Duration of engraftment Causes of rejection Signs of rejection Contraindications to implantation Types of implantation Engraftment above and below What to do with mobility?
Care after surgery Implantation is the only prosthetic method that restores the functionality of the entire tooth, and not just its crown part. A dental implant is a multicomponent structure made of biocompatible material (titanium and its alloys), introduced into the jaw bone to replace a missing tooth unit. It fully replaces a natural tooth, taking over all its functions. Those who decide to undergo implantation are usually interested in how dental implants take root, how long it will take, and what problems may arise.
The viability of an artificial root depends not only on the choice of its type, shape, and size according to the parameters of the jaw bone. But also on the general state of health, correct installation of the implant, compliance with the doctor’s instructions in the postoperative period.
How long do dental implants take to take root?
The process of fusion of an implant with bone is called osseointegration. It goes like this:
- In the first 30 days
after the introduction of the artificial root, trabeculae of spongy substance begin to actively form around it, forming the skeleton of bone tissue. During this period, the tissue around the implant is soft, loose, and easily injured. - about 3 months
, a soft, loose spongy structure forms into dense lamellar bone, firmly holding the titanium root. During this period, the implant can already be loaded with a prosthesis. - Complete fusion with the jaw bone occurs after 1.5 years
.
The survival rate of dental implants is influenced by various factors - from the implantation protocol used to the type of jaw the structure is integrated into (lower or upper). After implantation, enough time must pass for the bone tissue to “accept” the artificial root and begin to grow around it, ensuring a stable, strong fixation.
History of the first patient
The first attempts to replace lost teeth with artificial ones were made by people in antiquity and even earlier. In the form in which we know dental implants now, they appeared in the second half of the 20th century. The first successful implantation was performed in 1965 on an ordinary carpenter, Gust Larsson, who lost all his lower teeth at the age of 34, had a cleft palate, a deformed upper jaw and chin, and experienced constant pain and significant difficulty eating and speaking. Larsson volunteered for a new study led by Professor Ingvar Brånemark at the University of Gothenburg, which Güsta had heard about by chance from his dentist. After the treatment, he was able to chew, eat and speak normally. The installed implants served Gust Larsson all his life. The experience of this brave man proved that installing dental implants is the most effective way to restore lost teeth.
Why an implant may not take root
The worst thing that frightens patients is the risk of rejection of the structure. Thanks to modern protocols and materials, the implant survival rate is as high as possible ( 97-98%
). When installing original implant systems Astra Tech, Nobel Biocare, ROOTT, Straumann, rejection rates do not exceed 0.2-0.5%, that is, the survival rate is almost one hundred percent.
When asked why dental implants do not take root, the doctor will answer after examination and diagnosis. But the patient needs to be more careful, not ignore warning signs, and immediately contact an implantologist. The success of the operation and engraftment is influenced by:
- health status;
- quality of preparation for surgery;
- choice of implants;
- implantation protocol;
- correctly calculated prosthesis design;
- careful adherence to medical recommendations in the postoperative period.
Attention to all of the above points reduces the likelihood of design rejection to zero. Typically, engraftment of a titanium root with classic two-stage implantation takes at least 3 months
. After the structure has fused with the bone, an abutment is fixed on them, and an artificial crown or prosthesis is placed on top. With express implantation or basal complex, engraftment proceeds faster. The implanted roots are loaded with a temporary prosthesis 1-3 days after surgery.
What determines the success of osseointegration
Several factors influence the success of engraftment:
- Proper preparation and planning.
- Patient's health status.
- Use of high-quality implants.
- Selecting an implantation method that is appropriate for the clinical situation.
- Correct calculation of the prosthesis design.
- Compliance with recommendations after implantation.
Attentive attention to each point ensures engraftment without complications.
Risks at the diagnostic and preparation stage
In order for engraftment to proceed without problems, it is important to eliminate risks at the stage of preparation for implantation:
- An examination is carried out for general somatic diseases to identify contraindications to surgery.
- The doctor diagnoses diseases of the oral cavity that are in the acute stage, paying close attention to the future site of implantation and surrounding tissues. The oral cavity is sanitized, adjacent teeth are treated, and plaque and stone are removed.
- An implant treatment plan is drawn up, and recommendations are given to the patient on the rules of preparation for the operation.
- 3D computer modeling helps to choose the shape and size of the implant. This is necessary so that the design fits the patient’s bone characteristics and does not reject it.
Patient's health status
Successful implantation is impossible in case of serious diseases that can cause implant rejection. The main contraindications for which implantation is strictly prohibited:
- malignant tumors;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- blood clotting disorder;
- mental illness;
- tuberculosis;
- pathological diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- risk of heart attack or cardiac arrest;
- disruption of the immune system;
- thyroid diseases.
The patient should not hide his condition and agree to the procedure without prior diagnosis. In addition, diagnostics will help identify hidden diseases that you may not be aware of. Therefore, before the procedure, the doctor collects anamnesis and prescribes tomography, blood tests, and ECG for patients at risk.
Main reasons for rejection
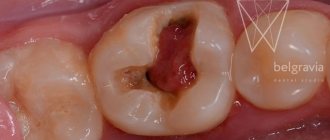
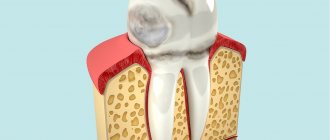
- Peri-implantitis
- the tissues around the implant become inflamed for various reasons: due to undetected contraindications to implantation, poor preparation of the oral cavity for surgery (untreated caries, active gum disease, etc.), violations of the installation protocol, failure to comply with medical instructions after surgery . - Features of the structure of the jawbone
- in loose, porous bone, even with sufficient volume, the titanium structure will not hold. To avoid problems, the bone is additionally strengthened with special materials. - Intolerance to the implant material
- although titanium and its alloys are biocompatible with bone structures, allergies sometimes develop. This usually happens if implantation systems of dubious quality that contain various harmful impurities are used. - Systemic diseases
- endocrine, immune, cardiovascular pathologies, oncological processes significantly increase the risk of artificial root rejection. - Incorrect osseointegration
- when installing low-quality systems, their components come into contact with the jaw structures and provoke the formation of fibrous tissue rather than bone. As a result, instead of strong bone tissue, a connective tissue capsule is formed around the implant, which cannot hold the structure, and it falls out.
The network of RUTT clinics in Moscow uses reliable, proven implantation systems. Before surgery, patients undergo a comprehensive examination to assess the characteristics of the dental system and contraindications. Implantation is performed after all risks have been eliminated, so the listed points are kept to a minimum.
Price
For your information, here are the average prices for services related to dental implantation in Moscow dental centers:
| Name of service | Cost in rub. |
| Diagnostics | |
| X-ray of one tooth | 340 |
| Orthopantomogram | 1100 |
| Specialist consultation | |
| Dentist-therapist | 600 |
| Periodontologist | 740 |
| Implantologist | 850 |
| Treatment of complications | |
| Cleaning the implant from dental plaque | 180 |
| Periodontal applications in the area of one tooth | 370 |
| Applying a periodontal bandage | 400 |
| Laser therapy of the gum mucosa | 490 |
| Implant removal | 6900 |
| Filling the gingival pocket with osteoconductive material | 10900 |
| Installing a protective membrane | 12900 |
| Professional oral hygiene | |
| Ultrasound | 2000 |
| Air Flow method | 3500 |
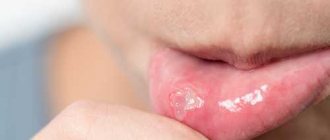
Signs of implant failure
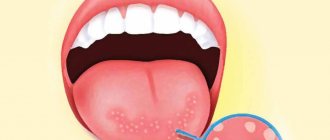
Swelling, pain, slight fever, bleeding gums 3-5 days after implantation
– a normal reaction to intervention. Within a week, these symptoms disappear. If symptoms persist longer than the specified time and increase, you should immediately contact an implantologist.
Signs of peri-implantitis on x-ray
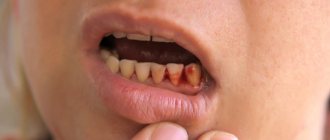
Signs of rejection may appear not only during the rehabilitation period, but also later. How to understand that the implant is not taking root:
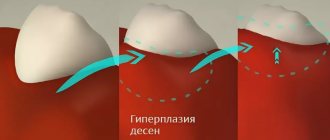
- severe swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, persisting longer than 5 days after the intervention;
- acute pain, aggravated by pressure on the gum;
- the appearance of a bad odor;
- purulent discharge;
- bleeding for more than 2 days, ichor for more than 7 days;
- temperature 38°C and above, not reduced by antipyretics;
- implant mobility, its loss.
Sometimes there are no visual signs of rejection, the artificial root simply falls out. As a rule, if the implanted root has not been rejected within a month, osseointegration proceeds normally. But it happens when the artificial root is rejected at a later stage, after the installation of the prosthesis. The causes may be previous viral diseases, acquired after implantation, immune diseases, or injuries.
Contraindications to implantation
Contraindications to the procedure are divided into absolute and relative. Absolute conditions in which the operation is impossible include:
- oncology in the active phase;
- diabetes mellitus in the decompensated stage;
- mental disorders;
- acute tuberculosis;
- blood clotting pathologies;
- severe cardiovascular pathologies;
- a heart attack or stroke suffered less than 6 months ago;
- allergy to anesthetics, implant material;
- connective tissue diseases.
Relative restrictions:
- age under 18 years;
- poor oral hygiene;
- bad habits (alcoholism, smoking abuse);
- pregnancy, actuation;
- systemic diseases during exacerbation;
- infectious and inflammatory processes.
The ability to combine installation protocols significantly reduces the list of contraindications, allowing you to solve almost any clinical problem. One-stage protocols make it possible to carry out implantation in patients with HIV, periodontitis, periodontal disease, endocrine pathologies, hepatitis B, C, and other complex diseases that were previously considered an absolute contraindication to implantation.
Patients with periodontal pathologies are interested in the question of whether implants survive periodontal disease.
. One-stage protocols combine different models of implants (compression, basal). They have high rates of resistance immediately after surgery. Basal models are installed not in spongy bone, but in deeper bone sections - basal, bicortical, not subject to atrophy. The inclined position increases the area of contact between the implants and the bone and accelerates osseointegration.
How long does it take for an implant to take root?
Osseointegration is influenced by the type of implantation system (type, shape, coating, type of thread, connection to the abutment), and the method of its installation. The doctor chooses the type of implants and implantation method according to the clinical picture. One- and two-stage technologies are used:
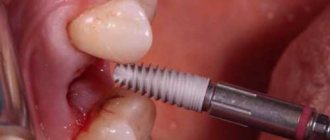
- Classical implantation (two-stage protocol) – two-component, root-shaped models are used. The root part of the implant is installed in the jaw, closed with a plug and sutured. After osseointegration of the titanium structure with the bone, the abutment and crown are fixed. Engraftment lasts 2-4 months (how the body reacts).
- One-stage methods with immediate loading - the prosthesis is attached to the implants after implantation (within 72 hours). Instant loading with the prosthesis stimulates bone formation around the implant, reducing the time of osseointegration. In the protocol, one-component models are more often used, in which the root-shaped part and the abutment form a single whole.
- Single-stage implantation - a titanium root is installed in the tooth socket immediately after its removal. The blood clot triggers the synthesis of osteoblasts, which accelerates engraftment. But this method is possible if there is sufficient volume and quality of the jaw bone, and the absence of even the slightest signs of inflammation. The implant is loaded with a prosthesis after complete engraftment.
With single-stage implantation, it is possible to install a temporary crown immediately after implantation
. But in this case, the structure is removed from the chewing process (the crown is made in height below the general row of teeth).
Questions and answers
3 years ago I had implants placed on my lower jaw and the remaining teeth were removed.
And in March, all the implants were removed. The result is changes in bone tissue and flat gums. Is it possible to install a flexible prosthesis there? I have a removable denture on top. 3 years ago I had implants placed on my lower jaw with the removal of the remaining teeth. And in March, all the implants were removed. The result is changes in bone tissue and flat gums. Is it possible to install a flexible prosthesis there? On top of my head there is a removable denture
Hello! Prosthetics with soft dentures in such cases is possible, but a preliminary examination of the oral cavity is necessary. Come visit us for a free consultation. Based on the results of the examination, our orthopedists will offer you the best options for dental prosthetics in your case. You can make an appointment by calling + 7 (495) 789-42-02. Sincerely, Patient Support Center SIMPLADENT++8 800 333-53-41
I would like to know how safe it is to carry out implantation and prosthetics at once and whether installing a prosthesis will harm the healing of the implants?
Good afternoon. I have four teeth in a row on my upper jaw on the left side that need to be removed, including two front incisors. The doctor recommends immediate implantation and prosthetics. I would like to know how safe it is and whether installing a prosthesis will harm the healing of the implants. Of course, you don’t want to walk around with a hole in your mouth, but you also don’t want to make things worse.
Hello. Modern implantation systems used in implantation protocols with the possibility of immediate dentures are equipped with special aggressive threads. Implants are screwed into the bone, providing maximum tissue compression. That is, the bone becomes stronger and firmly holds the artificial root in the hole.
The adaptation prosthesis, which is installed on implanted implants, has a metal base that works on the principle of a beam - the implants and prosthesis are a single system, which ensures high primary stability and immobility in the jaw bone. Artificial teeth fixed on a metal beam are made of metal-plastic.
This is a lightweight material that is strong enough to fully participate in the chewing process, but does not overload the implants. Only with this material is it possible to correct the bite at the time of engraftment of the implants. The prosthesis is permanently fixed and should be worn until the osseointegration process is completed - on average this takes about 6-12 months. It is then replaced with a permanent structure made from more durable and aesthetic materials. More detailed information can be obtained at a free consultation with a specialist in one of our clinics.
SIMPLADENT specialists will answer all questions by phone: + 800 333-53-41 Other questions
What to do if the implant is mobile and does not take root
If any sign of rejection appears, you should contact the implantologist who performed the operation. Based on the diagnostic results, it will be clear whether the implant can be saved with conservative therapy or whether it will need to be removed. In most situations, after eliminating the inflammatory process and restoring the jaw tissue, re-installation of the implant is possible. In the absence of contraindications, reinstallation is carried out after 1-2 months. If the bone tissue is severely damaged due to rejection, surgery to build it up will first be required.