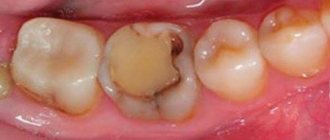
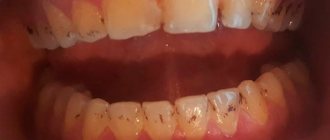
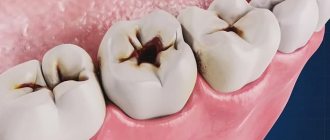
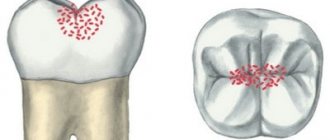
Cemental caries, or root caries, is less common than cervical caries, but is considered more dangerous and destructive to the tooth. The fact is that the root walls are thin and therefore caries destroys them faster and reaches the pulp. Root caries often becomes a complication of cervical caries or occurs as an independent disease. Its official name is cement caries, which indicates the location of the lesion - under the gum. This is precisely the problem. Ordinary caries can be seen with the naked eye by characteristic spots, but root caries is invisible.
Different types of caries: WHO classification
Caries is a slowly occurring pathological process in hard dental tissues, which develops under the influence of unfavorable external and internal factors. According to statistics, this disease occurs in more than 90% of people in the world.
In this article
- Different types of caries: WHO classification
- How does dental caries develop in the root area?
- Features of the progression of dental caries
- Dental cement caries - main clinical manifestations
- Diagnosis of cement caries: basic and additional methods
- Treatment of cement caries: main stages
- Prevention of root caries
According to the classification of the World Health Organization, there are several types of caries: enamel, dentin, cement, as well as suspended, other, unspecified caries, and odontoplasia. In this article we will talk about dental cement caries, better known as tooth root caries.
Preparation and filling
Once the pathological process has spread to dentin, it is impossible to do without a drill. In this case, the doctor assesses the size of the carious cavity using an x-ray. Then he carries out treatment according to the classical scheme:
- applies local anesthesia to numb the affected area;
- treats the carious cavity with a dental bur to remove the affected tissue;
- installs a protective seal to isolate the pulp;
- restores the natural shape of the crown by filling.
Treatment of deep carious lesions can be carried out in two to three visits.
How does dental caries develop in the root area?
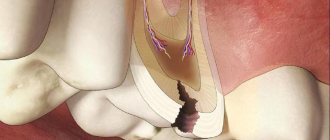
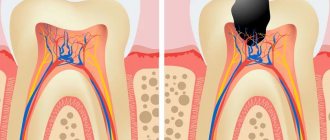
A tooth consists of a visible crown, neck and root. The crown is the visible part that is located above the gum. The neck is located lower and covered with soft gum tissue. The area where the root, or cementum, of the tooth is located is the alveoli (the depressions in the upper and lower jaws).
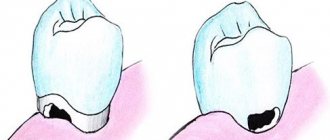
Root caries can develop as an independent dental disease or as a complication of cervical caries. It is considered more dangerous for the tooth because it reaches the pulp faster. With cement caries, the lesion is usually located under the gum, it is not noticeable during external examination, and therefore is more difficult to diagnose.
The main cause of root caries is usually inflammation or gum disease. With this pathology, the gum does not adhere tightly enough to the tooth, resulting in the formation of a periodontal pocket where food debris and plaque accumulate. Gradually it hardens and turns into tartar, which provokes carious lesions.
Other risk factors for developing root caries are:
- cariogenic bacteria in dental plaque are one of the leading risk factors that leads to periodontal diseases (the tissues surrounding the tooth) and, as a result, exposure of the root surface;
- carbohydrate foods that serve as a breeding ground for bacteria;
- insufficient intake of fluoride into the body;
- impaired characteristics of saliva;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- features of the anatomy of the dental system;
- critical pH (approximately 6.2 - 6.7);
- cervical caries, which gradually moves to the tooth root;
- violation of crown installation technology, as a result of which the gums recede and expose the root.
Some researchers also name low resistance of teeth to carious lesions, endocrine diseases, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as possible risk factors for root caries.
Deep root caries is usually called elderly caries because it most often develops in people over 45-50 years of age. This is due to age-related changes in the oral cavity, decreased immunity, and loss of hygiene skills. Together, this leads to the active proliferation of microbes in the oral cavity, which provoke carious lesions of the tooth root.
Advantages of visiting the clinic "Kariesu.net"
In any clinic in our network you will be provided with professional assistance for various types of carious lesions. Doctors at our clinics provide treatment with minimal invasive intervention. Local anesthesia is used to maintain the patient's comfort during manipulations.
You can find out how much it costs to treat dental caries in our clinic by calling or visiting a dentist. The doctor will conduct an examination, make a diagnosis and tell you the exact cost. Make an appointment with a dentist at our clinic by phone or on the website.
Features of the progression of dental caries
In the area of cement, caries can occur in different ways, and on this basis it is classified into 4 types:
- progressive;
- rapidly progressive;
- remission;
- relapse.
Progressive root caries is characterized by a relatively slow rate of tooth root destruction. With rapidly progressing lesions, the lesion spreads in depth and breadth at high speed. The remission stage is when root cement caries does not progress. Relapse suggests that root caries develops along the edges of a previously placed filling.
Dental cement caries - main clinical manifestations
At an early stage, there may be no symptoms of cement caries at all, making early diagnosis difficult. When a cavity grows, the following symptoms may appear:
- Discomfort while eating.
With root caries, mobility of the damaged tooth is often observed, which causes discomfort while eating. In addition, minor pain can result from food particles getting into the gum pocket or directly into the carious cavity.
- External defects.
If caries spreads from the root upward to the cervical area, during the examination the dentist may detect visible changes in the color and structure of the tooth.
- Pain.
It can appear when the tooth is exposed to cold or hot, or when eating salty, sweet, or sour foods. It is impossible to detect root caries on your own, so you need to visit the dentist twice a year. This is especially important for older people and those with gum disease. In such patients, root caries and deep caries are quite common.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for treatment of the disease are both visual and tactile; these include:
- color change, enamel pigmentation;
- painful reaction to hot or cold, sweet or salty;
- enamel chipping;
- darkening of the cervical segment;
- carious cavity;
- a dark gap located along the border of the filling.
There are also contraindications to caries treatment:
- acute respiratory diseases;
- first and third trimesters of pregnancy;
- acute stage of periodontal disease, which is accompanied by severe bleeding of the gums;
- herpes in the acute stage.
Diagnosis of cement caries: basic and additional methods
Diagnostic methods that help identify dental caries are divided into basic and additional.
The main ones include:
- patient interview;
- external visual inspection;
- probing - determining the depth of the cavity, as well as the density and tenderness of tissues, using a dental probe;
- percussion (tapping on the tooth).
Additional diagnostic methods are:
- staining with a special dye to see the affected areas;
- thermal test - the tooth is irrigated with cold water and the pain reaction is assessed;
- radiography - helps to detect hidden carious cavities and caries of contact surfaces;
- electroodontometry - prescribed to determine the condition of the pulp;
- luminescent method - illumination of teeth with ultraviolet rays, under which tissues affected by caries change their shade.
Root caries itself is most often diagnosed through sequential manipulations:
- remove deposits from under the gums using ultrasonic and manual instruments;
- isolate the tooth root from saliva using a special plate;
- using a probe, assess the condition of the root surface;
- with the help of x-rays or radiovisiography, even small defects under the gum, in the gingival zone, and carious lesions at any stage are detected;
- if necessary, confirm the diagnosis of “cemental caries” or differentiate it from pulpitis, thermometry or electrical odontometry is prescribed.
Treatment
After making a diagnosis, determining the type and stage of caries, the doctor determines a treatment plan for this disease. Modern dentistry uses various methods. At the stain stage, it is enough to remineralize the enamel by saturating it with fluoride and calcium. First, the doctor removes the soft plaque and isolates the gums. Then he applies special preparations to the enamel.
Also, in the initial stages, other conservative methods of therapy can be used:
- Infiltration. A minimally invasive treatment method in which the enamel is etched and then its pores are sealed with a special material.
- Ozone therapy. The carious lesion is treated with a special dental instrument that supplies ozone.
- Air abrasive processing. The carious cavity is cleaned of diseased tissues with a powerful stream of air and water with small particles of a special powder.
After treating the carious surface at the superficial stage of the disease, it may be necessary to restore the shape of the crown with a filling. As a rule, the cost of treating dental caries using conservative methods is higher than using a drill.
Treatment of cement caries: main stages
With root caries, the most difficult task is to gain access to the affected area, especially if the carious lesion is located under the gum. Traditionally, treatment of root caries takes place in several stages:
- Retraction. First, the dentist artificially exposes the neck of the tooth and part of the root, lowering the gums with special devices.
- Coagulation of the gums. It is carried out if indicated using laser exposure to gum tissue. The essence of the manipulation is to remove overgrown tissue.
- Direct treatment of caries. The choice of tactics depends on the degree and depth of the lesion. If caries is in the initial stage of the stain, then remineralizing therapy will be sufficient - restoring the mineral composition of tissues with the help of fluoride preparations. If the doctor reveals more extensive and deep caries with the formation of a cavity, then surgical treatment with preparation and filling will be required.
- Installation of an inlay or crown if the volume of destroyed tissue is more than 50%.
It is necessary to treat cement caries only in a trusted clinic with a reliable specialist, since violation of treatment technology and the use of low-quality materials can cause secondary caries, provoke the development of infection and inflammation of the gums, and lead to tooth loss.
What determines the choice of filling?
Fillings are divided into temporary and permanent. Temporary fillings are also called diagnostic fillings. They are used to identify symptoms that will define the disease.
If not only the tooth structure is damaged, but also deeper layers, then a temporary filling helps diagnose the disease.
A permanent filling is used for completely different purposes and its quality is significantly different from a temporary one. The purpose of a permanent filling is to hermetically seal the tooth opening and for aesthetic purposes.
Fillings can be made of different materials, depending on the purpose. There are fillings: cement-based, plastic, amalgam, ceramic, etc. The dentist will determine which filling is right for you during a consultation.
Prevention of root caries
The following preventive measures will help reduce the risk of root caries:
- Maintaining oral hygiene. In addition to brushing your teeth, it is important to pay increased attention to careful and thorough gum care and high-quality cleaning of periodontal pockets. For this purpose, it is convenient to use irrigators, which with a powerful stream of water remove food debris even from under the gums, massage the gums, helping to strengthen them.
- Timely treatment of gum disease, as this is one of the main causes of root caries.
- A rational and balanced diet with a minimum amount of fast carbohydrates and a large amount of vitamins and minerals.
- Limited consumption of hard foods that can injure the gums.
- Regular visits to the dental clinic at least twice a year.
Following simple preventive measures will help prevent root caries and maintain dental health even in old age.
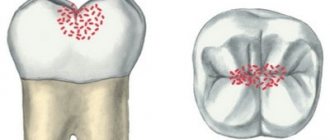
Stage 1: White spots
The first stage of tooth decay begins when chalky white patches appear on the surface of the tooth due to calcium loss and plaque accumulation. These areas are caused by plaque bacteria metabolizing sugars from the food consumed. Bacteria produce acid as a product of the metabolic process. The accumulation of these acids causes the destruction of tooth enamel, a process called demineralization of the tooth surface. At this stage, tooth decay may still be reversible with proper treatment, which should be discussed with your dentist, such as using appropriate brushing techniques, fluoride toothpaste, and topical fluoride treatments. One of the best ways to prevent plaque buildup is to brush your teeth at least twice a day using stannous fluoride toothpaste and an electric toothbrush.