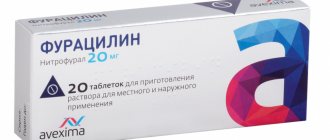
The yellow solution called “Furacilin” has established itself as a powerful antiviral drug. The product for external and local use is used for various infectious lesions of the oral cavity and external defects of the body. The finely crystalline powder has a bitter taste, but is odorless, slightly soluble in water and alcohol and completely insoluble in ether. It belongs to the group of nitrofurans.
What diseases does Furacilin treat?
More often, an antimicrobial drug is prescribed when the throat hurts due to seasonal colds. It is recommended when a person is infected:
- staphylococcal sore throat;
- acute or chronic form of tonsillitis;
- glossitis (local inflammation of the tongue);
- stomatitis (damage to the mucous membrane in the mouth);
- gingivitis (infection of the gums).
Furacilin is also prescribed for purulent otitis, conjunctivitis, bedsores, bacterial and fungal infections of the nasal cavity and other infectious diseases.
For sore throat
In acute tonsillitis, the tonsils become inflamed. The disease is accompanied by:
- high temperature;
- sore throat;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of the tonsils;
- accumulation of plaque on the tonsils.
In severe cases, infusion therapy is used and immunoglobulins are administered. In acute tonsillitis, purulent plaque always forms in the oral cavity. It is removed mechanically. Rinsing with furatsilin solution relieves pain. The procedure helps to destroy microbes, and the healing process is shortened.
For pharyngitis
Inflammation of the lymph and tonsils is accompanied by a sore throat. Treatment with furatsilin up to three times a day is prescribed to relieve inflammation and acute symptoms along with other antiseptics.
Causes of candidiasis
Thrush in the mouth of an adult is a lesion of the mucous membrane, which may indicate serious health problems. For the fungus to multiply, special conditions are required. Most often, the disease occurs in patients who neglect oral hygiene. The presence of caries and inflammatory gum diseases increases the chances of developing fungal inflammation. This is explained by the fact that a large number of pathogenic microorganisms depletes the defense mechanisms.
The second group of reasons is weakened immunity due to a number of diseases and conditions:
- HIV, diabetes mellitus;
- oncological diseases;
- dystrophy, deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- previous operations, severe infections, etc.
There are also specific reasons for the development of thrush. It can appear after prolonged and powerful antibacterial therapy. The use of antibiotics leads to the destruction of beneficial flora and imbalance. This causes active reproduction of Candida.
Oral candidiasis also develops while taking inhaled corticosteroids. Usually the lesion has the appearance of erythema and appears in areas where the medicine came into contact with the mucous membrane: on the palate, tongue.
Dietary features affect the likelihood of developing candidiasis. Thus, the predominance of carbohydrates predisposes to fungal activity. The growth of Candida and its attachment to the mucosa are enhanced in the presence of sugars.
Bad habits increase the chances of developing leukoplakia, lichen planus and other diseases. This is especially true when it comes to smoking. Candidiasis often develops in patients with tongue piercings.
The presence of removable dentures is also a risk factor if the patient does not comply with hygiene rules. In the absence of high-quality cleansing, the prosthesis becomes covered with a biofilm, which contains a lot of fungi. Disinfection is the main measure of disease prevention and part of complex treatment for progressive oral candidiasis. If the patient does not remove the structure at night, this also increases the likelihood of developing the disease. The mucous membrane remains without oxygen for a long time and is not washed by saliva - these conditions are suitable for the development of fungi and anaerobic microorganisms. The prosthesis can injure the mucous membranes if it does not fit. Microtraumas weaken local defenses and contribute to the onset of fungal infection. Injuries can also be associated with sharp chips of teeth and fillings, chemical and thermal burns.
Dry mouth due to decreased salivation, changes in saliva viscosity and its composition is one of the causes of candidiasis. This can be caused by other diseases, so it is important to find out the causes of dryness in order to effectively combat the consequences.
Candidiasis in the mouth of a child is more common. The immaturity of the immune system and the colonization of the oral cavity by Candida from the mother’s vaginal canal during natural childbirth lead to the development of the disease in early infancy. However, older children can also suffer from the disease, which is associated with weakening immune forces.
Ask a Question
How to make a solution of furatsilin
Ready-made liquid cannot always be bought at a pharmacy. More often Furacilin is found in tablets. The treatment regimen, duration, and dosage form are determined by the doctor, and each patient’s prescriptions are different. The doctor takes into account individual characteristics. Usually 1 – 2 tablets are crushed to a powder and stirred in a glass of warm water.
For faster dilution, it is recommended to use boiling water. For stomatitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, a solution is prepared to rinse the oropharynx: per 100 ml - 2 mg (1 tablet) of furatsilin. The duration depends on the nature of the localization of the infection. Take a small sip of the prepared product, throw back your head and rinse your larynx for 2 – 3 minutes.
Types of oral candidiasis and symptoms
The manifestations of oral candidiasis may vary between patients. This is due to the degree of damage to the mucous membranes, as well as the specific type of disease. There are four forms:
- acute pseudomembranous;
- acute atrophic;
- chronic atrophic;
- chronic hyperplastic.
Despite the fact that the treatment regimen for all forms is almost the same, the symptoms can differ significantly. Let's take a closer look at them.
Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
This form of candidiasis of the oral mucosa can be asymptomatic. There is minor discomfort due to a white film or small plaques rising above the mucosa. With a mild course, one or several plaques appear; they are easily removed by scraping, and the area of the mucous membrane under them has a bright red color. In severe cases, large plaques appear in large numbers. They can merge, forming large affected areas. Sometimes symptoms cover the entire mucous membrane. When plaques thicken, their removal becomes problematic. A severe course is more typical for infants, as well as in adult patients after antibiotic therapy, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
Acute and chronic atrophic candidiasis
Acute atrophic candidiasis is accompanied by a strong burning sensation. There may be no white plaque, and the mucous membrane becomes bright red. Many patients report a metallic, sour, salty or bitter taste in the mouth. A characteristic manifestation of the disease is dry mouth. This form of the disease is often associated with drug therapy.
With chronic atrophic candidiasis, redness and burning are less pronounced. Usually the disease develops against the background of the installation and wearing of prostheses.
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
This form of the disease is typical for adults. Oral thrush can spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, corners of the mouth and lips, back of the tongue, and soft palate. One of the symptoms is the appearance of white plaques that tend to merge with each other. As the disease progresses, their surface becomes rough and rough. Over time, the elements may turn yellow. The formations merge with the mucous membranes and cannot be removed.
Can children rinse their mouths?
Children from the age of six can already independently perform many hygiene procedures, including rinsing their throats. But it is better for adults to be present so that the child does not swallow the contents. If he has not mastered sanitary skills, then antibacterial lozenges are recommended instead of rinsing.
Mechanical treatment is used for a one-year-old baby. From two years old, the baby is given a rinse. A weak solution of furatsilin is taken into a special “bulb” for douching. The head is slightly tilted forward and the mouth is sprayed.
A safe method for treating the oral cavity for children is inhalation with Furacilin. Sessions cannot be performed without agreement with the pediatrician. If approved by a doctor, inhalations are done using a fresh solution each time. Depending on the degree of the disease, the doctor prescribes the number of sessions and the individual concentration of the drug. Its saturation should be low.
Stomatitis: features of the disease
Stomatitis is a disease related to dental pathologies in which inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs. Infection of the tongue with stomatitis in adults is also called “glossitis.”
The inflammatory process affects the mucous membrane and causes severe symptoms:
- redness and swelling of the tongue;
- formation of white plaque;
- severe pain;
- the formation of many small blisters and ulcers.
Due to severe sensitivity and soreness of the tongue, the patient cannot eat food, fever, insomnia and irritability are possible.
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults, as in other parts of the oral cavity, is classified into two types.
- Aphthous. A form of inflammation in which the tongue becomes covered with papules and ulcers that turn into erosions (aphthae).
- Herpetic. The inflammatory process is manifested by swelling and redness of the tongue. Small bubbles are localized in groups.
Prosthetic stomatitis and ulcerative-necrotic form of pathology are extremely rare.
Without treatment, the signs of stomatitis completely disappear, but this does not mean that the patient is cured of the pathology. The inflammatory process becomes chronic and when the immune system is weakened or exposed to an irritant, a relapse occurs.
Trade names
The active substance in known dosage forms is nitrofural (a word synonymous with “furatsilin”). Pharmaceutical companies now produce antimicrobial agents under different names:
- "Chlorhexidine";
- "Kombutek";
- "Lifuzol";
- "Miramestin";
- "Betadine";
- "Antiseptol".
There are also other names. The drugs are over-the-counter and it is recommended to follow general recommendations on storage conditions for drugs and use.
How does furatsilin work?
Furacilin, consisting of nitrofural and sodium chloride, has pronounced antiseptic properties, so many believe that this is the best remedy for stomatitis. One of its main features is the ability to act on most bacteria known to medicine. For this reason, it is widely used for a variety of purposes, from treating wounds to gargling.
The drug not only eliminates symptoms; upon contact with pathogenic microflora, it dissolves the cell membrane, which leads to their death and a reduction in the number of colonies.
Several forms of the drug are used in different fields of medicine:
- solutions (alcohol, water);
- pills;
- ointment;
- aerosol.
In dentistry, solutions are most often prescribed - ready-made or prepared independently from tablets.
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of a large number of aphthous stomatitis on the oral mucosa. These are round or oval ulcers covered with plaque. The causes of this disease are as follows:
- past infectious diseases: influenza, measles;
- lack of vitamin B12 and microelements in the body;
- oral injuries;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
For the most effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children, our specialists pay special attention to identifying the cause that caused it. Treatment of acute stomatitis in children is simply necessary, since the disease itself is very difficult. Its characteristic feature is unpleasant pain symptoms, which intensify when the ulcers are touched with hot or sweet food.
Treatment of purulent stomatitis in children requires an integrated approach. It consists not only in local treatment of ulcers with medications, but also in proper diet, frequent drinking and regular oral hygiene.
Treatment of stomatitis in a child
The main rule is to immediately contact a specialist and not use any gels or ointments based on recommendations from the Internet. Each type of pathology is treated differently, so the dentist conducts a comprehensive examination. Additional consultation with an otolaryngologist or dermatologist is often required.
In complex therapy, proper oral care is prescribed and professional toothpaste is selected. Solutions and gels are required. If the form is viral, then antibiotics are used, and if it is allergic, then antihistamines are used. If necessary, medications are used to reduce the temperature (if there is fever and chills).
How to care for a child after stomatitis appears?
Without the help of parents, a child will never get rid of the disease, because strict discipline is needed. You must follow all the requirements of the pediatric dentist and pay special attention to diet and pain medications.
Prefer soft food with a temperature of no more than 28o C. It is important that it has a balanced composition of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Allergens, as well as spicy, sweet, sour and very salty foods, must be excluded from the diet. It is advisable to exclude citrus fruits due to their high acid content. After eating, rinse your mouth with filtered or boiled water.
Treatment includes the use of painkillers. The child will feel severe pain at first, which will interfere with sleep. Therefore, you need to regularly rinse your mouth not only with clean water, but also with medicinal balms. The affected area should be smeared with medicinal gel. All recommendations for treatment and pain relief will be given to you by your pediatric dentist during your consultation.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
How to get rid of stomatitis
07.12.2021
Stomatitis is a lesion of the oral . While scientists are thinking about the mechanism of its occurrence, one thing is clear: stomatitis causes obvious discomfort and one must be able to get rid of it - quickly and effectively.
Stomatitis: causes and symptoms
on the oral - on the gums, tongue, inside of the cheeks and lips. In this case, the mucous membrane swells, turns red, and becomes covered with plaque. There is increased salivation, bleeding gums, pain, and discomfort when eating. The mechanism of the disease is not fully understood; it is assumed that the immune system to irritants. The causes of stomatitis can be: poor hygiene, viral infection, concomitant diseases (gastrointestinal diseases, the presence of worms, HIV , endocrine disorders), mechanical or thermal damage, lack of vitamins and minerals.
Diagnosis of the disease does not involve laboratory and technical research - the doctor is guided by the results of a visual examination: the appearance of the ulcers, the presence or absence of other complaints and symptoms.
Treatment of stomatitis
Stomatitis can be caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi. Treatment procedures and remedies depend on this. Depending on the damaging factors, treatment is carried out with antifungal, antiviral, antihistamine drugs, and the underlying diseases are treated. If there are none, specific treatment is not applied. In all cases you can use:
- Immunomodulators - to increase the body's defenses: immunal, anaferon, echinacea, etc.
- Painkillers are better for topical use, in the form of ointments, gels, aerosols. For fever and worsening general condition, use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic and antipyretic properties.
- Antiseptics - solutions, ointments or aerosols: Miramistin, Hexoral, Ingalipt, Orasept, Stomatofit, Stomatidine, Metrogil-denta and many others.
- Wound healing agents - solcoseryl (ointment), carotolin (oil solution), chlorophyllipt (spray and lozenges), vinylin (balm) and others.
- In severe cases, use antibiotics together with probiotics and vitamins. The most effective: gentamicin, ofloxacin, augmentin and others.
Oral hygiene
Uncomplicated stomatitis resolves within a week when rinsing or treating the mouth with disinfectants. For hygiene, the following measures are taken.
- Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic lotions and compresses . To do this, use: aloe leaf - cut and apply to the sores; fresh plantain - extract the juice and wipe the mucous membrane; lingonberry juice - apply a napkin soaked in juice; red beets - use raw pulp; garlic brewed in black tea - attach a soaked napkin; propolis - infuse with alcohol and apply moistened cotton pads or apply with a toothbrush; honey with sea salt - make applications.
- Rinsing the mouth with the following means: St. John's wort - a decoction of the herb relieves inflammation and swelling ; Kalanchoe - juice or decoction of leaves is used; Potentilla – root tincture has medicinal properties; oak bark, chamomile, thyme, calendula, sage - a decoction of herbs; salt solution - sea or regular; a mixture of soda, peroxide and lemon juice - for cleaning.
- Using standard mouth rinses .
- Use of special toothpastes recommended by dentists.
How not to get sick
Since the causes of the disease are not fully understood, there is no specific answer to this question. However, it has been established that a decrease in immunity due to various accompanying circumstances plays an important role. For prevention you should:
- observe the rules of oral hygiene , if necessary, have sanitation at the dentist
- disinfect dishes, toothbrushes and other personal hygiene items
- Contact your dentist to clean tartar and enamel
- quit smoking and alcohol abuse
- strengthen the general condition of the body, preventing the development of chronic diseases
- eat right, consume the right amount of calcium and other minerals, take vitamins if necessary
- avoid foods rich in carbohydrates, which create a favorable environment for bacterial growth, increase the amount of dairy products
- choose a suitable toothbrush that is hard enough but does not damage the gums
When treating stomatitis, keep in mind that it can be a manifestation of other, more serious diseases. Despite the undeniable benefits of the listed remedies, if the disease does not go away within a week, be sure to consult a doctor . And the best protection against any disease is a healthy lifestyle and strengthening the immune system .
Published in Dentistry Premium Clinic