During the period of intrauterine development, the baby’s body completely depends on the lifestyle of the expectant mother. If a woman does not experience nervous overload, gets full rest, and eats right, then the child feels protected. Particularly conscious young ladies switch to a proper diet even when planning a pregnancy. However, in most cases, questions about nutrition during the perinatal period arise after an event has occurred. Advice from gynecologists, nutritionists, and pediatricians will help you develop a personal menu.
Nutrition during pregnancy raises many questions. Firstly, the older generation advises “eating for two”, and women are afraid of gaining extra pounds. Secondly, hormonal changes in the body dictate new gastronomic preferences. Fearing harm to the child, the expectant mother is lost between “would I like to” and “can I?” Thirdly, the pseudo-medical advice on nutrition that is poured in abundance on women from social networks is confusing. How to choose healthy foods, safe cooking methods, and create a diet during pregnancy? Read our article.
Nutrition during pregnancy
Organization of nutrition during the perinatal period is aimed at maintaining the health of the woman and ensuring the harmonious development of the baby. The main tool in achieving the goal is the responsible attitude of the expectant mother to her daily diet. Poor nutrition during pregnancy results in nutritional deficiency. This leads to the occurrence of intrauterine pathologies, complications of gestation, increases the chances of the child developing autoimmune reactions, and activation of unfavorable genetics (hereditary predisposition to diseases).
The causes of nutritional imbalance in the body of a pregnant woman are:
• Calorie deficit and surplus. The low energy value of the diet forces the baby’s body to turn on the mechanism of accelerated absorption of everything that the mother eats. Nutrigeneticists claim that the habit of eating everything continues after birth, threatening obesity. In the female body, a lack of calories is reflected in the weakness of the uterine muscles. There is a danger of miscarriage. Excess calories lead to excess weight gain, and this puts stress on joints, blood vessels, and the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and varicose veins. • Lack of vitamins. Hypovitaminosis during pregnancy is a direct threat to the life and health of the child. Deficiency of vitamins A and E slows down fetal growth and provokes premature birth. Deficiency of B1, B9 causes defects in the development of the nervous system. Vitamin D deficiency is the cause of neonatal rickets and visual impairment. Hypovitaminosis B2 results in heart defects, cleft palate, and deformation of the arms and legs of a newborn. • Lack of minerals. Microelements participate in embryonic development no less than vitamins. Copper deficiency leads to a decrease in the immune status of mother and child, calcium, phosphorus - to demineralization of fetal bone tissue, iodine - to a delay in the neuropsychic development of the baby, iron - to iron deficiency anemia in a pregnant woman, the threat of miscarriage, magnesium - to premature birth, development arrhythmias in the mother, zinc - to slow growth of the embryo.
Eating right means ensuring your child’s stable growth and development, and protecting yourself from perinatal risks and complicated childbirth. A pregnant woman needs to eat not “for two,” but “for two.”
Approximate vitamin and mineral norm per day (in mg)
Minerals
- calcium - 1200
- phosphorus - 700
- magnesium – 360
- iodine - 200
- zinc - 15
- iron - 30
- copper - 2-3
Vitamins
- retinol (A) - 1.2
- thiamine (B1) - 1.8
- pyridoxine (B6) - 2.1
- folic acid (B9) - 400 mcg
- tocopherol (E) – 10
- ergocalciferol (D) – 500IU
- ascorbic acid (C) – 100
To prevent vitamin and mineral deficiency, it is recommended to supplement your diet with special vitamins for pregnant women.
Why do expectant mothers so often complain of heartburn and indigestion?
There are two main causes of heartburn and indigestion during pregnancy:
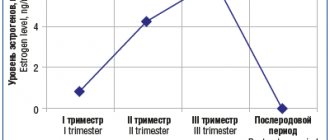
Hormonal changes in the body of the expectant mother
During pregnancy, the amount of progesterone produced increases, causing muscle relaxation. Accordingly, increased production of progesterone provokes relaxation of the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter. The sphincter is a ring of muscle that prevents stomach contents from entering the esophagus. As a result, when the sphincter muscles relax, the contents of the stomach (including gastric juice) can freely pass into the esophagus, causing irritation of its mucous membrane. The esophageal mucosa is not designed to accept large amounts of gastric acid for a long time. This is why we feel pain.
Child's height
As your baby grows, it begins to put more and more pressure on the organs of your digestive tract, stomach and intestines. This pressure can cause stomach acid to flow into the esophagus.
Most often, problems with the digestive system during pregnancy are faced by those who had similar problems before pregnancy, as well as those for whom this is not their first baby.
Heartburn and indigestion can also be caused by other reasons. For example, some foods and drinks also cause excessive stomach acid production, which can destroy the protective lining of the stomach. The protective layer is the mucous membrane, which is in direct contact with the contents of the stomach, including gastric juice. If its destruction occurs, it can lead to discomfort and unpleasant sensations.
Difficult first trimester
The female body adapts to new conditions. Fatigue, drowsiness, and unstable mood are typical for a pregnant woman. There are problems with urination and bowel movements, acute reactions to tastes and smells. And at this time, the foundation of the baby’s health is laid. His nervous and circulatory systems are formed, and his heart begins to work intensively. Proper nutrition in the first trimester is a way to stabilize the mother’s condition and mitigate the risks of intrauterine anomalies.
Principles for creating a diet in the 1st trimester:
• Don't be greedy. Overeating increases the symptoms of toxicosis and provokes digestive failure. You need to eat in modest portions at intervals of 3-3.5 hours. • Take care of “building materials”. The basis for the formation of fetal cells is protein. From it the body receives 20 essential amino acids that it cannot produce on its own. The menu should include lean meat - turkey, chicken, veal. Twice a week you need to eat fish, alternating low-fat varieties (pollock, cod) with fatty ones (salmon, pink salmon, salmon). • “Agree” with the intestines. The problem for many women at the beginning of pregnancy is constipation. Fiber, which is found in raw vegetables, hard fruits, and bran, helps to cope with them. • Replenish supplies. During the formation of the nervous system, the baby squeezes iodine and B vitamins from the mother’s body. To prevent vitamin and mineral deficiency, shrimp, squid, seaweed and cauliflower, buckwheat porridge, eggs, and nuts should be introduced into the diet. • Do not experiment with drinks. It is recommended to drink water - still bottled or filtered. Adding freshly squeezed lemon juice will help calm nausea.
Daily caloric intake is 2500-2700. Nutrient distribution: proteins - 110 g, carbohydrates - 350 g, fats (vegetable + animal) - 75 g.
What are the symptoms of heartburn and indigestion?
Broadly speaking, symptoms of reflux may include:
- Sour taste in the mouth, sometimes accompanied by nausea;
Hoarseness and a bitter taste in the mouth – this condition is also called “silent reflux” or reflux esophagitis.
If we talk about heartburn, it is characterized by the following sensations:
- Burning pain in the chest area, most often behind the sternum;
- Sensations of compression in the chest area.
Heartburn may last for a few minutes or several hours, especially if you suffer from severe heartburn.
Indigestion usually manifests itself in the form of:
- Pain in the lower chest, abdomen and stomach (usually occurs after eating, although this is not a necessary condition);
- Feelings of fullness; in this case, you feel bloating in the stomach area;
- Belching;
- Nausea and even vomiting.
Second trimester - needs increase
By about 14-15 weeks, the woman’s well-being returns to normal - toxicosis goes away, physical and emotional activity increases. The baby begins to produce blood cells, strengthens bone tissue, the pituitary gland begins to work, the first hair and nails appear, bone mineralization progresses, and muscles begin to contract. To meet the increased needs of the child, the mother needs to eat more. At the same time, it is not the caloric intake that needs to be increased, but the amount of nutrients. At this time, both organisms need vitamin D, calcium, and iron.
Mandatory foods in the diet:
• to provide calcium - cheese, cottage cheese, milk, almonds, sesame seeds; • sources of vitamin D - fatty fish, cod liver, eggs, butter, flaxseed, olive oil; • for the prevention of iron deficiency - beef and pork liver, cocoa, beans, cabbage, apples, blueberries, greens (spinach, parsley, mint). In the second trimester, it is important to control the amount of table salt and fluid you drink. This will help avoid surges in blood pressure and cardiac overload. Recommended values: calories - 2800-3000, proteins - 120 g, fats - 85 g, carbohydrates - 400 g.
Third trimester - diet correction
From the 27th week of pregnancy, the female body begins to prepare for childbirth, and the baby begins to be born. At this time, gastronomic fads give way to heartburn, constipation, shortness of breath, swelling, and rapid weight gain.
A properly composed menu will help you adjust your well-being in the 3rd trimester. What should be done:
• Reduce the amount of protein foods. A protein surplus leads to kidney dysfunction and the accumulation of uric acid. • Avoid heartburn triggers - sour foods, black coffee, fried foods. • Replace 50% of animal fats with vegetable oils. They contain essential polyunsaturated acids Omega-3 and Omega-6, which are not synthesized by the body, but are needed for the absorption of minerals and vitamins. • Limit salty foods. Salt is the cause of edema, unstable functioning of the kidneys, heart, and blood vessels. • Set a limit on sweets. Simple carbohydrates quickly turn into extra pounds, causing flatulence, dyspepsia, and skin problems. • Eat more vegetables, fruits, berries, greens. Natural sources of vitamins provide energy and strengthen the immune system - this will come in handy during childbirth. Standards for KBJU: calories - 2900-3100, proteins - 100 g, fats - 75 g, carbohydrates - 400 g.
Metal
The reason may be unhealthy teeth or gums.
A metallic taste in the mouth can be caused by metal crowns or fragments of dentures. In this case, you should discuss with your dentist the issue of replacing them. When making a diagnosis, exclude:
- diseases of the periodontium and maxillofacial system with obvious signs of a purulent process;
- bleeding from the gums;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals - such taste sensations are caused by mercury, zinc, arsenic, copper;
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation with a slight change in blood sugar levels;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- chronic bleeding due to stomach ulcers;
- hormonal disorders;
- taking certain medications. The appearance of such sensations is facilitated by drugs from the NSAID group and anticonvulsants. When the drug is discontinued, the metallic taste disappears on its own.
What should you not eat or drink?
There is no place for harmful foods in a properly composed diet for a pregnant woman. Throughout the perinatal period, the following are blacklisted:
• fast food; • flavored snacks; • hot sauces; • smoked meats; • products containing many preservatives; • alcohol.
The expectant mother is advised to limit the consumption of sausages, confectionery products, and sweet pastries. You also need to be careful with citrus fruits, strawberries, mushrooms, and coffee. It is advisable to exclude packaged juices, bottled tea, sweet cocktails, and soda from the grocery basket.
Dieting is difficult, but necessary. This will help minimize the harmful effects on the fetus, maintain pregnancy, improve well-being, avoid weight gain, and the development of gestational complications - preeclampsia, pyelonephritis, diabetes.
Diet rules
The principles of constructing a diet during the perinatal period differ little from the general rules of healthy eating. After all, pregnancy is not a disease.
Organizing a proper diet includes:
• Refusal of junk food and drinks. Carcinogens, preservatives, flavorings, flavor enhancers, and alcohol increase perinatal risks. • Control of KBJU. Helps maintain stable weight and nutritional balance. • Daily consumption of healthy foods containing protein, minerals, vitamins. These substances are necessary for the development of the fetus and the health of the mother. • Compliance with the drinking regime (1.5-2 liters per day). Clean water ensures normal blood flow, regulates the functioning of the urinary organs and intestines. • Small meals: 5-6 times a day with an interval of 3-4 hours. This schedule helps you not to overeat and properly absorb nutrients. • Cooking foods in healthy ways. Cooking dishes by boiling, stewing, and baking allows you to reduce calories, reduce the load on the digestive organs, and get rid of nausea and heartburn. • Limiting salt. A slight salt deficiency during pregnancy reduces the load on the kidneys and heart muscle and prevents the appearance of swelling. • Limit on fast carbohydrates. The body gets glucose from sweet foods, the main source of energy, so you can’t give them up completely. But excessive passion for confectionery products leads to metabolic failure, obesity, and the development of insulin resistance. • Keeping a food diary.
The diet for pregnant women has its bonuses. A woman will master healthy menu recipes, get used to eating right, and easily get into shape after giving birth. Of course, you shouldn’t make a cult out of food, forgetting about your own comfort and appearance. Special underwear for pregnant women will help you feel confident, and hypoallergenic products will take care of the beauty of your skin - stretch mark creams, gels, balms. Today, all products for pregnant women and nursing mothers can be ordered from an online pharmacy with home delivery.
Features of treatment
Before eliminating an unpleasant taste in the mouth, it is imperative to find out the cause of its appearance. To do this, you first need to consult with a therapist, who, after an initial examination and interview, will refer you to a gastroenterologist. Depending on the disease, treatment may involve taking medications or adjusting your diet.
Diet food
If an unpleasant taste appears, especially if it is a symptom of a digestive tract disease, the pregnant woman needs to change her diet. A few recommendations for creating a diet menu:
- exclude smoked, fatty, fried foods from the menu;
- include fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet, but do not get carried away with cabbage and legumes;
- eat more iron-containing foods - buckwheat, apples, pomegranates, seaweed and liver;
- The basis of the dishes should be lean meat and fish, which can be boiled, baked in the oven or steamed.
Equally important is the frequency and regularity of food intake. If you have gastrointestinal diseases, you need to eat often, but the portions should be small. Under no circumstances should you overeat, but you shouldn’t starve either.
Drug therapy
What medications can help with bitterness or sourness in the mouth? Medicines for pregnant women are prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account medical indications. The treatment regimen directly depends on the cause of the unpleasant taste in the mouth. The following groups of medications are most often prescribed:
- prokinetics - affect the motor function of the stomach (Domperidone, Cerucal, Motilium, Itoprid, Fractal, Osetron);
- antisecretory drugs - Rennie, Almagel, Maalox, Phosphalugel;
- preparations containing iron - Maltofer, Aktiferrin, Sorbifer, Ferlatum, Venofer;
- enzymes to improve digestion - Pancreatin, Creon, Mezim, Festal, Somilase;
- multivitamin complexes - Elevit, Vitrum, Complivit Mama, Pregnakea, Materna, Femibion.
Traditional medicine
How to get rid of acid or bitterness in the mouth using traditional methods? The most effective decoctions of medicinal herbs and vegetable juices are:
- To eliminate bitterness, it is recommended to regularly drink vegetable juices, especially carrot juice;
- Potato juice is suitable for rinsing;
- if the unpleasant taste in the mouth is associated with dental problems and inflammation of the gums, rinsing with chamomile decoction will help;
- To disinfect the oral cavity, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a solution of soda and salt.