Many people often complain of pain that occurs when opening their mouth. This pathology occurs for a variety of reasons. An experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. It is recommended to visit the dentistry on Oktyabrskaya Street. The doctor will examine the patient’s medical history and prescribe a number of additional tests. Before you begin to eliminate this problem, you need to establish the exact cause of its occurrence.
Do not self-medicate; complications are much more difficult to treat than the cause. We are ready to answer your questions by phone, +7
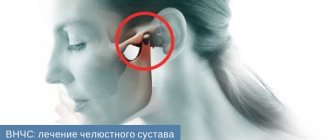
Jaw pain near the ear: what causes the discomfort and how to cope with it
Jaw pain is an unpleasant symptom that causes significant discomfort. The problem requires immediate medical attention. When examining and making a diagnosis, he takes into account the location of the problem area. If your jaw hurts near your ear, this may indicate problems with the temporomandibular joint, which provides mobility to the lower jaw and its connection to the skull. Soreness in this area often indicates a number of other diseases. A specialist will help determine the cause.
Neurological pathologies
Neurogenic pain, i.e. sensations caused by pathologies of the facial or trigeminal nerve often occur after hypothermia, head and face injuries. They are always accompanied by a number of additional symptoms, which makes it possible to determine nerve damage.
Why does it hurt to open your mouth?
It is recommended to use anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, warming procedures, and neuroprotectors
Opening the mouth is accompanied by pain because the affected nerve is irritated.
The nature of the sensations and accompanying symptoms
The pain can be completely different in nature.
Associated symptoms depend on which nerve is affected - pain in neighboring areas of the face, dry mouth, impaired facial expressions, cough, sore throat, swallowing problems, sore throat, inability to chew, impaired diction.
Treatment methods
The use of anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, warming procedures, and neuroprotectors is recommended. Operative methods are ineffective.
Why does the jaw hurt near the ear: the main causative factors
Soreness in the jaw with radiation to the ear can provoke various pathologies.
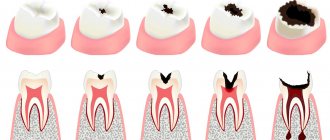
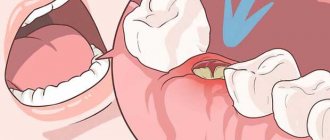
Dental problems
Dental diseases are often accompanied by pain, which can radiate to different parts of the head, including the area near the ear. Possible reasons for the appearance of an unpleasant symptom:
- caries at different stages of development, pulpitis;
- abscess;
- damage to prostheses - crowns or implants;
- glossitis - inflammation of the tongue;
- cyst or granuloma of the tooth root;
- gum disease – gingivitis, periodontitis;
- periostitis is an inflammatory process in the periosteum.
Pain in the jaw is often associated with procedures performed by the dentist, for example, teeth cleaning or whitening, their treatment or removal, implantation, or installation of braces. Irradiation into the ear is observed when the figure eight erupts and its position is incorrect.
A problem such as bruxism can also provoke pain. When it is present, the jaw muscles unconsciously contract, causing severe teeth clenching and friction. A characteristic grinding sound occurs. Often a person is not aware of the presence of bruxism, since it usually occurs at night. A disorder can be suspected by the presence of discomfort in the facial muscles in the morning. Due to the strong tension, pain is also felt in the jaw, and microcracks form on the enamel.
Disorders of the temporomandibular joint
TMJ problems are the most common cause of non-dental pain in the facial area. Joint dysfunction is provoked by various disorders in the mobility of the system of muscles, ligaments, cartilage and bones. Pain may appear on the left or right, as well as on both sides. The main symptoms of TMJ dysfunction:
- pain near the ear when swallowing, chewing, yawning, talking;
- dizziness;
- visual impairment;
- noise in ears;
- headache.
The disease is also diagnosed by a characteristic click when opening the mouth. TMJ injuries (dislocations, fractures) are accompanied by bruising, swelling, and redness. You can get them from a blow or bruise. Often the jaw disc is displaced forward, and the head of the lower jaw is shifted backward. This provokes stretching of the anterior and posterior disc ligaments and pressure on the bilaminar area of the joint, where pain receptors are located.
The TMJ can be affected by arthritis and arthrosis. In the first case, severe night pain, crunching and clicking, and stiffness in the morning appear. In the second, the pain is aching and chronic in nature and increases with yawning and opening the mouth. Pathology is provoked by various reasons: age-related changes, stress, inflammation, trauma and genetic predisposition.
Disturbances in the functioning of the TMJ are observed with the habit of clenching or moving the jaw, with bruxism, and constant chewing of gum (the joint does not have time to rest after eating food). Causes wear and tear and malocclusion. Chewing food on one side provokes increased pressure in this area. Over time, damage to the TMJ affects the nerve endings, which explains why pain occurs.
Neurological diseases and vascular pathologies
Trigeminal neuralgia is a disease that causes sharp pain in different parts of the face. It all depends on which branch is affected (there are three of them). Unpleasant symptoms may intensify when chewing, talking, pressing on the face, or brushing teeth. In addition to the trigeminal nerve, pain near the ear can provoke damage to other nerves:
- wandering;
- glossopharyngeal;
- occipital
Arteritis, in which acute pain appears due to muscle spasms, can provoke malaise. Deformation is visually observed, and compaction is visible on the x-ray. Characteristic symptoms include swelling and redness of the affected area. Pain in the jaw, which radiates to the ear area and other areas of the face, may indicate diseases of the brain, in particular, circulatory disorders of this organ.
Painful sensations near the ear can be the result of damage to blood vessels, for example, the carotid artery. In this case, the neck, jaw and facial part are affected.
Oncological factor
As cancer develops, pain often appears on the right side. The tumor can be malignant or benign. In the first case, the nerve endings first lose sensitivity, and numbness of the face appears. After this there is pain in the jaw. In the second case, unpleasant sensations in this area are also observed. A lump appears near or behind the ear - a consequence of the growth of a lymph node. In this case, it is important to take measures to prevent an inflammatory or purulent process from starting. In addition to pain near the ear, other symptoms associated with a benign tumor include:
- deterioration of general condition;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- redness of the tumor.
If suppuration occurs, this already poses a danger to the patient’s life. Lack of proper care can lead to infection entering the bloodstream.
Prevention
Based on what was written above, we can conclude that painful sensations when opening the mouth do not just arise. They are a manifestation of dangerous illnesses. To prevent this phenomenon from occurring, it is necessary to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air, exercise your jaw, and strengthen the immune system. It is also recommended to respond in a timely manner to disruptions in the body, even minor ones, and undergo preventive examinations from specialized specialists. As mentioned above, a crooked bite can cause pain when opening the mouth. Therefore, this pathology must be eliminated at an early age. The price of veneers is quite affordable, and their installation does not take much time and is carried out by experienced specialists in a dental office.
Possible complications
If an unpleasant symptom occurs, you should immediately contact your dentist. You should not postpone your visit, since the problem itself will not disappear, but may only get worse. Only a specialist can tell you what to do. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, a computed tomography scan is prescribed. If the doctor excludes the presence of dental problems, the patient will be referred to another specialist (neurologist, oncologist, phlebologist, etc.). Lack of help for muscle tension can lead to the following problems:
- the appearance of back pain;
- dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- blurred vision, pain in the eyes;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- depressive state.
If the discomfort is accompanied by congestion in the ear, there is a risk of partially or completely losing hearing. When the jaw does not open completely, it shifts. It becomes painful to chew. After some time, problems with teeth arise, enamel wears off, and sensitivity increases.
Inflammation
The inflammatory process (furuncle, osteomyelitis, abscess, phlegmon, etc.) on the skin of the lower jaw, oral mucosa, soft tissues of the cheek can involve the joint and masticatory muscles. Such conditions require urgent intervention.
Causes of pain
Impaired mouth opening is associated with the involvement of the joint, muscles or nerves that allow the mouth to open. Another reason is that when moving in the joint, the position of the inflamed tissues changes.
The nature of the sensations and accompanying symptoms
The pain is constant, sharp, twitching. Associated symptoms include fever, swelling of the face on the affected side, enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw and on the neck, and decreased jaw mobility.
If there is inflammation under the skin, the skin becomes hot and thins. A boil on the face (more common in men) is clearly visible.
Treatment methods
Purulent inflammatory processes are treated surgically. The doctor opens the affected area, washes it with antibiotics, and leaves a drainage to drain the pus. The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, regular dressings, and washing of the postoperative wound with antiseptic solutions.
How to eliminate jaw pain near the ear
Identifying the causative factor allows you to determine how to treat the pathology. Possible actions of the doctor:
- Dental problems require sanitation, which eliminates any sources of infection.
- For bruises, use cold compresses. A dislocation requires a visit to a surgeon who will realign the jaw. For fractures with bone displacement, surgery is performed. The patient is prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory external agents.
- In case of an abscess, the abscess is opened and antibiotics are prescribed.
- Oncology involves the use of surgical techniques, radiation and chemotherapy.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes are stopped with the help of antibiotics, compresses, and mouth rinses. Sometimes surgical treatment is required.
Also, depending on the provoking factors, different methods of physiotherapy are used: microwave, UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, diadynamic therapy.
Diagnostic methods
For effective treatment, it is important to determine the exact cause of the headache and facial area. It is impossible to carry out diagnosis on your own, since it requires the use of precise equipment and laboratory tests. The complex may include the following activities:
- blood tests - prescribed to determine inflammatory processes, bacterial infections and various diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- X-ray is one of the examination methods for suspected diseases of the teeth and temporomandibular joint;
- MRI, CT scan of the brain;
- ophthalmological examinations aimed at diagnosing vision and measuring intraocular pressure;
- assessment of the condition and conductivity of the vessels of the neck and head - carried out by radiography using a contrast agent.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers headache diagnostic programs. The set of measures is selected individually, based on the results of the inspection. To obtain accurate data, it is important to notify the doctor about all conditions for the occurrence of pain, their nature and intensity, and also undergo the prescribed examinations.
Pain when opening a child's mouth
The peculiarity of pain in children is that the child can rarely describe the symptom in detail, as well as assess its severity. In addition, children often tend to hide from adults if they are in pain, especially if they are afraid of doctors.
Parents should pay attention to the following features:
- The child began to speak slurredly and reluctantly;
- It is painful or impossible to open your mouth wide;
- Does not eat well, tries to avoid chewing food;
- There is noticeable swelling on one side of the face;
- The baby holds on to the ear or jaw and constantly touches them.
These signs can indirectly tell parents that the baby has a sore jaw.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Pain syndrome is relieved with analgesics. The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account the cause of the symptom. The following methods are used:
- Dental diseases
. For alveolitis, wash the hole with hydrogen peroxide or nitrofural, apply applications with anesthetics and analgesics. For pulpitis and periodontitis, the tooth cavity is treated and disinfected, regenerating and anti-inflammatory pastes are used, pain is eliminated with analgesics, and antibiotics and sulfonamides are prescribed to combat inflammation. - Traumatic injuries
. A conservative method of treating fractures of the upper jaw is the application of dental splints connected to a horseshoe-shaped bracket in the forehead area. To immobilize the alveolar process, a splint-bracket made of aluminum wire is used, fixed to the teeth using a light-curing composite and adhesive material or metal ligatures, if necessary, in combination with a chin sling. - Purulent processes and ENT pathologies
. Patients are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics; after a bacteriological examination, the drug is replaced taking into account sensitivity. Additionally, immunocorrectors, detoxifying, anti-inflammatory, and antihistamines are used. Local treatment includes rinsing and dressings. - Ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion
. To reduce pain, the nasal cavity is lubricated with dicaine, and turundas with novocaine are administered. In severe cases, ganglion blockers and ganglion blockades with anesthetics are recommended. Local administration of hydrocortisone is effective. Medicines with antiallergic and restorative effects are indicated.