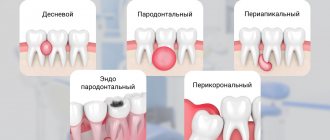
Current problem
For most people, heartburn is simply an occasional discomfort. Approximately 20% of the population of highly developed countries experience it at least once a month.
But for the 6% of people who have a chronic form of heartburn known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), unresolved (untreated) symptoms can lead to various health complications. People with erosions in the lining of the esophagus due to acid reflux often do not realize the harm of GERD until they have advanced stages of the disease.
If you experience frequent or prolonged heartburn (twice a week on a regular basis), consult your doctor. Here are nine reasons why you shouldn't ignore the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Why does bitterness occur in the mouth? Recommendations for heartburn
14.04.2021
Bitterness in the mouth is a symptom that worries many people. And almost 100 percent of all people with a symptom of bitterness in the mouth are sure that talking about bile and gall bladder . Let's figure it out.
With what part of the tongue do we feel bitterness? We feel bitterness through the papillae on the tongue, usually the back wall of the tongue, that is, the root of the tongue. has absolutely nothing to do with bitterness in the mouth Bile is released into the duodenum, and then goes down the intestines , and our stool is colored brown, thanks to the pigments of bile. Bile cannot get into our mouths .
Therefore, the gallbladder and liver , and bile in general, in principle, have nothing to do with bitterness, and most often such sensations are associated with the effect of hydrochloric acid from the stomach on the walls of the esophagus . Why is this happening?
Everyone knows that the stomach contains hydrochloric acid. Ideally, hydrochloric acid should only be in the stomach and should not be thrown the esophagus For this purpose, there is a sphincter at the bottom of the esophagus - this is a muscle ring. It is closed all the time, opens only when food passes through the esophagus , lets food into the stomach , then closes again and should not return. It happens that it does not close or closes poorly. Acid from the stomach goes back into the esophagus and burns it. The esophagus is not used to the effects of acid, because the stomach is protected from acid, but the esophagus is not. Therefore, the esophagus immediately sends a signal to the brain , and the brain, in response to this signal, sends a signal to the salivary glands so that they secrete very alkaline saliva. This alkaline saliva, when swallowed, helps quench acid that irritates the esophagus . And this alkaline saliva has a very bitter taste.
The bitter taste in the mouth is the taste of alkaline saliva, which is produced in response to a burn in the esophagus . A disease that may be accompanied by a bitter taste is called gastroesophageal reflux disease , or popularly heartburn .
What should people who experience heartburn (bitterness in the mouth) not do?
In order to prevent this sphincter between the stomach and esophagus , some rules should be followed. Firstly, absolutely do not smoke. Secondly, avoid caffeinated products. It could be coffee, chocolate, cola, cocoa and so on. The next item is mint. All products containing mint should be avoided. These are chewing gum, candies, mint breath fresheners, mint teas. It is necessary to exclude onions, garlic in any form: fried, steamed, it doesn’t matter, any onion and garlic, as well as fatty, fried foods. And also after eating, you should not take a horizontal position for two to three hours.
But you must understand that all this will help alleviate the symptoms of heartburn and you will feel less bitterness, but this will not get rid of the causes of their occurrence, so you must additionally seek professional medical help. At the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor and have an examination - gastroscopy , so that the doctor can determine and help eliminate the cause of your heartburn . This could be a hernia , a burn, erosion, ulcer , or even the so-called Barrett's esophagus (and this is a precancerous disease).
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic
Development of inflammation in the esophagus (esophagitis)
In gastroesophageal reflux disease, food, acid, and digestive juices back up into the esophagus. Over time, this causes irritation and swelling of the mucous membrane lining the inside of the esophagus. This is esophagitis. If acid exposure in the esophagus is observed for just a few weeks, then inflammation of the mucous membrane can already develop. This can cause discomfort and even pain along the midline of the abdominal wall, “in the pit of the stomach,” where the right and left ribs meet at the sternum. This inflammation makes the esophagus vulnerable to even more dangerous conditions - erosions or scars.
The main diseases that cause belching
First of all, pathological belching is periodic and serves as a symptom of diseases such as:
- inflammatory process in the pancreas;
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa;
- dysfunction of the gallbladder;
- inflammation of the duodenal mucosa;
- stomach ulcer;
- displacement or compression of the esophageal tube;
The appearance of regular belching in combination with an unpleasant rotten smell should be alarming; a lump in the stomach may also be felt. These symptoms are typical for malignant neoplasms.
Esophageal stricture
If esophagitis continues for too long, the resulting scar tissue can narrow the esophagus. This stricture can lead to difficulty passing and swallowing food, which can become stuck at the level of scar tissue, causing pain.
Large pieces of food may become stuck and this situation may require endoscopic intervention to remove them. The stricture may cause frequent choking when eating. Because of this, patients often refuse to eat and lose a lot of weight.
Stricture is treated by widening or stretching the esophagus (bougienage or dilatation). These treatment procedures can have multiple effects on the stricture. But taking stomach acid blockers (proton pump inhibitors, PPIs, or H2 blockers) may prevent scarring in the esophagus from returning in the future.
The process of regurgitation at the end of a meal
Belching may occur after eating.
At the end of a meal, the process of belching can be a physiological norm.
However, in case of disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, belching after eating is also a characteristic symptom; it indicates:
- inflammation of the pancreas in a sluggish and acute form;
- inflammation of the duodenal bulb;
- violation of the patency of the bile ducts;
- inflammation of the intestinal mucosa with a high concentration of acid in the gastric juice;
- inflammatory processes in the esophagus.
Regurgitation that is periodic in nature may indicate disturbances not only in the functioning of the digestive organs, but also some hidden diseases of other systems. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain a conclusion about your health status from your attending physician.
To summarize, we can say that periodic belching occurs due to:
- insufficiently balanced diet;
- irregular eating habits;
- excessively active behavior at the table;
- swallowing large amounts of air;
- dysfunction of the digestive system;
- diseases of other organs not related to the process of digesting food. For example, problems with cardiac activity also contribute to the appearance of belching;
- hiatal hernia.
In addition, there are a number of diseases accompanied by belching phenomena:
- ulcerative lesions in the intestines and stomach;
- insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes;
- reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus;
- disruption of the outflow of bile and the functioning of the pancreas.
Throat and voice problems
The main symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease is heartburn, but not all people feel or report it. They may have other symptoms that are more difficult to diagnose. Doctors call these cases "silent reflux," or asymptomatic reflux. The patient may not have heartburn as classically described in textbooks, but they may have various other problems that occur outside the esophagus, such as hoarseness, voice changes, sore throat, or chronic cough. They feel as if there is a lump or hair in their throat and constantly have to clear their throat by coughing and clearing their throat.
Regurgitation at an early age
In young children, burping is considered normal after drinking milk.
During infancy, regurgitation of breast milk along with some air is a normal physiological process.
A certain amount of air masses enters the stomach during feeding and serves to normalize pressure.
Since the activity of the baby’s digestive tract is not properly regulated, air bubbles can enter the intestines, causing unpleasant pain and flatulence. All this goes away with a belch. Therefore, after feeding, it is recommended to carry the baby in your arms until excess air is released. As you grow older, the need for this disappears.
It is better to rock hyperactive children who cannot calmly suckle the breast before feeding and wait until the baby calms down. You should also interrupt feeding to allow the air to escape. It would not be superfluous to consult a neurologist. Belching in a one-year-old toddler should worry parents. In this case, medical attention is needed.
In young children, the state of the digestive organs directly depends on the stable functioning of the nervous system. Hyperactive children are more vulnerable in this regard. Baby burping can also be caused by:
- active distracting activities during meals;
- watching TV while eating;
- lack of discipline while eating;
- ENT diseases.
School-age children burp for the same reasons as adult patients:
- disruption of the digestive system;
- liver problems;
- violation of the outflow of bile.
Breathing problems
If stomach acid accidentally flows into the windpipe after gastroesophageal reflux disease causes it to enter the esophagus, GERD can worsen asthma or pneumonia. Even without lung problems, GERD can cause shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. And treatment in this situation can be a double-edged sword. Because GERD medications, such as proton pump inhibitors, may actually increase the risk of pneumonia. (They can promote bacterial growth and suppress coughing, which is designed to help clear the lungs.)
Pay your doctor's attention to your lung function when treating reflux.
Dental causes of halitosis
When bad breath appears, disease of the teeth or gums is first suspected. Bacteria use leftover food in the mouth to feed themselves. If you brush your teeth incorrectly or completely abandon this procedure, a large amount of plaque accumulates in your mouth. Its rotting causes a repulsive odor. If plaque is not removed for a long time, dense tartar forms, and the stench persists for a long time.
Caries and tooth decay can also cause an unpleasant odor. These are areas where large numbers of microbes accumulate. The breath of people who do not remove decayed tooth roots in a timely manner has a strong smell. A stench can occur when wearing braces, dental plates, dentures, under which food debris accumulates. Any foreign body in the mouth requires additional cleansing.
The condition of the oral cavity is affected by the production of saliva. In some diseases it is not liquid enough. Dryness of the oral mucosa occurs, self-cleaning processes are disrupted and bacterial growth is activated. A similar mechanism works in hot weather or when playing sports, if you actively breathe through your mouth.
Smoking also contributes to the appearance of halitosis. Components of tobacco smoke settle on the teeth and combine with soft plaque. Dry mouth contributes to changes in the composition of saliva and an increase in its viscosity. You can get rid of the smell only by defeating a bad habit.
Esophageal ulcers
Stomach acid can erode the lining of the esophagus, causing sores and ulcers. Esophageal ulcers are different from stomach ulcers, which are usually caused by bacteria. People with wounds and sores may spit up blood and may also vomit blood. They may see blood in their stool. The blood may be red, cherry red, or like coffee particles. In stool, blood from the esophagus and stomach usually turns black when passing through the small intestine, the color and appearance of oil - viscous, slippery, and difficult to wash off.
Contact your doctor immediately if you have these symptoms. Endoscopy can detect ulcers of the esophagus. Acid-blocking or acid-lowering medications may make them disappear.
Surveys
The diagnostic search is aimed at a comprehensive assessment of the functional and morphological state of the gastrointestinal tract. A gastroenterologist examines patients with bitter erection. Particular attention is paid to the study of the hepatobiliary system. To establish the root cause of belching with an unpleasant aftertaste, a set of laboratory and instrumental methods is recommended, the most informative of which are:
- Radiography
. For a detailed study of the gallbladder and biliary tract, RCCP or percutaneous cholangiopancreatography is used. Studies make it possible to assess the degree of contractile dysfunction, visualize stones, and signs of the inflammatory process. To exclude gastrointestinal pathology, radiography with oral contrast is performed. - Endoscopy
. Since belching can be associated with damage to the duodenal zone, patients are shown endoscopy, which visualizes the mucous membrane of the upper digestive tract and reveals signs of various organic diseases. If necessary, to clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of pathologically changed areas is performed with histological analysis of the material. - Duodenal sounding
. Consecutive collection of several portions of bile on an empty stomach and after the administration of drugs that stimulate bile secretion is a valuable method in detecting pathologies of the biliary tract. The doctor evaluates the amount of bile secretion received and studies its microscopic and biochemical composition. If necessary, bacteriological culture is carried out. - Ultrasonography
. Abdominal ultrasound is used as a non-invasive screening method that provides rapid scanning and determination of the pathology of individual organs. Targeted sonography of the gallbladder and bile ducts allows us to identify stones, signs of inflammation and suppuration of the organ. - Stool analysis
. For pathologies manifested by bitter erection, changes in the coprogram are typical, therefore all patients are prescribed macroscopic and microscopic analysis of stool. If the patient has signs of a probable infectious process, bacteriological culture is performed. Additionally, the Gregersen reaction to occult blood is performed.
As additional research methods, a biochemical blood test is used to determine the level of bilirubin fractions, the concentration of alkaline phosphatase, ALT and AST, and serological tests to detect antibodies to intestinal parasites. According to indications, in complex and doubtful cases, scintigraphy of the biliary tract and liver is performed.
Duodenal sounding
Barrett's esophagus
If left untreated for many years, persistent acid reflux can form changes in cells known as Barrett's esophagus, which is considered a precancerous condition. This condition does not cause many symptoms other than those of reflux. A doctor can diagnose it by performing an endoscopy.
If you have heartburn more than twice a week for a long time, or if you have symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease that are getting worse or you have discovered new ones that you didn't have before, these are all reasons to get checked and have an endoscopy.
Diagnostics
It is important to know that independently determining the cause and choosing treatment methods is strictly prohibited, since incorrectly selected drugs can only harm the body. The fight against this manifestation should begin and continue only after a specialist makes an accurate diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing this symptom:
- Blood tests: general and biochemical - help to identify the presence and degree of the inflammatory process, evaluate liver function, parameters of fat and pigment metabolism.
- Analysis of stool for the bacteriological composition of intestinal flora - detects dysbiosis.
- Fecal analysis (coprogram) - reveals disturbances in the digestion of food, provides information about the possible presence of parasites in the intestines.
- X-ray of the abdominal organs - prescribed to identify stones in the ducts and possible calcification of the pancreas.
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system (ultrasound) is an extremely informative method for diagnosing pathologies of the liver, gallbladder and ducts. With its help, you can determine the parameters and location of the gallbladder, bile stagnation, the presence of stones, neoplasms, and polyps.
- Computed tomography of the abdominal organs - with its help you can examine any area in the peritoneum layer by layer and assess the extent of organs affected by pathological changes.
- Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy) is carried out to check for the presence of concomitant diseases and for differential diagnosis.
- Immunogram and analysis for tumor markers - given if a malignant process is suspected.
Esophageal carcinoma
In very serious cases, untreated gastroesophageal reflux disease (and subsequent Barrett's esophagus) can lead to esophageal cancer. The main risk factors are alcohol consumption, smoking, poor nutrition, and chronic esophageal diseases with reflux.
Symptoms include weight loss, trouble swallowing, or gastrointestinal bleeding. This is something that happens over decades of untreated reflux (30-40 years), so those who are 30 and otherwise healthy have no reason to suspect cancer. But if you're over 50 and have had heartburn for years and suddenly lose weight, for example, this is definitely what your doctor will suspect first.
Symptomatic therapy
If the symptom is observed quite rarely and is not accompanied by other unpleasant signs of the gastrointestinal tract, belching can be dealt with using non-drug means. The main factor is the normalization of eating habits: avoiding fatty, smoked and fried foods, limiting alcohol and carbonated drinks, which cause stomach distension and gas formation. You need to eat food 4-5 times a day in small portions; after eating, you should not bend over or do heavy physical work.
Bitter belching that lasts more than 5 days is a sign of a disease of the digestive or biliary system and requires contacting a specialist. Before undergoing a full examination and making a clinical diagnosis, medications can be used to reduce unpleasant symptoms: prokinetics to improve gastrointestinal motility and prevent the reflux of duodenal contents into the gastric cavity, choleretic drugs to normalize the rhythm of bile secretion. For concomitant pain syndrome, antispasmodics are used.
Treatment of postcholicystectomy syndrome
Since PCES is not an independent disease, treatment of the syndrome is always determined by its causes. Not knowing how to properly treat postcholicystectomy syndrome can only aggravate the condition and increase unpleasant symptoms.
The principles of treatment for PCES include two key points:
- collection of anamnesis data - the doctor carefully studies old medical reports and records, paying close attention to preoperative diagnostics and the protocol of the operation;
- eliminating the causes of the syndrome;
- prevention and treatment of suspected complications.
Treatment is mainly based on:
- diet therapy;
- drug treatment;
- surgery (according to indications)7.
Together with comprehensive treatment, these measures can reduce the severity of symptoms of PCES8.