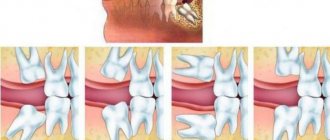
The concept of “eye” teeth does not relate to medical terminology - it is, rather, a popular term that refers to the upper, and with them, the lower canines. There is an assumption that this name arose due to the proximity of the facial nerve, the impact of which is accompanied by severe painful sensations radiating in the fundus of the eye. Fang extraction is a complex procedure that requires the use of strong painkillers.
Functional properties of elements
Teeth perform several functions at once. Each element has a distinctive shape according to its purpose. The main role of the units is digestive. The quality of assimilation of useful elements by the body depends on the thoroughness of grinding the products. Only after chewing and moistening with saliva will the food be ready for subsequent processing by the digestive organs.
Chewing one piece lasts on average 10-20 minutes. The force exerted by the teeth on food sometimes reaches 80 kg. Incomplete dentition can lead to disturbances in the digestive system.
Another function of the elements is aesthetic. With malocclusion, a person may develop psychological problems, since the first thing others pay attention to during a conversation is a smile. Teeth also play a role in the formation of syllables. In the absence of one or more elements, the pronunciation of syllables changes: a lisp appears, speech is distorted.
Alternative names for human teeth
In addition to the official names, there are also alternative names for human teeth. They are not written in dental records, but have long been used in informal communication, since these teeth in people are located or grow in certain places or at certain times.
Eye teeth
The upper canines are called eye teeth because of their close location to the branches of the facial nerve. When they become inflamed, the pain radiates to the eye area and upper face. How close the incisive canals and the dental nerve are located to each other is shown in the figure:
Wisdom tooth
The wisdom tooth is the posterior third molar. He was called “wise” because he grows up in adulthood - when a person has already gained wisdom (by about 20 years).
Tooth anatomy
The structure of all units is the same, but each tooth has a distinctive shape and dimensions, depending on the functions it performs.
Internal structure of teeth in the photo
What does a tooth consist of? The top layer (enamel) is predominantly composed of minerals. It protects the inner layers of the tooth from mechanical, thermal and chemical damage. The rest of the solid surface of the elements consists of proteins and liquid involved in metabolic processes. This layer tends to wear out and wear off over time. Typically, caries first affects the surface of the tooth. For this reason, you should carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity and carry out hygiene procedures in a timely manner.
If you examine a tooth in cross-section, you can also see dentin. It also consists of mineral substances and protects the pulp with the nerve fibers located in it. Many small channels are localized in dentin, with the help of which metabolic processes in bone tissue are carried out. Through these structures impulses are transmitted between nerve endings. For 1 sq. mm of dentin there are about 70,000 microscopic tubules.
The internal cavity of the elements is represented by pulp. It consists of nerve endings and lymph nodes.
The structure of the tooth should be considered depending on its location relative to the gum. The visible part of the element is the crown. The area of contact between the tooth and the gum is called the periodontium. The root is located in a special cavity, which dentists call the alveolus. The root of the tooth ends at an apex, which is supplied with blood vessels. Through these structures, the elements are fed.
No Ads
Grinding food
The human stomach is capable of fully digesting only finely ground food, which is abundantly moistened with saliva. For this purpose, there are premolars and molars in the mouth, which act like millstones - they grind large pieces of food, while simultaneously mixing it with the secretion of the salivary glands.
The absence or loss of one of these teeth leads to the fact that unprocessed large particles of food enter the gastrointestinal tract, which are difficult to respond to enzymes and can cause various chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Kinds
What are the units? Teeth in the oral cavity are divided into 4 types: incisors, canines, molars and premolars. The human jaw is symmetrical and each part (right and left) has the same number of elements. If this does not happen, then they talk about malocclusion development, which requires immediate correction.
Incisors
Incisors are the elements located in the center of the jaw. There are 8 such units in total - 4 at the bottom and 4 at the top. The peculiarity of the anatomy of the incisors is that they have a flat crown with a sharp cutting surface. There are 3 tubercles on the cuts of the incisors, which wear off over time. The centrally located elements are usually larger than the lateral incisors, since they bear more load when chewing food.
The upper central teeth are most susceptible to damage in the form of cracks in the enamel and chips. It is in these areas that aesthetic defects associated with improper placement of elements in the oral cavity and trema are usually noted.
Crown – part of the tooth protruding above the gum
It should be noted the main functions of the incisors are the primary capture of food, cutting pieces and chewing them. The central elements are the first to begin to chop the food and pass it further. Due to the sharp cutting edge, units and twos crumble and crush food for further normal absorption. The incisors protect the remaining elements from severe damage during chewing loads. In addition, they protect the digestive organs from the development of chronic diseases associated with insufficient absorption of nutrients by the intestines.
On the upper jaw, the units have impressive dimensions - up to 23 mm including the root system. Unit width is from 4 to 6 mm. Thanks to the flat crown, the chewing load is distributed evenly between all areas of the tooth. The thinnest enamel of the incisors is in the area of contact with the gum. It is this part that is most vulnerable to carious processes.
Several features of incisors should be noted:
- rounded root shape;
- the presence of grooves on the surface of the root;
- chisel shape;
- greater curvature of the incisors located on the sides.
Fangs
A person has 2 fangs on each jaw. They resemble a triangle in shape and are easily recognized among other elements of the series. With the help of fangs, a person can bite off pieces of hard foods - apples, carrots, crackers. The elements have only one long root. The upper units are larger than the lower ones. Some patients resort to extension procedures to give greater effect to the canines on the upper jaw.
No ads 2
Premolars
The first premolar is also called a quadruple. The main function of the tooth is transitional and exciting. Due to the wider crown, the elements take part not only in biting off pieces of food, but also in grinding it to the desired state.
On the chewing surface of the element there are several types of chewing tubercles - flat and vestibular. The first tubercle is located closer to the cheek, and the last one is directed towards the oral cavity. In rare cases, three-tubercle or four-tubercle teeth are found. An anomaly is observed if the palatine tubercle passes into the median tubercle.
Due to the many grooves and fissures, pathogenic bacteria can accumulate on the surface of premolar teeth, especially if oral hygiene is insufficient. For this reason, these segments should be given the most attention when brushing your teeth. The second premolar of the upper and lower rows has larger dimensions, but is shaped like a quad.
Molars
Molars have the same structure as the rest of the series. But, despite this, several features can be identified that are characteristic only of sixes and sevens. The main function of molars is to grind and grind food during chewing. They play an important role in the formation of an anatomically correct bite.
Each half of the jaw has 4 molars below and above. Molars have several chewing surfaces. The buccal surface of the tooth is convex. There is a groove on it, which is a place where pathogenic flora accumulates. These areas also need to be given special attention when brushing your teeth, since the salivary glands are located near the buccal surface, which are affected during the development of carious processes.
There are 3 tubercles on the chewing surface: paracone, protocone and metacone. On the buccal side there is also the most important morphological structure of bone tissue - the Carabelli tubercle. The degree of expression of the structure is varied.
In some cases, the Carabelli tubercle may have its own process
The mesial border of the molars has a slightly convex shape. The root system on this side varies in shape among different patients. It can be cylindrical or barrel-shaped. The structure of the distal surface of the molars is similar to the mesial one. The only difference is inaccessibility during hygiene measures. For high-quality cleaning of the last elements, it is better to use floss or irrigator.
Wisdom tooth
Eight, or wisdom teeth, usually appear on the surface of the gums in adulthood. The shape of the element is similar to 6, but has more powerful roots. The number eight is considered the most problematic tooth: it is difficult to break through to the surface and quickly collapses. Dentists may have difficulty removing figure eights due to their abnormal position in the mouth and crooked roots, which can be diagnosed using x-rays. In such cases, the problem area is immediately extracted, otherwise purulent inflammation of the soft tissues may develop. Another serious complication of improperly positioned wisdom teeth is the destruction of the roots of adjacent units.
No ads 3
Function and role of fangs
The main function of the fangs is to tear and hold food. In addition, canines are the teeth that are least susceptible to caries. These are the most powerful and strong teeth, which bear quite a large load. If a person suddenly lost his fangs, then:
- perhaps he would have problems with diction;
- the entire load would fall on the weaker neighboring teeth, which in the near future would either become deformed or become loose;
- the dentition would lose its aesthetic appeal;
- the process of infection of teeth with caries has accelerated, since it is the fangs that are the barrier to the “creeping” of this problem from the molars that are most susceptible to it to the incisors;
- Tooth enamel is the hardest human tissue the body produces, but even it can wear down and wear down over time. Fangs are an excellent shock absorber for the contact of the upper and lower jaws; in their absence, tooth enamel would wear down several times faster.
Classification of dental surfaces
To conveniently describe the localization of the pathological process, dentists use a term such as “crown surface”. There are 4 types of such surfaces:
Where is the eye tooth + photo
- Chewable. This part of the tooth faces the elements on the opposite jaw. In canines and incisors, this area is represented by the cutting edge.
- Vestibular. Located in the vestibule of the oral cavity. The vestibular surface of the anterior teeth has an area of contact with the lips. In the molars, this part is in contact with the inner shell of the cheek and is called the buccal surface.
- Lingual or lingual - the area of elements facing the tongue. It is in this area that the largest amount of plaque accumulates due to the difficulty of carrying out hygiene measures. The lingual side of the elements is not visible to others during a conversation, so many patients seek to install corrective systems on the inside of the tooth.
- Approximal. This type of surface is divided into medial and distal. In the first case, the area is located closer to the middle of the dentition, in the second case, closer to the edge of the arch.
Tooth surfaces
On what basis are teeth numbered according to different classification systems?
In addition to the Latin names of teeth, digital designations are used in dentistry. The numbering of teeth is based on the order in which they erupt. It starts from the front incisors (from the middle of the jaw) and runs to the left and right of them.
There are several generally accepted systems for numbering human teeth.
Universal system
Most often, dentists name teeth not by the Latin alphabet, but according to their location in the oral cavity (ordinal number). Moreover, using not Roman, but familiar Arabic numerals.
Names of teeth according to the universal classification system:
- two central incisors are located at number 1 and are called ones;
- the second incisors are numbered 2;
- the fangs are called triplets;
- chewing teeth or premolars are called fours and fives;
- molars are called sixes, sevens and eights.
According to the universal system of classification of dental units, the jaw is divided into 4 segments:
- top left;
- top right;
- bottom right:
- bottom left.
The further name indicates not only the serial number, but also the location of the dental unit in the human oral cavity.
The universal dental numbering system is the most popular and frequently used. It is used by dental therapists and surgeons in various countries.
The picture shows a diagram of the designation of teeth in the oral cavity of an adult according to the universal numbering system:
European system
The European Viola system is one of the newest and most advanced methods for naming human teeth. It is characterized by the division of the jaw into segments (two at the bottom and two at the top). Each segment is numbered (from 1 to 4).
Based on these numbers, each tooth receives a two-digit number. The first digit indicates the segment, and the second is the actual sequence number.
The Viola system is recognized internationally and is therefore popular all over the world. It is used in radiography, making panoramic images and allows dentists from different countries to exchange information about patients, overcoming the language barrier.
Haderup system
To designate dental units according to the Haderup system, Arabic numerals are used and segmentation into the lower and upper jaws is used:
- the “+” sign indicates that it belongs to the upper jaw;
- the “–” sign indicates the lower jaw.
The only disadvantage of such numbering is that it is necessary to additionally indicate whether the dental unit belongs to the left or right side of the jaw.
Zsigmond-Palmer system
The Zsigmond-Palmer system is considered the most imperfect, since it only indicates the numbers of teeth without their location. Standard Arabic numerals are used for numbering.
This tooth numbering system is practically not used in therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. It is used only by orthodontists and maxillofacial surgeons.
Features of milk elements
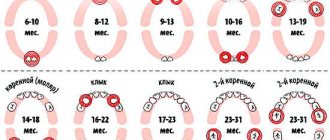
Milk units act as precursors of permanent elements. They usually appear in the first year of a baby's life. Usually the period of eruption of the first incisors is accompanied by painful symptoms for the baby. About 2-3 years may pass between the appearance of the first and the eruption of the last milk tooth. A 3-4 year old child has 20 fully formed baby teeth in his mouth.
The structure of teeth in children
The change of the primary occlusion to a permanent one is carried out from 6-7 years of age. The shape of the permanent elements will differ little from their predecessors. The only difference is the more massive crown part and dense enamel.
In children, the degree of mineralization of enamel and dentin is weaker than in adults. Therefore, their dental care should be carried out with special care. The milk tooth is designed in such a way that most of its volume is occupied by the pulp, so caries in children becomes more complicated faster.
Another difference between milk units and permanent ones is short roots. For this reason, tooth loss in children sometimes occurs unnoticed and painlessly.
What is a dental formula
A dental formula or diagram is a brief description of the dental structure of the human dentition using numbers and Latin letters.
The letters are abbreviations from the Latin names of teeth accepted in medicine:
- I – these are dentes incisivi or incisors.
- C is for dentes canini or fangs.
- P stands for dentes premolars or premolars.
- M stands for dentes molars or molars.
The alphanumeric dental formula is common in many countries, including America, which is why it is sometimes called American. After the letters in the formula there is always a digital fraction, where the numerator indicates the number of teeth on the upper jaw, and the denominator on the lower jaw.
The dental formula of a healthy adult with a normal bite and 32 teeth looks like this:
This formula indicates that on each human jaw there is:
- 2 pairs of incisors;
- 1 pair of fangs;
- 2 pairs of premolars;
- 3 pairs of molars.
Dental formula in the absence of some teeth
It is not difficult to correctly number dental units with a healthy dentofacial apparatus; it is much more difficult to indicate the location of the teeth if a person does not have any molars, incisors, canines or premolars. In this case, the dentist indicates the number 0 opposite a certain group of teeth, rather than shifting the number series.
If the patient has any anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus, for example, teething in the wrong place (hyperdontia, polydontia), the dentist prescribes an individual formula. In addition to numerical designations, the doctor generates a detailed report on the structure of a person’s dentition.
Malocclusions
With a correct bite, the teeth of the upper jaw protrude onto the elements of the lower jaw by no more than 1/3. This position will make it easier for the jaws to chop food. Malocclusions are usually associated with the following conditions:
- The upper units overlap the lower ones by more than ½. This type of bite is usually called a deep bite.
- Certain groups of teeth may not fit together at all. In this case, they talk about an open bite.
- Distal bite. What it is? The problem is said to occur when the upper jaw is overdeveloped.
- If the lower jaw is pushed forward, then there is a mesial deviation.
- When the structures are displaced relative to each other, a cross anomaly occurs.
If not treated promptly, malocclusions can cause toothless jaws. For this reason, it is important to contact an orthodontist at the first sign of a problem.
Eruption of canines in infancy
The order of formation of the primary occlusion provides for the appearance of fangs after the incisors and the first chewing units have erupted. The upper elements emerge at the age of 1.2-1.5 years, which is slightly earlier than the period of formation of the lower molars. Late eruption is determined by the deep position of the units in the structure of the jaw, which also determines the characteristic painful sensations that may occur during growth.
To relieve the discomfort experienced by the child, the following techniques are recommended:
- Massage of gum tissue - before the procedure, you need to thoroughly wash your hands, then use your index finger to massage the area above the canine for a couple of minutes. It is recommended to repeat the massage several times a day;
- The use of teethers that provide a cooling effect - a product filled with distilled water does not pose a danger to the baby’s health even if the baby manages to chew the shell;
- Applying anesthetic gels that relieve inflammation within a few minutes;
- For nasal congestion, use children's nasal medications that promote vasoconstriction;
- At elevated temperatures (more than 38 degrees) - take fever medications, available in the form of syrup or suppository.
It is worth emphasizing that the use of medications must be agreed with a doctor, who will determine the appropriate list, as well as the duration of the course.
Indicative
Teeth are an indicator of the general condition of the body. The presence of any metabolic disorders, chronic diseases of the endocrine, digestive and other systems, vitamin deficiencies, unbalanced nutrition - all this negatively affects the condition of the dentition - the teeth change their shade and begin to crumble.
Therefore, caring for your smile includes not only regular hygiene procedures and visits to the dentist’s office, but also treatment of concomitant pathologies.
As you can see from the article, teeth are not only about comfortable eating. The loss of at least one element of the dentition is fraught with possible problems with digestion, speech, as well as the development of complexes against the background of a cosmetic defect.