If a person feels pain in the jaw, radiating to the ear and temple, we may be talking about arthritis of the mandibular joint. The pathology is not just painful, but also dangerous. If not diagnosed in a timely manner, it can lead to severe complications, including paralysis of the facial nerves. Therefore, the first thing to do when such symptoms appear is to consult a specialist. In 10-18% of cases, diagnosis and treatment of TMJ arthritis is the responsibility of dentists and occurs in people from 25 to 45 years old.
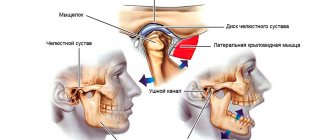
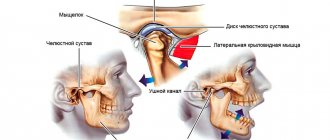
What is the temporomandibular joint - TMJ
We use this joint while talking, chewing, yawning, laughing - very often. Around it are muscles and tendons that allow the jaw to move in different directions for different purposes.
TMJ problems occur for many reasons:
- violation of the dental system, for example, congenital anomalies of teeth, gums or bone tissue, malocclusions, injuries, poor-quality prosthetics;
- congenital anatomical abnormalities of this joint;
- increased or decreased tone of muscle fibers around the TMJ;
- active conversational load, for example, among actors, singers, speakers;
- central nervous system problems;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- excessive tension of the jaw muscles, for example, due to the bad habit of biting nails.
What is the temporomandibular joint and why do problems arise with it? Detailed and clear - in the video:
Actors and singers with active oratorical articulation are at risk for TMJ arthrosis
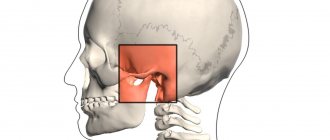
Why does TMJ hurt?
If muscle pain can also occur for natural reasons, then the appearance of unpleasant sensations when chewing food or moving the lower jaw always indicates a dysfunction of the joint. This condition causes not only physical, but also psychological discomfort. In the absence of medical intervention, diseases or injuries of the TMJ provoke disruption of the functioning of other human vital systems. For example, as a result of poor grinding of food, serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract can develop.
Injuries
Typically, a person suffers TMJ injuries from a blow or fall. With minor injuries, pain in the joints is felt for 1-2 days, and then disappears without a trace. But if their intensity does not change or increases, then this indicates serious injury to one or more structures of the temporomandibular joint:
- rupture of the synovial bursa;
- ligament rupture or complete separation from the bone base;
- formation of a crack in the lower jaw bone;
- fracture of the lower jaw;
- hemorrhage into the joint cavity.
Dislocation of the mandibular joint is one of the causes of pain.
With any of these injuries, there is a high probability of developing an acute inflammatory process and its spread to healthy tissue.
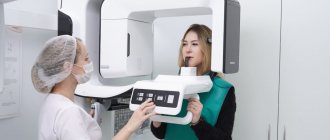
The type of damage is determined by a traumatologist only after studying radiographic images, since their clinical manifestations are very similar. The pathological focus concentrates bioactive substances - inflammatory mediators, serotonin, histamine. Under their influence, blood vessels dilate, and excess fluid from the blood accumulates in the intercellular space. The lower jaw swells, a hematoma or small pinpoint hemorrhages forms on it. The victim deliberately limits his movements so as not to experience sharp or aching pain. Sometimes the skin in the area of injury turns red and becomes hot to the touch.
Infections
The risk of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the TMJ is much higher in the presence of teeth affected by caries - the process of demineralization and destruction of hard tissues with the formation of a cavity defect. Inflammation occurs, clinically manifested by swelling and pain. Pathogenic bacteria enter the joint in several ways:
- straight. Infection occurs as a result of injury - a fracture, bruise with the formation of a hematoma, a knife or gunshot wound. In most cases, inflammation is provoked by microorganisms located on the surface of the skin: Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, streptococci;
- contact. Bacteria enter the joint from nearby infected bone, cartilage, soft tissue, ligaments or tendons. The most common cause of pain in the TMJ is the penetration of microbes from the salivary glands, ears, mouth, facial skin, and hair follicles. Purulent inflammation of the joint is possible with furunculosis, osteomyelitis, otitis media, mumps;
- hematogenous. Scarlet fever, acute tonsillitis, tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, as well as pathologies of the genitourinary system can provoke damage to the temporomandibular joint by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi. Particularly dangerous is sepsis, which occurs as a result of the penetration and spread of microorganisms in the bloodstream.
Only antibiotic therapy will allow you to get rid of pain in the lower jaw.
In addition to antibacterial agents, the patient is prescribed drugs to eliminate symptoms. When the TMJ is infected, signs of general intoxication often occur due to the entry of bacterial waste products into the systemic bloodstream. In addition to joint pain, a person suffers from fever, neurological and dyspeptic disorders.
Joint diseases
The development of inflammatory or degenerative-dystrophic pathology of the TMJ is directly indicated by an increase in the severity of pain over several months or years. The danger of joint diseases lies in the absence of any symptoms in the initial stages. A person does not take into account mild discomfort, especially since they quickly disappear. Therefore, the patient often consults a doctor with persistent pain that occurs as a result of irreversible changes in the joint structures.
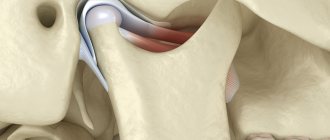
Arthrosis of the TMJ.
Many TMJ pathologies respond quite well to treatment at the initial stage. But if the disease is diagnosed at stages 2 or 3, then the main tasks of doctors are to weaken the clinical manifestations and prevent the spread of the degenerative or inflammatory process to neighboring, healthy tissues. Therefore, even mild pain in the temporomandibular joint should be a signal to determine its cause.
| Pathologies whose characteristic symptom is pain in the TMJ | Reasons for the development of the disease | Characteristic symptoms |
| Arthrosis | Previous injuries, systemic inflammatory pathologies, increased joint loads, circulatory disorders, endocrine and metabolic disorders | Pain that intensifies when chewing food, occurring even at rest, gradually increasing stiffness of movements, a decrease in their volume, morning swelling of the lower jaw |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Impaired immunological responses, infection with Epstein-Barr viruses, retroviruses, cytomegaloviruses, mycoplasmas, herpes virus, rubella | Bilateral symmetrical damage to the temporomandibular joints. Fatigue, weakness, asthenia, joint pain, excessive sweating, elevated body temperature, morning stiffness |
| Reactive arthritis | Genetic predisposition to a hyperreaction of the immune system to microbial agents of intestinal and urogenital infections against the background of decreased immunity | Watery eyes, redness and pain in the eyes, frequent urination, pain in the TMJ, swelling, increased local and (or) general body temperature, swelling, local hyperthermia, redness of the skin |
| Gout | Metabolic disorders that provoke the accumulation of uric acid and its derivatives - acid urate salts, excess weight, abuse of fatty foods and alcohol | Pain in the joints, often in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the 1st toe, a slight increase in general temperature, swelling, shine and hyperemia of the skin over the joints, disruption of their functions |
How to understand what is bothering you with TMJ: 4 obvious signs
If you feel discomfort while talking, chewing, or yawning, look out for these signs:
- Are there any clicks or popping sounds during jaw operation (only 20% of people who notice this symptom complain of pain, however, this is a reason to suspect arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint and go for a diagnosis);
- Is there a feeling of jamming of the joint (if the fossa and the articular head are not in perfect contact, you have to open your mouth as much as possible, trying to find the right point);
- How severe is the pain (can occur when chewing, radiate to the temples, under the tongue, ears, neck, sternoclavicular region);
- Has your general health changed (headache and dizziness, insomnia, hearing impairment, depression and other uncharacteristic manifestations are possible).
With TMJ dysfunction, some patients develop snoring
Diagnostics
To find out what may be causing your jaw pain, you must immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
List of sources
- Isaykin A.I., Smirnova D.S. Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint // RMJ. 2022. No. 24. pp. 1750-1755 https://www.rmj.ru/articles/bolevoy_sindrom/Disfunkciya_visochno-nighnechelyustnogo_sustava/#ixzz6EmX7dOtR (access date: 02/23/2020).
- Dentistry. Textbook Aleksandrov M.T., Bazhanov N.N., Medvedev Yu.A., Platonova V.V., Sergeev Yu.N. / Ed. N.N. Bazhanova. - M.: GEOTAR, 2008.
- Gingivitis and Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease) // WebMD Medical Reference Reviewed by Michael Friedman, DDS on March 17, 2019 https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/gingivitis-periodontal-disease#1 (access date : 02/23/2020).
- Fedorova I.N. Bruxism. Unsolved problem. – Moscow, 2009, pp. 1-2.
- Bezzubikova M.V. Dental and somatic manifestations of bruxism syndrome // BMIK. 2022. No. 2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/stomatologicheskie-i-somaticheskie-proyavleniya-sindroma-bruksizma (date of access: 01/31/2020).
- Why Your Jaw Hurts // WebMD Medical Reference Reviewed by Alfred D. Wyatt Jr., DMD on March 21, 2022. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/why-your-jaw-hurts#1 (date access: 01/30/2020).
- Gaifullina R.F., Kim Z.F. and others. Infarction-like myocarditis: difficulties and solutions in diagnosis // Bulletin of modern clinical medicine. 2022. No. 1. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/infarktopodobnyy-miokardit-trudnosti-i-puti-resheniya-v-diagnostike (date of access: 02/23/2020).
Treatment tactics
If there is no arthrosis, but there is dysfunction, the tactics are as follows:
- determine the root cause and eliminate it, for example, grind teeth and fillings that impede the functioning of the joint, correct prosthetic errors, and correct the bite;
- reduce the load on the joint - the patient is recommended to switch to soft foods, massage the facial muscles and exercises to relax the jaws;
- if the defects are serious, surgical treatment is performed - bone or muscle plastic surgery of the area of dysfunction.
If the doctor determines degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue, treatment for osteoarthritis will be prescribed. With the help of painkillers, they relieve pain. If necessary, a complex of physical therapy is prescribed, for example, laser or ultrasound. Good results are achieved by intra-articular injections of the Noltrex synovial fluid prosthesis, which restore the functionality of the joint by replenishing the missing lubrication.
Arthrosis of the TMJ is successfully treated with intra-articular injections of Noltrex
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
The earlier the diagnosis is made, the more favorable the prognosis. So seek help if:
- you experience pain in the lower jaw - intense or mild;
- you cannot fully move your jaw, you feel limited;
- hear a painful clicking or crunching sound when opening and closing your mouth;
- pain and noise in the ears appeared (especially if the otolaryngologist did not find any pathologies);
- There was a feeling of incomplete bite.
Arthrosis of the TMJ is not a very common phenomenon, but quite dangerous. Our usual comfort during conversation, eating, and other household activities is at risk. To avoid this, do not attribute alarming symptoms to fatigue and do not rely on “it will go away on its own”: be sure to find time for yourself and your health!
Classification of TMJ arthritis
The nature of the course of arthritis implies the presence of acute and chronic forms. The acute form of this disease is characterized by a serous and purulent course. There is also a classification of TMJ arthritis, depending on the etiological origin:
- traumatic arthritis;
- infectious arthritis (nonspecific and specific);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- other rare forms (reactive arthritis and others).
Specific infectious inflammations of the TMJ include: syphilitic, tuberculous, actinomycotic, gonorrheal, etc.