07.03.2012
Author: Dentist-therapist Kuzub Yana Nikolaevna, Dentist-periodontist, therapist Stopinskaya Ulyana Yuryevna
Undoubtedly, we all know that during pregnancy the body of the expectant mother undergoes very strong changes associated with hormonal changes.
We will look at what changes occur in a woman’s dental health during pregnancy.
- From the gum side. The so-called “gingivitis of pregnant women” develops. This is a gum condition that affects most expectant mothers. Gingivitis occurs due to changes in the balance of hormones in the blood. In this case, the gums become inflamed, increase in volume and bleed under mechanical stress. And gingivitis is supported by microorganisms that are normally found in the oral cavity, but due to a decrease in local immunity, they have a detrimental effect on the tissues of the oral cavity. And the harmful products of their vital activity, toxins, enter the bloodstream of the expectant mother and have a negative impact on the development of the fetus.
- From the side of the teeth. The mother's body spends a huge amount of resources on bearing and forming the fetus. For the normal formation of a child’s skeleton, a woman’s body requires a very large amount of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine, vitamin D and other minerals. And if a woman does not receive enough of these substances from food, then microelements are taken from the bones and teeth of the expectant mother. And, of course, dental health is greatly deteriorated. Due to weakening of teeth and deterioration of local immunity, as well as the predominance of harmful microorganisms, teeth are several times more susceptible to the development of caries. Which can even be complicated by pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve of the tooth) or periodontitis (infection from the canal into the bone tissue). When these diagnoses occur, the tooth requires urgent treatment, which is difficult due to the special condition of the female body, which often leads to tooth loss. It is important to realize that caries and its complications, and gum disease during pregnancy are a source of infection that must be eliminated. Otherwise, all this can affect the child’s health in the form of a tendency to allergies and a decrease in the newborn’s immunity.
We answer popular questions
The COVID-19 pandemic, announced by WHO in March 2022, has made serious adjustments to the life of modern society. News reports are full of figures about the number of people infected, recovered and those who could not cope with the disease. The infection itself and its complications can cause serious harm to the adult body. What will happen to the fetus, does COVID affect pregnancy, how to protect yourself? These and not only these questions are often asked by young couples who are just planning to become parents or are already waiting for a miracle. Let's talk to the experts at the SM-Clinic Reproductive Health Center about how to behave correctly.
Treatment
If you notice any symptoms of the disease, you should not delay visiting a doctor. Self-medication is a risk not only that the disease will not go away, but that the pathology will become chronic.
Only a specialist will select the optimal treatment option for the disease for the expectant mother.
The primary task is pain relief. Most often, gels and ointments are used for this purpose for the eruption of the child’s first teeth. Such drugs are absolutely harmless for a pregnant woman, and at the same time, very effective. In addition to the analgesic effect, such products have an antiseptic effect.
The viral type of pathology is treated with the mandatory use of antiviral agents.
If the disease is caused by a fungus, then it should be treated with antifungal drugs that are suitable for the expectant mother.
Is coronavirus dangerous for pregnant women?
Pregnancy during the coronavirus period is especially dangerous if a woman is at risk. In this case, the likelihood of a more severe course of infection compared to the population is increased due to existing immune disorders and concomitant diseases.
Although the infection is new and much is still being studied, risk factors have been identified. These include:
- anamnestic indications of blood clots in arteries and veins before pregnancy;
- an established diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome - a condition in which antibodies to the cell membrane are formed in the body;
- inherited forms of thrombophilic disorders - increased blood clotting caused by genetic characteristics;
- confirmed autoimmune diseases, in which the immune system “works” against the cells of its body;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- obesity;
- metabolic syndrome is a pathological complex that includes impaired glucose tolerance, excess weight and a number of endocrine disorders;
- lung diseases characterized by a chronic course (bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, etc.);
- pregnancy resulting from the use of assisted reproduction methods;
- oncological processes in the body.
However, the presence of risk factors alone does not mean that in 100% of cases COVID during pregnancy will be severe. Coronavirus during pregnancy can go unnoticed (asymptomatic). Only positive results of an antibody test will help determine that a pregnant woman has had a new coronavirus infection.
What to do? How to treat?
To get rid of dry lips, it is necessary to eliminate the negative provoking factor:
- Drink more fluids. But the main thing is not to overdo it, otherwise dryness will be replaced by swelling;
- Take the necessary vitamins. Eat fruits and fresh vegetables. It is imperative that you take vitamin complexes in consultation with your doctor and drink them strictly as prescribed. Excessive consumption of vitamins can have a negative effect on the fetus;
- Change lipstick, toothpaste, gloss , the use of which provokes allergies;
- Moisturize your lips with balms. This can be done using store-bought cosmetic and hygiene products. But such products must be chosen carefully: without dyes. It’s better to make your own moisturizing balms.
Natural balms
- "Natural moisturizer." Lubricate your lips twice a day with any of these natural products: butter, carrot juice, sour cream, sea buckthorn oil.
- "Rose petals". Mix 2 pinches of fresh rose petals thoroughly with 1 tablespoon of rendered lard. Place the product in a tightly closed container (cream jar). Store in the refrigerator, lubricate lips several times a day;
- "Oil and honey." Mix liquid fresh honey in equal proportions with vegetable oil (olive, peach, almond). Warm the product slightly before applying.
- "Vitamins" Instead of balm, use liquid vitamins. Take either one capsule of vitamin A, or make a mixture by adding the contents of capsules with vitamins E and C.
- Provide special nutrition for your lips. Nutrients, entering the lip tissue, activate cell regeneration processes, the synthesis of elastin and collagen, increase blood circulation and normalize water balance.
Masks
It is useful to make the following homemade masks to nourish your lips:
- "Sour cream and lemon." 1 spoon of fat sour cream mixed with a few drops of lemon juice and any essential oil. Apply to lips for 10-15 minutes. If you are allergic to citrus fruits, lemon should be replaced with honey.
- "Fruit and butter." Butter (can be ghee) - 1 spoon, and the same amount of fruit puree (banana, kiwi, apricot, apple) are mixed and applied for 15-20 minutes. Puree can be made from cucumber, carrots, strawberries.
- "Cottage cheese and medicinal decoction." Prepare a decoction of medicinal herbs in advance by brewing a pinch of the herb in 100 g of hot water and let it brew. Gently dilute 2 tablespoons of fatty cottage cheese with the broth so that you get a mass with a consistency similar to thick sour cream.
How do expectant mothers cope with COVID-19? Course of the disease during pregnancy
COVID-19 during pregnancy can occur in different ways. The symptoms of coronavirus during pregnancy are in many ways similar to the clinical manifestations in “ordinary” patients. Women note a decrease in sense of smell or its complete loss, an increase in body temperature, a cough (mostly dry), body aches and severe weakness. As with any viral respiratory infection, a severe runny nose is not typical.
However, pregnant women have one important feature. COVID during pregnancy can suddenly worsen, even if the disease was relatively stable and mild before. Therefore, you should not self-medicate and hope that “maybe it will pass.” Only a doctor can notice the alarming symptoms of COVID during pregnancy and take preventive measures in time to avoid serious complications.
Coronavirus in the 1st trimester
COVID and early pregnancy can act like a common cold. If a woman’s immunity is sufficiently tense, then there will be no negative consequences for the fetus. If the immune system malfunctions, the risks of an adverse effect of a viral infection on the developing chorion, that is, on the future placenta, which is responsible for feeding the fetus until the due date, increase. Severe consequences of COVID in the early stages of pregnancy may include spontaneous and failed (fading pregnancy) miscarriage, fetoplacental insufficiency, which can subsequently lead to fetal growth retardation and oxygen deficiency at the intrauterine stage of development.
Coronavirus in the 2nd trimester
Does coronavirus affect pregnancy at 14-28 weeks? Yes. And the degree of this influence depends, on the one hand, on the infecting dose, and on the other, on the state of the mother’s body. A favorable scenario is a common cold without obvious consequences. An unfavorable scenario is the development of complications in the mother (pneumonia, “long COVID”, etc.), complications from the feto- and utero-placental complex (placental insufficiency, fetal growth restriction, intrauterine hypoxia, shortening of the cervix).
Coronavirus in the 3rd trimester
How does coronavirus affect pregnancy in the 3rd trimester? According to epidemiological studies around the world, pregnant women who have had COVID-19 for 28 weeks or more have a 2-3 times increased rate of preterm birth. Coronavirus in late pregnancy either increases the contractile activity of the uterine body or promotes dilatation of the cervix, which ultimately ends in premature birth.
There are still no reported cases of intrauterine infection of the fetus with coronavirus. All situations where newborns test positive for COVID are associated with infection after birth.
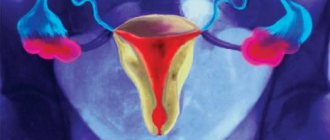
Cervix: structure and functions
This organ is the lower segment of the uterus, through which passes the narrow cervical canal connecting the uterine cavity and the vagina. The normal length of the cervix is 3-4 cm, its outer part protrudes into the vagina and, at the junction with its walls, forms the vaginal fornix, which serves as a kind of reservoir for sperm. The vaginal segment is dome-shaped and covered with pink stratified squamous epithelium. The cervical canal, on the contrary, is lined with columnar epithelium, which has a brighter shade. The color of the vaginal segment of the cervix is one of the criteria for its health.
In a woman’s reproductive system, this organ performs several important functions:
- protects the uterine cavity from penetration of pathogenic organisms, as well as from sperm (after conception) by closing the cervical canal with a “plug” of glycoprotein mucus;
- promotes the penetration of sperm during the ovulation period, filtering the most viable of them with a counter current of mucus produced by the glands of the cervix;
- ensures free outflow of blood and desquamated endometrial cells from the uterine cavity during menstruation;
- prevents premature birth of the fetus during pregnancy and promotes its correct passage through the genital tract during childbirth.
The condition of the cervix is an important diagnostic indicator that allows you to determine the presence of pregnancy or various pathologies of the female reproductive system. To do this, the gynecologist evaluates such characteristics as the color, size and consistency of the vaginal part, the diameter of the cervical canal, and its position relative to other genital organs (the uterus itself, vagina, etc.).
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Consequences of coronavirus during pregnancy
Research into how coronavirus will affect pregnancy is still ongoing. The infection is new, so much remains to be learned. And this process for pregnant women is associated with certain difficulties, so new data appears in doses. Today we have the following information.
- Chinese scientists have found that the consequences of COVID during pregnancy may include an increased risk of premature birth.
- Other researchers have found a link between positive COVID during pregnancy and a greater likelihood of fetal growth restriction and distress syndrome (lack of oxygen for the baby in utero).
Observations are ongoing to help analyze how COVID affects the fetus during pregnancy. There are now reports that this virus can lead to low platelet levels and liver dysfunction in newborns. However, this information needs further verification and is not unambiguous.
Symptoms and complaints of perineal varicose veins
In the classic version, there is a triad of symptoms:
- Pelvic pain.
- Varicose veins of the labia and perineum.
- Dysmenorrhea is a cyclical process, when during menstruation severe pain in the lower abdomen, heavy menstrual bleeding, and menstrual irregularities may appear.
- With a long course of the disease, the development of dyspareunia is possible - painful sensations in the lower abdomen that occur during or after sexual intercourse. A peculiarity of this symptom is the persistence of pain for at least 30 minutes and up to a day after sexual intercourse.
How can this affect the child? Can his mother infect him with the virus in the womb?
The impact of COVID on the fetus during pregnancy is not completely known. To date, there is no data that would confirm the fact of intrauterine infection (penetration of the virus to the fetus) or intrauterine infection (development of symptoms in the fetus). However, there is no reverse data that would reliably exclude the possibility of vertical transmission of the virus. Coronavirus during pregnancy before childbirth can be dangerous because an infected mother can infect the child immediately after birth. This happens through the traditional airborne or household contact route.
Should you postpone pregnancy?
There are quite a lot of “blank spots” in the answer to the question of how COVID affects pregnancy in the immediate and long-term period after infection. However, clinical recommendations state that after an illness, conception should be postponed for at least 3 months. This duration of the time pause is explained by 2 arguments. On the one hand, in the 3-month period after an acute infection, there is a possibility of developing delayed complications, especially for thrombosis of various locations. On the other hand, 3 months are necessary for the complete elimination of pharmacological drugs used to treat the infection. Their negative impact can be much more serious than the direct consequences of COVID on pregnancy.
The average spermatogenesis cycle lasts 3 months. In other words, during this time, renewed sperm mature, which do not contain toxic substances formed during the metabolism of pharmaceuticals. In women, the period of folliculogenesis (the complete cycle of egg maturation) is shorter. Therefore, doctors advise focusing on a larger gap, that is, on the male factor.
Unpleasant sensations in intimate areas, video
Gynecologist Irina Garyaeva about vaginal dryness.
Source - KVD - dermatovenerological dispensary Sources:
- THERAPY OF UROGENITAL DISORDERS CAUSED BY ESTROGEN DEFICIENCY. Serov V.N. // Obstetrics, gynecology and reproduction. – 2010. – No. 1. – P. 21-35.
- PROBLEMS OF UROGENITAL DYSTROPHY IN WOMEN OF REPRODUCTIVE AND PERIMENOPAUSAL AGE. Karahalis L.Yu. // Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin. – 2007.
- Features of urogenital disorders in perimenopause. Balan V. E., Ankirskaya A. S., Muravyova V. V., Tikhomirova E. V. // Materials of the V Russian Forum “Mother and Child”. - 2003. - P. 290.
- The overactive bladder. Bulmer P., Abrams P. // Rev Contemp Pharmocother. – 2000. – No. 11. R. 1–11.
- Characteristics of hot flashes in women of different age groups. Karahalis L. Yu., Fedorovich O. K. // AG-info. - 2006. - No. 2. - P. 26–31.
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/natural-remedies-for-vaginal-dryness-90070
- https://www.healthline.com/health/vaginal-itching
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321615.php
- https://www.webmd.com/women/guide/vaginal-dryness-causes-moisturizing-treatments#1
In what cases do doctors advise terminating a pregnancy?
The impact of coronavirus on pregnancy continues to be studied. Today, there are no direct indications for artificially interrupting the gestational process due to the fact that COVID-19 developed during pregnancy. Interruption can be recommended only for those indications that were previously prescribed in the Order. First of all, this is the cessation of pregnancy, which could potentially be associated with coronavirus. The second is the diagnosis of chromosomal pathology and developmental anomalies incompatible with life. Whether coronavirus causes such conditions or not has not been reliably determined today.
Why does stomatitis develop during pregnancy?
There are quite a few reasons. The most common include:
- Poor oral care.
- Untreated carious cavities in which bacteria actively multiply, which provoke the development of stomatitis.
- Injury to the oral mucosa (cut or burn). If you accidentally bite your cheek, stomatitis can also develop.
- Eating unwashed fruits or vegetables. Seeds and nuts are also breeding grounds for bacteria.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- An allergic rash that can appear on any part of the body, even on the cheeks or tongue.
- Contact with an already infected person.
- Reduced immunity.
Can pregnant women get vaccinated?
Considering the fact that COVID during pregnancy is especially severe in patients at risk, timely vaccination is recommended for this category. Vaccination is allowed from 22 weeks; the recommended vaccine is Sputnik V.
Experimental clinical studies on animals did not reveal a negative effect of the vaccine on the body of the female and her offspring. Also in world medicine there is data on the impact of anti-Covid immune drugs on the body of pregnant women, who at the time of vaccination were not aware of their “interesting situation.” No negative consequences were registered.
Thus, vaccination during pregnancy is carried out when the expected benefits outweigh the possible risks.
Detection of cervical diseases
To determine the presence or absence of pathological changes, the doctor conducts a screening examination of the cervix, including:
- cytological examination - analysis of particles of the epithelium of the cervix and cervical canal for the presence of atypical cells, including cancer cells;
- microflora smear - analysis of vaginal or cervical mucus for the ratio of beneficial, opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms, indicating the general condition of the body, the reproductive system, the presence or absence of inflammatory diseases;
- smear for infection - examination of the mucous discharge from the vagina for the presence of clearly pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa), indicating the presence of an infectious process in the genital tract.
Also, as part of a screening study, hystroscopy may be prescribed - a visual examination of the cervix using a thin and flexible instrument equipped with a camera or optical system (hystroscope). It is inserted directly into the vagina and cervical canal, allows you to evaluate the color and thickness of their mucous membranes, determine the presence of polyps and other neoplasms, the size of the cervical lumen, etc.
The combination of these methods gives doctors the opportunity to determine the general condition of a woman’s body and her reproductive system, and promptly identify possible pathologies and complications. This increases the likelihood of their successful treatment, including gentle conservative methods.
How can a pregnant woman protect herself during COVID?
During pregnancy, even if you have been vaccinated against COVID in advance, you should follow sanitary rules that will help reduce the risk of infection:
- maintain a distance of at least 1.5 meters;
- wash your hands or use sanitizer;
- do not touch your eyes, mouth and nose with unwashed (untreated) hands;
- ventilate the premises;
- avoid crowded places.
When the first suspicious symptoms of a new coronavirus infection appear, you should immediately contact a medical facility. It is easier to prevent complications than to eliminate them later.
Prevention measures
Despite the fact that the exact impact of COVID on pregnancy has not been fully established, one thing is clear - it is worth protecting yourself from the infection in advance. Vaccination is considered the best way. It promotes the formation of specific immunity. Even if the virus enters the body, the immune system will be ready to meet it. The pathogen is immediately attacked by immunoglobulins (antibodies) and most or the entire pool of viruses can be neutralized. Therefore, the consequences of coronavirus during pregnancy in such a situation will be minimal - the infection will not develop or will be mild.