What does bitterness in the mouth mean after eating or in the morning: causes and treatment
Bitterness in the mouth is a fairly widespread phenomenon, many people are familiar with it. This is especially true for those who suffer from pathologies associated with the gallbladder, liver, bile ducts, and organs of the digestive system. Why does this symptom occur?
The causes of altered taste are often spicy, fatty, spicy foods, and medications used over a certain period of time. A person suffering from congenital problems with the bile ducts also “puts up” with the taste of bitterness. Constant bitterness in the mouth (and not only after eating) indicates the presence of a serious disease that requires correct diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Bitterness in the mouth - what does it mean?
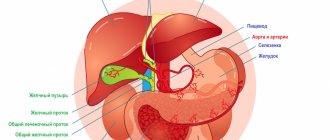
The main cause of a bitter taste in the mouth is the reflux of bile into the esophagus, which occurs when the liver, gallbladder and biliary tract are not functioning properly. Bile is a digestive fluid that is produced by liver cells and accumulates in the bladder. Here it is not only stored, but also “ripens” and acquires a full acid-salt composition. After “ripening,” the bile enters the duodenum, where it initiates the digestion process.
Bile secretion has a characteristic bitter taste. Healthy mature bile has a certain composition. In addition to acids and metal salts (sodium and potassium), the secretion contains proteins, phospholipids (fats for building cell membranes), cholesterol, chlorine and calcium ions. An unbalanced composition of bile leads to the precipitation of salts. This is how clots, flakes, sand and stones form in the gallbladder. They impede the outflow of secretions, forming stagnation in the bladder and ducts. In addition, the cause of stagnation is often a spasm that accompanies stress and nervous experiences (fear, hostility, anger, hatred).
Against the background of stagnation, the release of new bile continues, which tends to enter the bladder. The human liver secretes up to 1 liter of bile secretion per day. This creates pressure, which forcefully pushes the stagnant secretion, throwing it into the stomach and esophagus.
When and how often does the bitter taste occur?
From when bitterness appears in the mouth, we can guess what causes this symptom:
- During physical activity, if it is also accompanied by heaviness in the right side, it may be a sign of liver disease.
- In the morning - the reason most likely lies in problems with the liver and gall bladder.
- Only after eating too heavy, fatty foods, after overeating - diseases of the gallbladder, bile ducts, liver.
- Bitterness appears after any meal - diseases of the stomach, duodenum, gall bladder, and some liver pathologies.
- Short-term bitterness in the mouth - during a stressful situation or the use of medications that affect the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
- Constant bitterness in the mouth - a possible cause is cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, endocrine or mental illness.
Lip care
The lip skin care procedure is as follows:
- Using lip balm. It is applied before going outside, and before bed, a moisturizing, nourishing, restoring balm is used.
- Perform exfoliation. Exfoliation is a beneficial procedure, including the skin of the lips. To eliminate peeling and restore microcirculation, lip massage is performed with soft scrubs.
- Applying primer under lipstick. The primer can be replaced with a gentle balm. It is applied in a thin layer and pressed into the skin using your fingertips or distributed over the lips with a brush.
- Proper removal of lip makeup. You should not wash your face with soap. Apply milk or micellar water to a cotton pad.
To cleanse your lips of stubborn lipstick, you should use a nourishing balm. It needs to be applied to the lips in a thick layer and wait 30 seconds. The balm softens the pigment, and then it is removed with a napkin. This method allows you to keep your lips healthy.
Seasonality should also be taken into account when caring for your lips. Then the skin will be healthy and beautiful throughout the year:
- For summer it is better to choose light textures of products. Regular lipstick without balms will do. In hot weather, sunscreen balms are used.
- In winter, in addition to nutrition, moisturizing, and exfoliation, you need to make masks. If a ready-made product is not available, a restorative cream is applied to the lips and left for several hours. Balm for winter should contain glycerin, oils and ceramides.
Appears after eating cedar
After eating pine nuts, even a completely healthy person may experience bitterness in the mouth. Usually this phenomenon is mistakenly attributed to the choleretic properties of the product, but such a reaction cannot occur with high-quality pine nuts.
Meanwhile, bitterness in the mouth appears immediately after eating and lasts for several days; sometimes other symptoms of intoxication may appear - nausea and pain in the liver area. All this clearly indicates that the pine nuts were artificially grown and imported from China. Many suppliers pass off Chinese nuts as domestic products, since they are cheaper to purchase. But there are many reasons why it is better to refuse such a food product.
Features of lip skin
Lip care is an important daily procedure. It is necessary to take care of the skin to prevent many unpleasant phenomena. The number of sebaceous glands in the lip area is reduced, a small number of them are located in the corners. Therefore, in the absence of care, dryness, peeling, and cracks appear.
Dry, chapped lips cause discomfort. Therefore, it is better to constantly maintain skin health than to restore it. There should be several balms in your cosmetic bag, including sunscreen.
The main causes of bitterness
What does bitterness in the mouth indicate? There are actually a lot of reasons why a person begins to feel this. In this way, the body may try to “indicate” diseases of the digestive system or a gallbladder disease. This sensation may also be a sign of poor nutrition or taking medications of various spectrums for too long (mainly those used to treat the liver).
The main causes are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT):
- Diseases of the duodenum. Bile from the duodenum, entering the stomach, causes corrosion of its walls. Bile contains acids that cause a feeling of bitterness.
- Gastritis (see symptoms and treatment of gastritis). With this disease, the composition and amount of gastric juice produced by the body changes, the process is also accompanied by poor digestibility of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other vitamins, and the removal of toxins worsens. Together, this causes heartburn, bad breath, constant belching and, accordingly, an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Gastric dyspepsia. The cause of the bitter taste may be difficult digestion caused by disruptions in the functioning of the stomach.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. This disease provokes surges of concentrated gastric juice to the very top of the esophagus, from where it enters the oral cavity. It can develop due to the abuse of spicy and fatty foods, as well as constant overeating (even healthy food rich in vitamins and minerals - an excess of it is also harmful).
- Disturbances in motor activity of the stomach. With reduced motility of the biliary tract, bile stagnates in them; with increased motility, there are sharp releases of bile into the duodenum, then into the stomach, esophagus and oral cavity, causing bitterness, burning and heartburn.
- Dysbacteriosis. Under normal conditions, a large number of beneficial bacteria live and function in the human intestine, capable of synthesizing vitamins, creating microflora and generally increasing the body’s immune strength. If the intestinal microflora is normal, then no problems are observed, but if an imbalance occurs, then dysbacteriosis appears, causing bitterness in the mouth.
- Giardiasis. A disease caused by the penetration of Giardia (intestinal parasites) into the body, causing disorders in the functioning of the small intestine. Nausea, bitterness occurs, and sleep is disturbed.
Dental diseases:
- Inflammation of the gums, mucous membrane of the tongue. This occurs if a person carelessly takes care of their teeth, and bad breath adds to the bitterness.
- Increased sensitivity to external interventions - implantation of dental crowns, dentures or fillings. The bitter taste is often caused by raw materials for dentures, fillings or gel for fixing an artificial jaw.
Other reasons include:
- If there is liver dysfunction (any disease), then increasing inflammatory processes negatively affect the production of bile and its transportation through the relevant systems of the body.
- Nervous system disorders, in which the peripheral nerves responsible for the taste buds and sense of smell become inflamed, also alter the perception of the taste of food and make it bitter.
- At moments when the level of glucose in the blood rises, vision begins to deteriorate, a feeling of weakness and heat appears in the palms and soles, along with this, a bitter taste becomes very noticeable in the mouth.
- General intoxication of the body, which is observed when it is damaged by heavy metals such as mercury, lead, copper and others.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system lead to the fact that the thyroid gland, together with the adrenal glands, begins to produce huge amounts of adrenaline. As a result of this, the bile ducts narrow, which provokes the release of bile towards the esophagus and the appearance of bitterness.
- Lack of zinc - an important trace element that is necessary for the normal functioning of cells and taste buds in particular.
- Smoking for many years. Long-term exposure to tobacco and its derivatives has a detrimental effect on the taste buds, as a result of which the smoker begins to feel an unpleasant bitterness.
Causes of bitterness in the mouth while eating
Sometimes you feel a bitter taste in your mouth while eating. When this phenomenon is one-time in nature, the cause may be the type and method of cooking.
But what to do if the bitterness in the mouth becomes chronic? First, you should consult a doctor. He will be able to determine what disease such a symptom relates to and then prescribe treatment. The main causes of bitterness in the mouth while eating are:
- Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the gallbladder, which is accompanied by painful sensations in the side, dry mucous membranes, and high body temperature.
- Dysfunction of internal organs. Diseases of the digestive organs, liver, kidneys, gall bladder.
- Poor nutrition. It is not recommended to eat fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods, soda, and fast food. As a result of their consumption, a feeling of bitterness may occur.
- Acid reflux, vomiting aftertaste. The cause of bitterness is gastric juice, which from the stomach begins to rise through the esophagus to the oral cavity.
- Disturbance of taste buds. The receptors that are responsible for the perception and recognition of taste stop working. All products that a person consumes do not differ in taste for him. This occurs due to excess amounts of phenylthiocabamide in the body.
- Hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy.
- Dental diseases of the teeth, gums, the body’s reaction to a filling or crown.
- Violation of acid-base balance. Accompanied by lethargy, muscle fatigue, joint pain.
If such a symptom appears after eating, it is recommended to adhere to the rules of a healthy diet. Avoid eating fatty, fried, salty, bitter, sour foods, soda, sweets, and baked goods. It is advisable not to convey that food should be easily processed and absorbed by the body.
Food poisoning and bitter saliva
Foodborne toxic infection is very often accompanied by a taste of bile due to general toxicosis of the body and malfunctions of the digestive system. This includes vomiting bile and bile reflux. Often, after poisoning, a person temporarily lacks appetite. Food does not enter the stomach, and bile, despite this, is produced by the liver around the clock. It stagnates and some of it is thrown into the stomach and esophagus.
It takes time to normalize the functioning of the digestive tract after the symptoms of poisoning disappear. Then the unpleasant taste sensations will pass.
Bitterness in the mouth in the morning
It is not possible to determine the cause of bitterness in the mouth by one symptom, because the causes of this symptom can be various dysfunctions of internal organs:
- Overeating before bed.
- Reaction of the gastrointestinal tract to foods: salty, fatty, bitter, fried foods, spices, nuts.
- Disruption of the gallbladder. There is a failure in the production and excretion of bile as a result of the manifestation of diseases such as cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, congestion, and neoplasms.
- The material was chosen incorrectly or the prosthesis, crown, or filling was made. The result is bad breath.
- Diseases and dysfunctions of the digestive organs.
- Intestinal dysbiosis, which occurs after taking antibiotics.
- Diseases in the oral cavity, teeth, gums, white coating on the tongue.
- Bad habits: smoking, alcohol.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Liver dysfunction: jaundice, cirrhosis, hepatitis.
- Unstable psycho-emotional state: stress, neurosis, depression.
- Kidney disorders.
- Pathologies of ENT organs.
- Intoxication of the body with metals: lead, mercury, copper.
- Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine dysfunctions.
Liver inflammation
The symptoms and treatment of liver inflammation are interrelated. When the disease occurs, belching, heartburn, nausea, fever, change in urine color, and severe sweating appear.
You should consult your doctor about the symptoms and treatment of liver inflammation (hepatitis). Bitterness arises from the production of bile by liver cells, which penetrates the intestines and then rises up the throat. Pathology is indicated by yellowing of the skin and coating on the tongue. This disease requires effective treatment, which will be prescribed by a doctor based on diagnosis. Self-medication can lead to negative consequences.
Constant feeling of bitterness
When a bitter taste in the mouth appears regularly, this indicates serious disorders and diseases. If you experience persistent bitterness, you should urgently visit a doctor who will help determine the diagnosis of the condition. A regularly occurring bitter sensation in the oral cavity may be a sign of cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine or mental.
Diabetes
This is a disease of the endocrine system, which is based on a deficiency in the formation of its own insulin and an increase in blood glucose levels.
With this disease, a symptom such as bitterness in the throat is likely to appear. If you have diabetes, you must constantly be under the supervision of a doctor. Depending on your health condition, treatment may be adjusted.
Bitterness in the mouth during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes such dramatic changes, both hormonal and physiological, that the appearance of any unusual taste or other strange symptom should be perceived as normal. In the 1st trimester, an increase in progesterone has a relaxing effect on the valve separating the esophagus and stomach, so acid and bile can enter the esophagus, causing a bitter taste, nausea, and vomiting.
In the later stages, heartburn and a bitter taste cause a woman very strong discomfort, this is explained by the growth of the fetus and its pressure on the gallbladder and stomach; this symptom haunts the pregnant woman until childbirth. To reduce the frequency and intensity of this unpleasant manifestation, a woman should adhere to a certain diet - exclude fried and fatty foods, coffee, sour and spicy foods, eat little and often, avoid drinking liquids during meals, and drink only in between meals.
Diagnostics
It is important to know that independently determining the cause and choosing treatment methods is strictly prohibited, since incorrectly selected drugs can only harm the body. The fight against this manifestation should begin and continue only after a specialist makes an accurate diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing this symptom:
- Blood tests: general and biochemical - help to identify the presence and degree of the inflammatory process, evaluate liver function, parameters of fat and pigment metabolism.
- Analysis of stool for the bacteriological composition of intestinal flora - detects dysbiosis.
- Fecal analysis (coprogram) - reveals disturbances in the digestion of food, provides information about the possible presence of parasites in the intestines.
- X-ray of the abdominal organs - prescribed to identify stones in the ducts and possible calcification of the pancreas.
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system (ultrasound) is an extremely informative method for diagnosing pathologies of the liver, gallbladder and ducts. With its help, you can determine the parameters and location of the gallbladder, bile stagnation, the presence of stones, neoplasms, and polyps.
- Computed tomography of the abdominal organs - with its help you can examine any area in the peritoneum layer by layer and assess the extent of organs affected by pathological changes.
- Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy) is carried out to check for the presence of concomitant diseases and for differential diagnosis.
- Immunogram and analysis for tumor markers - given if a malignant process is suspected.
Does COVID-19 therapy affect the liver?
In addition to the toxic waste products of the coronavirus, the liver is also subject to serious stress during treatment of the infection. The drugs used to treat COVID-19 have a fairly strong hepatotoxic effect.
In addition, some patients have various chronic diseases, for example, tuberculosis or neoplasms, which significantly aggravate the situation. In this regard, doctors, when developing a treatment plan for coronavirus disease, focus on mandatory hepatoprotective therapy if the patient has signs of liver damage.
The European Societies for Infectious Diseases and the Study of the Liver also adhere to this position and recommend that patients with signs of liver damage from COVID-19 continue treatment under the close supervision of doctors. During therapy, hepatoprotectors and essential phospholipids are used, which will restore the parenchyma and reduce the clinical manifestations of the pathology.
How to remove bitterness in the mouth, the cause of which has not been established?
If the cause of bitterness in the mouth is not determined, it is recommended:
- Frequent meals in small portions are effective for women in late pregnancy, in whom bitterness is caused by the pressure of the fetus on the digestive organs;
- Smoking cessation or restrictions – if bitterness is caused by disorders of the taste buds due to constant exposure to tobacco smoke;
- Taking probiotic medications to normalize the microflora and cleanse them from parasites is an effective method if the bitterness is caused by a parasitic invasion, as is the case with giardiasis;
- Detoxification of the body and cleansing of the intestines with the help of sorbents - helps with bitterness caused by food poisoning;
- A diet that excludes fatty and heavy foods, as well as spices, spicy, smoked foods - helps if a bitter taste in the mouth appears due to indigestion;
- Normalizing sleep and rest patterns, eliminating stress factors, playing sports and walking in the fresh air - if bitterness accompanies neurological pathologies and mental disorders.
Bitterness in the mouth cannot be treated at home with the help of medications, since this is not a disease, but just one of the symptoms of body disorders, each of which requires an individual approach to treatment.
1.General information
Modern medicine knows a monstrous, incalculable number of clearly defined and described symptoms, i.e. objective signs of a particular disease. At the same time, with the accumulation of statistical data and research results, as well as with the development of the theoretical paradigm, the number of symptoms classified as pathognomonic (this term implies an unambiguous sign that is always observed in a given disease and is not found in any other diseases) is rapidly and steadily decreasing. The tendency to blur the informativeness of diagnostic signs is to some extent promoted by both pathomorphosis (changes in the typical clinical picture of diseases over the years and decades), and the tendency of modern man to self-medicate, which often “blurs” or distorts the symptoms.
There are almost universal symptoms that accompany most known diseases - for example, headache or “general malaise”, i.e. decrease in subjective well-being. Based on these complaints alone, it is impossible not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but even to suggest the field to which it will relate (neurology, endocrinology, virology, and many others). Other symptoms seem to more clearly indicate the most likely source of the problem, but upon closer examination it turns out that not everything is so simple here either. Such “understandable” but sometimes very misleading symptoms include, in particular, bitterness in the mouth.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!