How does a bitter taste in the mouth occur?
The taste in your mouth doesn't have to be overtly bitter; it can feel metallic, sour, or just plain unpleasant. Usually its appearance is associated with certain conditions:
- immediately after eating (if you overeat or eat certain foods);
- after taking medications, especially if a person takes them on an empty stomach;
- after physical activity;
- immediately after waking up.
Bitterness is felt as a foreign, strong, unpleasant taste that comes from the oropharynx or has no obvious source. It may be part of a symptom complex. Along with a bitter taste, the following may appear:
- heaviness in the side;
- abdominal pain;
- white coating on the tongue;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- dry mouth or, on the contrary, excessive salivation;
- dizziness;
- bloating;
- bleeding gums;
- cold symptoms (sore throat, cough, fever, weakness);
- decreased appetite;
- deterioration of smell and other symptoms.
By exactly when bitterness appears and what other symptoms arise, one can judge the causes of the condition. To make a diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and describe to him in detail how you feel.
Why does the bitter taste appear?
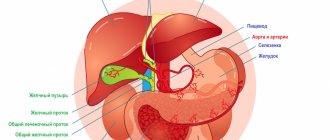
A bitter taste in the mouth appears due to the reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach or esophagus and oral cavity.
This feeling is troubling not only because of gastrointestinal diseases. The reason may be the presence of an infection in the body, exposure to medications, insufficient oral hygiene, during pregnancy, due to a lack of vitamins, an excess of fried heavy foods, alcohol, and coffee drinks. Gum disease is accompanied by a feeling of taste in the mouth due to the growth of bacterial flora. With dentures and poor oral hygiene, bacteria accumulate, multiply, and a bitter taste appears in the mouth.
When taking chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, or antihistamines, bitterness in the mouth can be a side effect.
Dysgeusia is a taste disorder in which taste perception is altered. Dysgeusia can occur during pregnancy, in smokers, in older people, and in mental illness.
Symptoms
Bitterness in the mouth can manifest itself in different ways, for example:
- after overeating and eating certain foods - indicates the reflux of bile into the esophagus and diseases of the bile ducts,
- aftertaste after taking medications means a disruption of the normal microflora, a negative effect on the liver and the destruction of beneficial bacteria,
- after sports training - speaks of liver pathologies.
Bitterness can occur at different times of the day, after physical activity and during the abuse of bad habits. Often the symptom is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, dizziness, heaviness in the side and abdominal pain, white coating on the tongue and a feeling of bloating, heartburn and belching, dry mouth. At the appointment, you need to inform the doctor in detail about each sign.
How to get rid of bitterness in your mouth
Treatment depends on the diagnosis.
If these are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gallbladder, pancreas, liver), then the doctor prescribes drug therapy and dietary nutrition. Medicines used include choleretic drugs, antibiotics, antispasmodics for pain, prokinetics for synchronous functioning of the gallbladder and ducts, and sedatives. If bitterness in the mouth appears after eating fatty, fried, spicy foods, then it is necessary to adjust the diet and introduce healthy foods into the diet.
If you have GERD, you must follow some recommendations - do not lie down after eating for half an hour, do not bend over after eating, do not wear tight clothes that compress the stomach, sleep with the head of the bed raised.
Diagnostics
You can start diagnosing with a consultation and examination with a doctor. To do this, you need to contact a therapist, gastroenterologist, hepatologist or dentist. The doctor will conduct a survey and refer the patient for examination.
Photo: okfoto / freepik.com
During the consultation, the doctor needs to describe in detail the existing symptoms, tell how often and under what circumstances bitterness appears. Information about lifestyle, diet, and existing diseases will be useful.
For diagnosis, the following studies are carried out:
- Duodenal sounding. If a malfunction of the biliary tract is suspected, portions of bile are taken using a probe for bacteriological examination, and the rate of excretion of bile into the duodenum is also assessed.
- Gastroscopy (EGDS, FGDS) is a study using a gastroscope. Allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the digestive organs and do a biopsy (take tissue samples for laboratory testing).
- Ultrasound of the liver, gall bladder and other organs. It is carried out to assess the size and presence of changes in internal organs.
- Lab tests. If diseases of the digestive organs or biliary tract are suspected, a stool test is prescribed. A biochemical blood test is performed if cholecystitis is suspected. A test for hCG and sex hormones, as well as a serological test if viral hepatitis is suspected, can also be performed.
Diet
The diet should include soft, well-chopped food. Gentle cooking methods - steam, bake, boil, stew. Include puree soups and cream soup in your diet. Bread can be consumed dried, yesterday's bread made from first and second grade flour. Meat – chicken, turkey, lean parts of beef, lean fish. Eggs should be in the form of omelettes, steamed in the oven. Food should be warm, not cold or hot. If there is a symptom of bitterness in the mouth, it is necessary to exclude sausages, smoked foods, fatty, fried, canned, and pickled foods from the diet. It is completely necessary to exclude alcohol, spicy foods, coffee, chocolate, carbonated drinks, pork, and some legumes.
Treatment methods
Basically, the treatment of bitterness in the mouth comes down to taking medications. The specialist selects complex therapy based on the results of tests and instrumental examinations. The gastroenterologist identifies one of three problems:
- Liver disorders. Means are prescribed to stabilize the operation of the “filter”,
- Digestive tract dysfunction. Drugs that affect the digestive system normalize the work
- Uncontrolled bile production. Eliminated by drugs that affect the level of secretion, for example, anticholinergics.
Why is the tincture bitter? How to remove bitterness from tincture
It often happens that when preparing homemade tincture recipes, bitterness appears in the final drink. The reasons for this effect may be different. For some drinks this is normal (for example, in the case of tincture of galangal, rowan, cranberry, anise and some other herbs and berries). Almost always, bitterness accompanies tinctures on nut shells, especially if the infusion period was long. However, the appearance of a bitter taste is not always due to the specifics of the raw material. Let's look at the main reasons and methods for getting rid of excessive bitterness.
Why is the tincture bitter?
There may be several reasons for this:
- features of the nature of the ingredients (herbs, nuts and their shells, rich in bitter and tannin substances);
- low quality ingredients (long-stored or old herbs, nuts, dried berries);
- long infusion period (the longer, the more substances pass into alcohol. For example, from berry seeds).
Sometimes the tincture becomes bitter if the quality of the alcohol base is poor (for example, if low-quality moonshine was used). To avoid the influence of this reason, it is best to use a pure, high-quality product obtained using modern equipment (we recommend paying attention to the Luxstahl 8m moonshine still).
How to remove bitterness from tincture
If the result is too much bitterness or there shouldn’t have been any in the drink, you can use the following methods:
- use of special activated carbon brands BAU, KAU. These brands are specialized for the alcoholic beverage industry and help purify alcohol from impurities. However, remember that they will take on not only bitterness, but also other aromatic components. Therefore, the taste of the tincture as a whole will be a little poorer;
- adding juice/tonic. The result is a cocktail version, and do this immediately before consumption. In general, there are several recommendations on how to drink bitters. For example, tomato and citrus juices, as well as some types of other alcohol, go well with bitter and spicy liqueurs;
- softening bitterness with honey or glucose syrup. The sweetness will smooth out the harsh notes, but the main thing in this matter is not to overdo it.
How to remove bitterness from rowan tincture
Rowan itself is bitter, especially if it was collected before the first frost. If you overdosed the drink or added too many berries, you can try to soften the taste with honey, glucose solution or food glycerin. However, it is honey that will fit in as organically as possible. Start with minimal amounts of sweetener in a test volume of the tincture, and only after choosing the desired proportion, add honey to the main volume of the drink.
How to remove bitterness from alcohol tinctures
Any of the methods described above. Sometimes the bitterness is enhanced by the hardness of the alcohol (especially if it is of mediocre quality). In this case, softening will also help (you can use food grade glycerin), but cleaning with charcoal will not help, since a slight release of aldehyde during such cleaning will make the alcohol even more “vigorous”.
Gallbladder and liver problems
If bitterness causes you anxiety every day for a long time, it's time to get your liver and gallbladder checked. Perhaps, as a result of a malfunction or inflammation, the gallbladder does not have time to remove bile from the body on time, and it ends up in the esophagus. This is where the unpleasant taste comes from.
What to do
- A blood test is mandatory; it is advisable to do both a general and biochemical one, as well as an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- As a rule, the doctor recommends taking anti-inflammatory and choleretic drugs (prescription only).
- For patients with cholelithiasis and cholecystitis, a diet is prescribed: milk and light vegetable soups, low-fat cottage cheese and kefir, boiled fish, marmalade, and tea are allowed.
- It is recommended to drink about 2-3 liters of liquid per day
- Decoctions and infusions of chamomile and calendula are useful, for the preparation of which 1 tsp is used. dried inflorescences are brewed with a glass of boiling water for 15-20 minutes. Take the decoction 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. half an hour before meals.
Treatment of bitterness with folk remedies
Herbal medicine is appropriate in complex treatment under the supervision of a specialist. Chamomile infusion, flax seed jelly, and corn silk decoction will help get rid of such an unpleasant symptom. Therapy with freshly squeezed juices has proven itself well. For this purpose, potato is used, which activates the intestines and eliminates heartburn, carrot, beetroot, which is effective for diseases of the biliary tract, and cucumber. Juices have a general strengthening effect, help cleanse the organs of toxins and normalize digestion processes.
Causes of bitter taste in mouth
Poor quality food
When eating poorly prepared, burnt foods, a specific taste of bitterness appears in the mouth. The unpleasant sensation decreases after drinking water, but the residual aftertaste can last up to 30-40 minutes. A bitter taste on the mucous membranes of the mouth occurs when eating nuts and seeds, which contain fatty acids that break down to form bitter chemical compounds. The symptom is not accompanied by pain or dyspeptic disorders.
Age-related changes
In older people, gradual atrophy of the mucous membrane occurs, as a result of which the ability to distinguish tastes is lost. Therefore, during a meal, the bitter taste is most pronounced, and the remaining taste qualities of the food are not perceived. The elderly complain of bitterness felt in the mouth regardless of the type of food, associated with a decrease in saliva production and activation of pathogenic microflora.
Smoking
Nicotine and various harmful tars that make up cigarettes linger on the mucous membrane of the mouth and cause a bitter taste. Chewing gum or sucking on mints can help reduce the discomfort. Smokers also note a decrease in the ability to perceive the taste of food. If you feel a metallic taste in your mouth against the background of constant bitterness, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Pregnancy
The periodic development of a bitter taste in the mouth during gestation is caused by natural causes. Due to the increased production of the hormone progesterone, the flow of bile into the intestinal lumen is disrupted, bile acids are thrown into the overlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract and cause discomfort. A bitter taste in the first half of pregnancy can occur with severe toxicosis; the irritating taste intensifies after an attack of vomiting.
The symptom sometimes occurs in pathological conditions that are provoked by pregnancy. The most common etiological factor is cholestasis of pregnancy. Bitterness in the mouth begins to bother a woman from the 32nd week of gestation. The irritating bitter taste is accompanied by severe skin itching, lightening of the stool and darkening of the urine. If such signs appear, you should contact an antenatal clinic.
Functional dyspepsia
Periodic disturbances in the coordinated functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are recorded in more than 80% of adults. The bitter taste is caused by slow digestion of food and weakened intestinal motility. An unpleasant feeling often occurs immediately after eating against the background of heaviness in the stomach and flatulence. The feeling of bitterness can be relieved by drinking water with lemon juice or mint candies.
The clinical picture of dyspepsia is more typical for young, emotionally labile patients. Schoolchildren and students often experience a bitter taste in the mouth and abdominal cramps during exams. The symptoms are short-lived, in most cases the condition returns to normal within 1-2 days after the stress factor disappears. If bitterness is accompanied by severe unbearable pain and diarrhea, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Hepatitis
Liver damage has various causes, but the manifestations of all clinical variants are similar. A bitter taste in the mouth as an initial symptom of hepatitis is more often observed with chronic inflammation of the liver parenchyma. An unpleasant sensation develops half an hour to an hour after eating, but can also appear in the morning. If a patient with liver inflammation falls asleep during the day, he wakes up and feels a sharp, irritating taste in his mouth.
In patients with chronic viral hepatitis B and C, bitterness on the oral mucosa persists for 2-3 months, and in the case of fibrotic degeneration of the liver, it becomes a permanent symptom. Toxic hepatitis is characterized by short-term uncomfortable taste sensations that disappear after intensive therapy. The bitter taste is aggravated by pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting mixed with bile.
Biliary system damage
Disturbances in the functioning of the biliary organs cause erratic, uncontrolled secretion of bile, which is associated with the appearance of a feeling of bitterness. With mild severity of the disease, a bitter taste is provoked only by the abuse of fatty and fried foods and alcoholic beverages. The symptom is accompanied by nausea, dull pain in the right hypochondrium, and increased frequency of bowel movements. The condition improves after a few days of a gentle diet.
With severe inflammatory or destructive changes in the biliary system, a bitter taste constantly bothers a person. In the morning, severe bitterness and nausea are felt due to the flow of bile into the stomach and esophagus. The appearance of white or grayish feces is typical, and sometimes painful skin itching occurs. The main reasons for the development of a bitter sensation in the mouth:
- Functional disorders
: hyperkinetic dyskinesia, hypotonic insufficiency of the sphincter of Oddi. - Inflammatory causes
: cholecystitis, cholangitis, cholecystocholangitis. - Cholelithiasis
. - Parasitic infestations
: opisthorchiasis, echinococcosis, giardiasis.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
Almost all disorders of the digestive tract are accompanied by an unpleasant taste in the mouth, since they provoke disturbances in the digestion of food and the secretion of bile into the duodenum. With chronic gastritis and duodenitis, a person periodically experiences bitterness in the oral cavity against the background of errors in diet and nervous strain. Bitter taste is more often associated with food intake.
Pancreatitis and other pathological causes of the pancreas are manifested by a change in taste perception. There is an unpleasant bitter taste, which is often combined with a rotten odor from the mouth. With exacerbation of pancreatitis, the feeling of bitterness intensifies, nausea is noted, and vomiting with impurities of undigested food and bile is possible. Patients also notice a grayish or yellow coating on the tongue.
Dental diseases
The impact of a bacterial cause on the oral cavity causes the development of purulent stomatitis and ulcers, which are accompanied by the appearance of bitterness in the mouth. The symptom is a constant concern; the intensity of the unpleasant taste sensation does not depend on food intake. A specific bitter taste combined with bad breath is characteristic of deep caries.
A bitter taste is observed after medical manipulations in the mouth. When choosing a low-quality material for fillings, it gradually begins to react with salivary enzymes and is destroyed, causing an unpleasant taste. Such symptoms usually occur in the initial period after the installation of dentures. Bitterness is associated with the presence of a foreign object in the mouth. If the symptom is accompanied by toothache, you need to visit a doctor.
Neurological disorders
The symptom occurs when the taste nuclei of the brain are damaged. Patients complain of a bitter taste in the mouth, which appears for no apparent reason and does not disappear after brushing their teeth. The clinical picture is characterized by a perversion of taste: sweet is perceived as sour or salty and vice versa. Bitterness on the oral mucosa occurs after a stroke or traumatic brain injury. In older people, the symptom is often caused by Alzheimer's disease.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Most often, a bitter taste develops during antibiotic treatment. These drugs suppress beneficial microflora and disrupt the activity of salivary lysozyme, as a result of which fungal microorganisms are activated. Patients note a constant bitterness and burning sensation in the mouth, which intensifies while eating. The symptom is also provoked by other medicinal causes: taking chemotherapy drugs, antihistamines, cholekinetics.
Rare causes
- Diseases of the respiratory system
: alveolitis, pneumonia, purulent bronchitis. - Endocrine diseases
: hypothyroidism, hypocortisolism, diabetes mellitus. - Tumors
: hepatocellular carcinoma, stomach cancer, pancreatic head cancer. - Unloading
and
dietary therapy
.