloma is treated with a laser, which does not require tooth extraction. As a rule, it is necessary to carry out high-quality endodontic treatment of the canals: cleaning, rinsing with an antiseptic and filling. They must be carefully sealed so that infection cannot enter from the oral cavity. Subsequently, the dentist monitors the condition of the tooth and the tissues around it. After five to six months, an x-ray should be taken, and if the tumor decreases in size or disappears, the therapy is considered successful. If it continues to grow, this makes it possible to diagnose not a granuloma under the tooth crown, but a dental cyst and re-treatment, which is carried out by a surgeon.
Disease prevention
The occurrence of such inflammation can be prevented.
To do this, you need to follow preventive measures:
- brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day using not only a brush, but also dental floss;
- change the brush to a new one every 2-3 months;
- eat a balanced diet, limit your consumption of sweets;
- take multivitamins;
- visit the dentist annually for a preventive examination;
- carry out dental treatment in a timely manner and remove tartar.
An abscess is a serious pathology that, without treatment, can lead to dangerous consequences. To avoid this, you should immediately contact your dentist if you experience any problems or discomfort. Simple rules of prevention will help maintain health.
Removal of tooth granuloma
If therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma does not help, surgical intervention is used. From the outside, through the bone, access is made to the tooth root, the granuloma is scraped out, the place of its attachment is carefully processed, and the mucous membrane is sutured. In some cases, the infected root tip of the tooth is excised. Subsequently, the bone is restored, and the tooth continues to serve for a long time. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire root. This is also a common operation today. In this case, the desired root is excised along with the coronal part, and if the remaining roots are able to withstand the required load, a prosthesis is installed in this place.
If a tooth granuloma has been removed, but pain or inflammation remains, and it is painful to press on the tooth, you should contact a dentist in Moscow again. The situation when a tooth hurts after treatment or removal of a granuloma is common. The pain may persist for a long time, but you should make sure that there is no inflammation and that this pain is truly residual and not an indicator of another problem.
Tooth extraction using remote control is a quick, but not the best solution to the problem
Until now, especially among patients in the older age group, there is an opinion that the easiest way is to quickly and inexpensively remove a problematic tooth , thus getting rid of acute toothache. At first glance, it seems that you can really save your own time and money. But after removal, the lost tooth will have to be replaced with an artificial analogue, resorting to implantation or dental prosthetics.
These procedures are quite expensive and will require multiple visits to the clinic. And by refusing them, the patient risks encountering a whole series of new problems caused by malocclusion. The teeth adjacent to the removed ones will shift to the vacant space, the bone will begin to dissolve, the tone of the facial muscles will decrease, and the face will begin to age much faster. That's why dentists recommend endodontic treatment.
The dangers of treating periodontitis at home
The desire of some people to avoid visiting the dental office by any means and continue to endure pain cannot be explained. At the same time, patients persistently practice self-medication, search for recipes on the Internet, rinse their mouths with herbs and smear their sore teeth with homemade compounds of dubious content.
Unfortunately, none of the diseases mentioned in the article can be treated at home. Any method that has been proven over the years, which refers to grandmother’s recipes, will not heal, but will only ease the pain and help the outflow of purulent contents. Remember, the use of this or that non-traditional method of treatment must obtain the approval of a doctor.
Painkillers are also only allowed in limited quantities. Many drugs have a strong and negative effect on the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, it is unacceptable to constantly relieve pain with pills. And heating a sore tooth, trying to reduce the level of discomfort, is strictly prohibited!
Taking self-prescribed antibiotics will not be successful, because the drug is not able to penetrate into the root canals. It will also not be possible to disinfect and eliminate the source of inflammation by rinsing your mouth. In addition to the warnings voiced, let us remind you that the pathogenic microflora of carious tissues is extremely resistant to drugs, so it cannot be destroyed by taking drugs; drilling is required.
It is better to direct all unspent energy to the prevention of dental diseases. Choosing the right toothbrush, getting into the habit of flossing, and getting regular professional teeth cleanings at your doctor's office are the foundations of oral health.
Treatment of dental caries using the Icon method without preparation
Restoration of tooth enamel, price, drugs
Retreatment of tooth canals before prosthetics, with granuloma, cyst and aching pain
Mistakes and complications in the treatment of dental pulpitis
Dental treatment during pregnancy 2nd trimester
Root canal treatment for chronic periodontitis
Cervical caries on the front teeth: causes and treatment
Treatment of acute periodontitis and exacerbation of chronic
These forms of the disease are characterized by concomitant severe inflammation in the gums and the development of suppuration. The patient is in pain. If the situation is ignored, it sometimes leads to swelling of the soft tissues of the face and a rise in temperature.
Such symptoms should be treated urgently. When a person goes to the hospital, the doctor identifies an exacerbation of chronic or diagnoses acute periodontitis and performs an autopsy of the tooth. This way, the pus leaves the root canals, and the patient feels better.
If the abscess has spread further into the tissues of the mouth, even into the cheeks, the dentist will cut the gum.
After the operation, fillings are not placed and the treatment steps described above are not applied. The patient lives for several days with an open tooth or accessible canals to ensure the outflow of pathological contents. While eating, the tooth is closed with a cotton ball, then opens again. The main thing for the patient is to prevent pieces of food from getting into uncovered cavities, avoiding re-inflammation.
In a paid clinic, the mentioned procedures are performed at the patient’s expense; the cost depends on the rating of the institution and the category of the doctor. Usually - in the range of 2000-2500 rubles.
When visiting a hospital at the place of residence with an insurance policy and passport, the patient has the right to count on free medical care.
Stages of treatment of chronic periodontitis
Periodontitis of any form means that the tissue at the apex of the root canal is modified in an unnatural way.
With chronic damage, three characteristic types of the disease are distinguished:
- Fibrous;
- Granulating;
- Granulomatous.
The doctor determines the nature of the pathology by the accompanying symptoms. Additional instrumental studies are included, including percussion, canal probing and x-rays.
The fibrous type of periodontitis is uncommon. With this type, at the apical apex of the root, as a rule, there are no obvious abscesses with the discharge of pus and cardinal changes in the gums. Therefore, treatment is carried out in two visits. At the first appointment, the doctor treats and disinfects the canals, and at the second, he places a permanent filling.
The other two modifications require long-term treatment, sometimes up to a month, in four visits. This is due to massive purulent accumulations in the gum and area near the bone. The doctor here has to act thoughtfully and carefully, trying to save the tooth without harming the patient.
Let's consider an example of step-by-step treatment of granulating or granulomatous periodontitis in an adult.