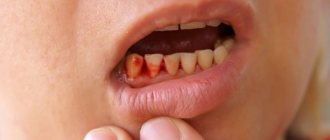
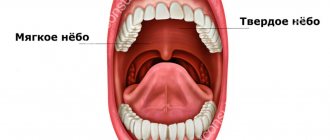
Bleeding is considered to be the loss of blood from the body. Bleeding can be both external and internal. Blood can flow both from body tissues damaged for certain reasons, and from natural orifices of the human body.
Healthy people can survive 15% blood loss without serious consequences. Blood from the mouth is a fairly rare phenomenon, and most often its occurrence indicates serious problems with a person’s health. What are the causes of blood from the mouth?
Content
- Types of food poisoning
- Signs and symptoms in children
- Causes of food poisoning in children
- What should you do if you are poisoned?
- Peculiarities of child nutrition after treatment
- Disease prevention
Food poisoning is a complex of painful symptoms that occur when the body is affected by poisonous and low-quality products of animal or plant origin. Toxins can enter in different ways: through the intestines, absorption through the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, or inhalation. In children under one year of age, absorption and distribution throughout the body occurs faster. Source: H.D. Abdikhakimovich Features of the course of foodborne toxic infections // Pediatrician, 2022, v. 8, special issue
Poisoning in children is more common than in adults, and its course is much more complicated. This is explained by the peculiarity of the child’s still fragile body. In the early years, the intestinal microflora is not yet formed, toxins are quickly absorbed and spread through the blood, and low acidity of gastric juice is noted.
Causes
Most often, the bacterium enters the human body through wounds and microcracks in the skin. The infection, having penetrated through the wound, begins to multiply in the blood, spreading throughout the body and affecting the lungs, heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and joints.
With staphylococcus, diseases can be very different, such as pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, sepsis and many others.
Staphylococcus infection can occur in the following ways:
● Through contact and household use when using the patient’s personal items;
● Airborne droplets during close contact with an infected person;
● Fecal-oral on dirty fruits, vegetables and other food products, dirty dishes and hands;
● Vertical when a child passes through the birth canal of an infected mother during childbirth.
● Infection often occurs during surgery through medical instruments and during various manipulations.
Types of food poisoning
- Microbial. This type includes poisoning from spoiled or contaminated products.
- Intoxication with chemicals. It occurs when toxins enter the gastrointestinal tract and requires urgent medical attention.
- Poisoning with poisonous mushrooms, fish or meat, plants. An urgent visit to a doctor is recommended. Source: B.Zh. Suleizhan, W.K. Keldikulova Foodborne toxic infections // Journal of the Almaty State Institute for Advanced Training of Doctors, 2011, No. 1
How to recognize a food allergy and not confuse it with other diseases?
Most often, in order to diagnose a food allergy, a doctor only needs an examination and a detailed interview with the mother. Mom can point out that she herself has a food allergy or point the doctor to a specific food. Sometimes it is difficult to make such a diagnosis right away. Then the doctor may order an examination. First, a general blood test. And then, if necessary, specific allergy tests: examination for immunoglobulins, and at a later age, provocative tests. It is these tests that were chosen as the most informative in the latest clinical recommendations. In addition, your baby may need to consult an allergist, dermatologist or gastroenterologist, depending on the symptoms that are bothering him. And also, additional examination from the gastrointestinal tract.
Signs and symptoms in children
Food poisoning in children occurs suddenly and manifests itself in an acute or mild form. The first signs are observed several hours after the child has consumed spoiled or poor quality food. Often this happens within 60 minutes, with a latent course of the disease – up to 8 days. The faster the symptoms of poisoning appear, the more dangerous it is.
Regardless of the pathogen, stomach poisoning in children may result in:
- cutting pain in the abdomen;
- general weakness and lethargy;
- the presence of nausea and/or vomiting;
- chills;
- dry mucous membranes;
- pale skin;
- increased or decreased temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- increased thirst;
- rapid breathing and pulse;
- loose stool.
The greatest danger to a baby's health is vomiting and loose stools , since they can quickly dehydrate the body and can cause kidney failure. The main signs of dehydration include: a decrease in the frequency of urination and a decrease in the amount of urine, dry skin and a decrease in its elasticity.
In difficult cases, botulism may occur with damage to the nervous system. With such poisoning, the baby experiences dry mouth, constipation, and visual acuity may decrease.
If a child is poisoned by plants, he is most often bothered by severe abdominal pain with profuse drooling. There may be changes in heart rate and rhythm disturbances.
Mushroom poisoning is characterized by painful sensations in the abdomen, pallor of the lips and skin, and upset stool. The child may experience nausea and frequent vomiting, sometimes with blood. Poisoning with poisonous mushrooms is the most dangerous type of poisoning.
Eating vegetable dishes and foods high in nitrates can cause a number of symptoms in a child. These include pain in the stomach, lethargy, headache, shortness of breath, gagging and tinnitus.
Symptoms of poisoning that require prompt medical attention:
- low body temperature;
- dyspnea;
- drowsiness;
- dark colored urine and a decrease in its quantity;
- blood in vomit or stool.
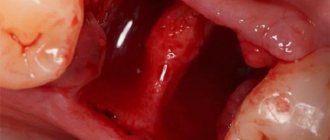
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Blood from the mouth may be accompanied by vomiting
Bleeding can occur in a variety of parts of the gastrointestinal tract. The main symptom is the appearance of blood in a person’s stool or vomit. It can be hidden and detected only with the help of specially conducted tests. In situations where blood from the mouth is caused by some kind of disease of the digestive system, it often goes along with vomiting.
In some cases, vomiting accompanied by slight bleeding may indicate a burst vessel in the throat or esophagus. But most often bleeding indicates the following diseases:
- stomach or duodenal ulcer
- erosion of the mucous membrane of the stomach or esophagus
- liver cirrhosis in severe stages
Ulcers provoke up to eighty cases of bleeding occurring in the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, due to bleeding, diseases such as enteritis, colitis, polyps, gastritis, duodenitis and others become aggravated. It also causes complications of cancer in any part of the digestive system.
The most severe form of blood effusion in the gastrointestinal tract is considered to be its loss through the veins of the esophagus, which occurs with portal hypertension. Sometimes severe bleeding occurs as a result of hemorrhoids. The use of certain medications in some situations causes the development of bleeding.
Causes of illness in a child
One of the main causes of food poisoning is the consumption of stale food . To avoid illness, you should pay attention to the appearance and smell of food, as well as storage conditions. Often, parents buy food for their child without paying attention to the expiration date. Even if you make purchases at a trusted retail outlet with an impeccable reputation, you must always look at the packaging of the product.
In addition to low-quality products, in medical practice there are cases of chemical poisons and toxic plants entering the baby’s body along with food. Toxins may be contained in medications or household chemicals that the child used accidentally or unknowingly.
Causes and routes of infection
The main cause is the HCMV-5 virus, which is transmitted from person to person. In children older than several months and adults, infection occurs almost asymptomatically and for the most part does not pose a particular health hazard.
But a child can become infected with this virus even before birth, i.e. in this case we are talking about a congenital virus. And then cytomegalovirus can cause serious damage to the body. developmental defects , serious disorders in the nervous system and digestive system, in the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems may occur Smirnova, E.V. Rossikhina, N.S. Dyupina The role of cytomegaloviruses in obstetric pathology and neonatology // Vyatka Medical Bulletin, 2010.
The virus penetrates the placenta, so it affects children even at the stage of intrauterine development, and can be transmitted during childbirth and breastfeeding.
The main routes of infection, which with a 98% probability lead to the disease:
- Blood transfusion - infection occurs during: organ transplantation;
- blood transfusion;
- using non-sterile syringes for intramuscular and intravenous injections.
What should you do if you are poisoned?
If your child has food poisoning, self-treatment is absolutely unacceptable. There is no need to give him activated carbon and wait for the effect. This is especially true for newborns, since they have the highest incidence of severe consequences.
The main task of parents is to provide timely assistance by contacting a specialist. To avoid complications, all medications are prescribed to the child by the doctor. It is not recommended to give children antibiotics, painkillers, antidiarrheals and antiemetics. Attempts to independently cure a child can harm his health and delay the recovery period. In addition, such actions will lead to the disappearance of symptoms, by which a specialist can determine the true cause of poisoning. Source: A.V. Gorelov Therapy of acute intestinal infections in children in modern conditions // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2004, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 72-78
Poisoning is diagnosed based on tests, an in-person examination of the child, and interviews with parents. All treatment measures are carried out in a hospital setting, in some cases at home.
Therapeutic measures are aimed at immediately removing toxins from the child’s body, eliminating symptoms and combating dehydration. The specialist may also prescribe diet and vitamin therapy.
If you have the slightest suspicion of poisoning in a child, contact the pediatric department of the SM-Clinic. We employ experienced specialists who will help determine the exact cause of the disease and provide a full range of medical services at a high level.
Treatment
Staphylococcus can be treated surgically if there is a purulent lesion in the area of infection. It may also be necessary to remove an infected implant, catheter, etc.
As a conservative treatment for staphylococcus, antibiotics and antibacterial agents are used in combination with immunomodulatory therapy. The drugs are selected taking into account the resistance of staphylococcus to a wide range of medications. The use of brilliant green solution for treating infected wounds has shown greater effectiveness.
What tests need to be taken
First of all, to determine the presence of infection, a staphylococcus test is taken.
For diseases of the respiratory tract, a swab is taken from the nasopharynx and oropharynx, for cystitis - urine, for gastrointestinal disorders - feces, for skin lesions - a scraping from the skin, and if there is a suspicion of extensive infection, they donate blood.
Also, before starting treatment with antibiotics, it is required to be tested for resistance to these medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
Advanced cases of the disease are dealt with by an infectious disease specialist.
But if you just have suspicions and want to get an accurate diagnosis, first you should consult a therapist, or with children, a pediatrician. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and, based on the results obtained, will write you a referral to the necessary doctor.
Peculiarities of child nutrition after treatment
During recovery, the child is prescribed a diet that is similar to the diet for any intestinal infections. Children are recommended:
- increasing the frequency of meals up to 6-8 times a day;
- drinking liquid, crushed and pureed food in fractional portions;
- exclusion of fried foods;
- ad libitum feeding (give food on demand, but do not overfeed).
The main rule of nutrition is that food should contain a minimum amount of fat. You should avoid whole milk, fruits and fresh baked goods, which can cause fermentation in the intestines. You can give more boiled water, crackers, low-fat cottage cheese, baked apples, cookies, rosehip decoction.
Disease prevention
- The child’s personal hygiene: washing hands before and after walking, after using the toilet, before eating.
- Lack of raw water, ready-made factory meals and unboiled milk in the diet.
- Compliance with food storage conditions.
- Careful selection of food products, taking into account expiration date and quality.
Treatment of small cracks, scratches and abrasions on the hands to prevent germs from entering the body.
Sources:
- H.D. Abdikhakimovich. Features of the course of food toxic infections // Pediatrician, 2022, v. 8, special issue
- B.Zh. Suleizhan, W.K. Keldikulova. Foodborne toxic infections // Journal of the Almaty State Institute for Advanced Medical Studies, 2011, No. 1
- A.V. Gorelov. Therapy of acute intestinal infections in children in modern conditions // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2004, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 72-78
Vostrikova Ekaterina Borisovna Clinic
Author of the article
Vostrikova Ekaterina Borisovna
Specialty: gastroenterologist
Experience: 14 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms
If the infection develops in children during the neonatal period, it may be accompanied by symptoms:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- tonsillitis;
- labored breathing;
- impaired swallowing and sucking reflexes;
- prematurity;
- strabismus;
- jaundice of newborns. Source: R.Zh. Seisebaeva, A.E. Almaganbetova, F.N. Kasymbekova, E.S. Ataibekova, G.M. Abdrakhmanova Epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus infection // Bulletin of KazNMU, 2022, No. 1.
Cytomegalovirus can develop asymptomatically, which is the most dangerous. Due to the asymptomatic course of the infection, children may develop changes in the skull skeleton, lack of body weight, and mental development disorders.
Acquired infection (when a child becomes infected at an older age) can occur with the following symptoms:
- enlarged lymph nodes (especially in the neck);
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- temperature increase;
- pain in muscles and joints.
Most often, the infection goes away without any specific treatment when infected at an older age than infants. But if the symptoms of infection do not go away after 2 months, consult a doctor immediately!
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a gastroenterologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2900 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space (and retroperitoneal lymph nodes) | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2900 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1600 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1600 rub. |
| Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection (HELPIL test) | 1200 rub. |
| Colonoscopy | 5050 rub. |
| Biopsy during endoscopic examination (1 biopsy) | 1000 rub. |
| Body composition assessment - bioimpedance analysis | 2150 rub. |
| Body composition assessment - repeated (bioimpedance analysis) | 1750 rub. |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EFGDS) | 3050 rub. |
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can diagnose the presence of infection based on the results of a staphylococcus test.
It is worth remembering that testing is recommended only if symptoms of the disease are present. The presence of bacteria in biological material may mean that a person is its carrier, which in itself is the norm.
For analysis, material is taken from the area where the infection is believed to be developing. To detect a pathological process, several tests are carried out to track the dynamics of bacterial growth. If their number increases rapidly, the presence of a staphylococcal infection can be diagnosed. Also, additional analysis will determine the specific type of infection so that the doctor can choose a personal treatment regimen.