Bad breath is one of the most common complaints with which patients turn not only to the dentist, but also to other specialists (therapist, gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist), since such a problem can be a consequence of a number of diseases.
In scientific and medical circles, special terms are used to refer to bad breath, such as “halitosis” or “ozonostomia”. In ICD-10, bad breath is classified as a clinical symptom related to gastrointestinal diseases and abdominal pathologies, and is designated by code R19.6.
Putrid odor from teeth and gums can also be the result of active growth of anaerobic bacterial flora in the mouth due to infectious and inflammatory dental diseases. If a sharp, unpleasant odor appears from the gums (in the absence of other symptoms), a dental examination and oral sanitation are recommended.
If the problem does not disappear after this, a comprehensive examination of the ENT organs and digestive tract is necessary.
Why does my breath smell bad?
The mechanism of formation of bad breath is represented mainly by the growth of pathogenic flora on the mucous membranes of the gums and the inner surface of the cheeks.
The reasons for this may be different, but the basis of the pathogenetic changes is a violation of the qualitative and quantitative relationship between pathogenic bacteria (some strains of streptococci, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the bacteria Bulleidia moorei) and aerobes that can suppress their activity.
Aerobic microorganisms are microorganisms whose ability to function is active only when exposed to atmospheric oxygen. Both microorganisms are opportunistic for humans and can cause a number of serious diseases (tuberculosis, Lyme disease, streptococcal pharyngitis, etc.), but it is their balance that allows maintaining a normal level of acidity and local immunity of the mucous membranes in the oral cavity.
A pungent odor from teeth and gums in a person who does not suffer from pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis and other pathologies of the digestive system and abdominal organs occurs as a result of excessive synthesis of volatile compounds that can penetrate into the environment in significant concentrations. Such compounds are secreted by representatives of the anaerobic flora, feeding on food debris contained in dense dental plaque and deposits, therefore, one of the leading factors in the development of ozonostomy is rightly considered to be the low quality of oral hygiene.
What does a dentist do?
First of all, he will check whether the prosthesis fits tightly. Then make sure that no caries or periodontal pocket has formed at the edge of the crown. An X-ray examination will be required. The image will show whether caries remains on the surface or has penetrated deep into the tissue, causing inflammatory processes.
In most cases, the crown will have to be removed. If the problem is caused by poor fixation, or the crown has already fallen out on its own, then it can be used again, but most often the prosthetics will have to be done again.
At the initial stage, caries is removed, the cavity is filled with filling material and prosthetics are performed.
In case of significant damage, but the root is intact, prosthetics on a pin is used. A fiberglass pin is inserted into the root. It provides stability to the tooth and prevents thin walls from collapsing. Then the crown is put on.
With significant ( more than 60%
) destruction, use a tab under the stump. This is a microprosthesis that consists of a root part and a crown part. The first is inserted into the root, and the second serves as the base on which the prosthesis is placed.
If pus is released from the gum pockets, the dentist performs an operation - curettage. It cleans the surface of plaque and stone and disinfects them. Additional treatment may be needed to prevent teeth from becoming loose and falling out.
What could the smell be?
The cause of halitosis can be guessed by the specific odor a person emits into the environment.
Types of volatile compounds and their relationship with bad breath
| Substances produced by bacteria in the mouth | What smell do they have? |
| Methanethiol (poisonous, colorless gas) | Rotten cabbage (even in minimal concentrations). |
| Allyl mercaptan | Garlic, rotten onions. |
| Propyl mercaptan | Pungent smell of rot. |
| Dihydrosulfide | Rotten eggs. |
| Dimethyl sulfide (organic volatile liquid) | Pungent smell of sulfur and petroleum products (gasoline). |
| ?-pentamethylenediamine | The smell of a decomposing corpse, the pungent smell of urine. |
| Indole and its derivatives | Naphthalene. |
| Ammonia derivatives | Feces (feces). |
| 1,4-diaminobutane | Spoiled meat. |
| Dimethylamine | Rotten fish. |
| Methylbutanoic (isovaleric) acid | Sour milk. |
Note! All the compounds listed in the table are produced primarily by pathogenic microorganisms, so dentists cite poor-quality hygienic care and dental diseases (especially chronic ones) as the main causes of unpleasant gum odor.
Bibliography
- Khitrov V. Yu., Zabolotny A. I. Halitosis - a medical and social problem // Practical medicine. - 2009. - No. 1 (33). — P. 12-17
- Gorobets S. M. et al. Risk factors for the development of halitosis (review) // Crimean Therapeutic Journal. — 2022. — No. 3. — P. 13-18
- Maksimova E.V., Stetsyuk N.S., Shelikhova E.O. Halitosis as a medical and social problem // Crimean Therapeutic Journal. — 2020. — No. 1. — P. 32-37
- Temkin E. S., Churikova A. S. Halitosis - modern diagnostic methods and their prospects // Volgograd Medical Scientific Journal. — 2022. — No. 3. — P. 15-18
- Vinogradova T. G. Bad breath - halitosis, causes and treatment options // Bulletin of VSMU. - 2014. - T. 13. - No. 2. - P. 129-131
- Ushakov R.V. et al. Modern methods of diagnosis, elimination and prevention of halitosis // Textbook: Moscow. - 2016. - 81 p.
- Instructions for the medical use of the drug Metrogyl Denta® Dental gel // Registration number P N015982/01 // State Register of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=9bc9a05c-d28b-473d-b8d4-60e8b8323762&t=
Modern aspects of the prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa in patients with xerostomia / L.D. Weisheim, L.M. Gavrikova, T.N. Gomenyuk, T.V. Motorkina, L.N. Shcherbakov, S.M. Dubacheva, G.V. Sorokoumova//Medicinal Bulletin.—2013.—No. 2 (50). -WITH. 32-37.
Dental reasons
If a putrid odor from the gums appears suddenly, the first thing to do is consult a dentist and rule out the presence of caries, inflammatory processes in the gingival and periodontal tissues, hilar cysts and granulomas, and abscesses. It is almost impossible to independently identify the source of bad breath (gums or teeth), so dental diagnostics are carried out comprehensively and often include not only a visual examination using a medical mirror, percussion of the teeth (if periodontitis is suspected), but also an X-ray or computed tomographic examination.
The causes that can provoke halitosis include a number of pathologies and diseases.
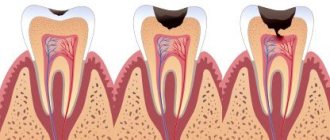
- Caries. This is the most common disease among all age populations, in which the hard tissues of the tooth are affected and necrotically modified. The causes of caries are dysbacteriosis, poor hygiene, lack of sufficient preventive measures, chronic infections (especially diseases of the ENT organs). A pungent odor from the gums and teeth with stage 3-4 caries appears in almost 100% of patients and is perceived by others as the smell of rotting food, feces or urine.
- Inflammatory and infectious gum diseases. This group includes infectious and non-infectious pathologies of the oral cavity, in which soft tissues (gums and tongue) are involved in the inflammatory process. These are stomatitis, gingivitis, desquamative glossitis, pharyngomycosis of the oral cavity and other diseases whose pathogenesis is based on catarrhal, herpetic, exfoliative, traumatic or eczematous inflammation.
- Periodontal diseases. Periodontium is a special type of fibrous collagen fibers with a low degree of elasticity that fill the space between the alveolar bone and the hilar cementum. One of the complications of periodontitis and periodontitis is the formation of periodontal (periodontal) pockets, into which food can become clogged, undergoing processes of fermentation, fermentation and decay. It is the decay products that cause the putrid odor from the gums in this case.
- Abscesses, cysts of the gums, tooth roots or dental alveoli. Bad breath with cysts may indicate that the cavity is inflamed and filled with purulent exudate, which can be a source of hematogenous spread of infection throughout the body. Treatment for a purulent cyst or abscess is surgical (followed by antibiotic therapy).
One of the causes of bad breath can also be xerostomia, a pathology of the salivary glands, in which an insufficient amount of saliva is produced in a person’s mouth. Saliva is necessary not only to maintain normal levels of moisture and acidity, but also for the primary processing of incoming food due to the action of digestive enzymes. If there is not enough saliva, food enters the stomach poorly processed, which can cause indigestion and the release of bad-smelling gases and acids that rise up the esophagus back into the oral cavity.
Important! If the patient has undergone orthodontic treatment (dental implantation, installation of braces, etc.), in addition to a dental examination, an orthodontist consultation is also indicated to exclude galvanic syndrome - poor survival or intolerance of installed dentures.
Express methods
There are many answers to the question of how to urgently remove bad breath. Here are the most effective express ways to get rid of bad breath.
- Chewing lemon, lime. This method will not eliminate the stench forever, but it will get rid of it for a few hours. You need to chew a piece of lemon or lime along with the peel. It is also recommended to use citrus zest as an emergency medicine, which you can always carry with you in a fabric bag.
- Coffee. Among coffee lovers, it is rare to find people with bad breath. Caffeine is known to kill unpleasant odors. If you can’t drink a cup of aromatic drink, it is recommended to gnaw 3-4 coffee beans (which you need to put in your pocket or purse in advance). This method will relieve the stench for 7-8 hours. It is not suitable for people suffering from periodic or constant increases in blood pressure. Hypertensive patients are better off chewing a few sprigs of dill or parsley. This method will not only freshen your breath for 8 hours, but also cleanse the oral cavity of bacteria.
- A sprig of cloves helps with terrible odor in the mouth. All you need to do is chew it for a few seconds. Clove essential oil extracted from the plant will not only refresh the oral cavity, but also lift your spirits.
- Juniper will help hide fumes well. It is recommended to chew the berries for several minutes. This method is capable of defeating even the strongest amber after active celebrations with the consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages.
- Sour apples can also combat this problem. Fruits will get rid of plaque, bad breath and improve the functioning of the digestive system.
- To get rid of the problem, it is recommended to chew pine nuts or roasted seeds for a few minutes. This will provide fresh breath for 1-2 hours and even get rid of the smell of garlic and onions.
- If you consume half a teaspoon of propolis daily, this will help eliminate stench and accelerate the regeneration of the mucous membrane during the development of inflammatory processes.
- A salt solution will also help get rid of the problem. To do this, you need to rinse your mouth with salty liquid (or sodium chloride 0.9%) for 2-3 minutes. It kills odor and destroys bacteria.
- If you rinse your mouth with any vegetable oil in the morning, it will relieve bad breath for several hours.
It is also recommended to use wormwood for chewing. The plant eliminates bacteria, restores the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminates bad breath. Magnolia has the same properties. All you need to do is chew the plant for 1 minute.
What other reasons can cause ozonostomy?
If an examination by a dentist does not reveal any diseases or pathologies, the doctor will refer the patient to specialized specialists to determine the possible causes. These may include:
- pathologies of the digestive system and abdominal organs (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, duodenitis, chronic colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, gastroduodenitis);
- untreated or recurrent infectious diseases of the nasopharynx and oropharynx (tonsillitis, sinusitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis);
- kidney pathologies accompanied by partial dysfunction of the renal system;
- diabetes mellitus (the smell of urine and acetone from the mouth is one of the signs of a lack of insulin);
- long-term use of certain medications that can cause xerostomia (proton pump blockers, heartburn medications, alpha-agonists, etc.);
- abuse of foods with a high content of purines and phytoncides (onions, garlic, green onions, all varieties of cabbage, sorrel);
- smoking (especially if a person smokes more than 10 cigarettes per day).
Often the unpleasant smell of sour milk or rotten eggs appears in women on diets. A prolonged absence of food in the stomach provokes increased activity of parietal cells, which are responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid. As a result, a colorless gas accumulates in the stomach, which is a compound of hydrogen and sulfur and has the characteristic smell of rotten eggs. If food does not enter the stomach, this gas rises to the top and is released into the environment through the mouth when a person talks, yawns or sneezes.
People who are susceptible to emotional instability and are often in a state of prolonged stress experience unpleasant gum odor 2.1 times more often than their peers who are in an emotionally stable state.
Important! A constant smell of rot, feces or urine from the mouth, especially if it intensifies or is combined with other symptoms (sore throat, sensation of a foreign body in the pharynx and esophagus, nausea, discomfort in the stomach, etc.), may be a manifestation of malignant tumors digestive system or larynx. Consultation with an oncologist is indicated in cases where it is not possible to get rid of the unpleasant odor within 3 months, despite a complete examination, sanitization of foci of chronic infection and adherence to personal hygiene measures.
Why is the smell of fish so difficult to remove?
No one enjoys the fishy smell. To most people it stinks. Fresh raw fish emits “aromas” of volatile alcohols, carbonyl compounds released from their fat and creating a plant-like flavor. Therefore, it is the fish oil that is smelled, not the fish itself.
Many desirable substances subsequently undergo both microbial and spontaneous degradation. For example, inosine monophosphate degrades slowly to enhance flavor, similar to glutamate. The overall aroma becomes weaker, gradually disappears, ammonia and sulfur compounds appear, due to which the fish will subsequently smell. Freshwater fish contain earthy compounds (geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol) absorbed from the environment, bacteria, and algae. Both compounds are noticeable even at very low concentrations.
But something else bothers people. This small but powerful compound, trimethylamine (TMA), comes from the parent molecule trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), found primarily in marine fish. It usually does not cause an unpleasant odor. The problem is bacteria that convert TMAO to TMA. They develop after 3–4 days of storage. As a result, the typical fishy aroma is enhanced, which is also associated with a decrease in the quality of the meat. Humans are very sensitive to TMA; its distinctive scent can be recognized at a concentration of 1 molecule per 1 million.
Important! Why do seafood contain more TMAO? The reason lies in salty sea water (35 g of salt in 1 liter).
Frying and other heat treatments can partially remove TMA from fish meat. But to get rid of the smell of fish on your hands, remove it from a wooden board, from dishes, or freshen the air in your apartment? Since amines are alkaline substances, they are easily neutralized by acids. For example, lemon is enough, which is often used when cooking fish.
Diagnosis at home
The patient himself very often does not notice that his breath smells bad, and the people around him are embarrassed to say so, for fear of offending a loved one. To independently assess the freshness of your breath and the intensity of odors, you can perform one of the tests below. All of them are simple to perform and do not require the help of outsiders or any special equipment or tools.
Method 1
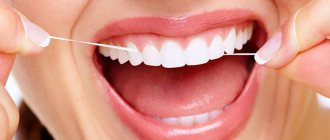
This method requires floss (dental floss) without adding flavoring or coloring additives.
- Clean the interdental spaces using the classic method. To assess the freshness of breath, it is necessary to treat molars (molars).
- After the procedure, carefully examine the color of the floss. The presence of a yellowish, light brown or creamy tint indicates a large amount of bacterial plaque on the inner surface of the tooth enamel. If a pinkish tint appears on the thread, you should check the condition of your gums.
- The smell can be assessed 20-30 seconds after the procedure.
The test cannot be considered reliable if colored or scented thread was used.
Method 2
To carry out this test, you need to use a soft silicone spoon or wooden spatula (can be purchased at a pharmacy).
Using a spatula, remove the plaque from the middle part of the tongue, then wait 10-15 seconds and evaluate the quality and intensity of the smell.
Method 3
This method is the simplest and allows you to carry out express diagnostics in 1 minute, from anywhere. To do this, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and lick the outer surface of your hand (near the thumb) or wrist. You can evaluate the result in 40-50 seconds.
In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
The smell of fish from the mouth is not always pathological - if it is caused by poor hygiene or the consumption of certain foods (eggs, dairy products), then it is enough to adjust the diet and improve oral care.
If after this the smell does not disappear, becomes more pronounced, bothers you for a long time, or other accompanying symptoms appear, in such cases you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and undergo an examination .
For children, especially younger children, symptoms that recur daily or every other day are considered especially dangerous. To check the presence of an odor, its character and severity, you need to bring your palm bent into a boat to your mouth, exhale sharply into it, and then smell or lick it.
How does a dentist diagnose?
To identify signs of ozonostomy, dentists use the organoleptic diagnostic method. Indicators are measured using special instruments and analyzed in accordance with established standards.
To ensure that the test result is as reliable as possible, 12-20 hours before the doctor’s visit, the patient is recommended to:
- stop smoking and chewing gum;
- do not use hot spices, seasonings, seasonings and products containing large amounts of flavorings, flavor enhancers and dyes;
- discontinue antimicrobial treatment (48 hours before the test), if possible;
- Do not use tooth balms or rinses.
Note! You cannot brush your teeth before the procedure. The last brushing of teeth is allowed 8-10 hours before the test.
Removing fishy aroma from the apartment
It is somewhat more difficult to freshen the air in a room where fish has been fried. The most effective is long-term ventilation. If you are preparing any type of seafood by frying or baking, be sure to immediately turn on the hood.
After airing the apartment, it is recommended to freshen the air in it using special means in the form of a spray.
If you don’t have an air freshener, you can use orange zest: place it in different corners of the room. Setting the zest on fire will have an even greater effect. It produces aromatic smoke that perfectly eliminates any unpleasant odor. This method also works for removing unpleasant odors from clothes: you need to fumigate your favorite items with aromatic smoke.
An unpleasant odor coming from your favorite coat that just can’t be washed? In this case, the item should be hung outside. Frost ideally removes various aromatic traces, so in winter it will be enough to hang the item on the balcony at night. In general, if things smell like fish, it’s better to just wash them.
Website www.sympaty.net – Beautiful and Successful. Author: Elena Burenyuk. Learn more about the site's authors.
How to deal with the smell?
Treatment of halitosis and its manifestations consists of complete sanitation of infectious foci. The patient is treated for carious cavities with the installation of fillings and cleaning of the canals. If the tooth cannot be saved, extraction is prescribed (installation of dentures is permissible only after high-quality sanitation and oral hygiene). For infectious or inflammatory pathologies, a course of local treatment (application, rinsing with antiseptics, instillation), antibiotic therapy and antimicrobial therapy is carried out.
For recurrent gingivitis, the doctor may prescribe Metronidazole at a dosage of 100-200 mg 2-3 times a day. The standard course of treatment is 7-10 days. In more severe cases, antibiotics are indicated - amoxicillin, tetracycline, cephalosporin. Local applications are made with medicinal ointments and gels, some of which can be placed directly into periodontal pockets (Cholisal, Metrogil Denta, Asepta, Kamistad).
For fungal infections (candidal stomatitis, pharyngomycosis), systemic and local antimycotics are used - Fluconazole, Candide, Miconazole. In all cases, rinsing with antiseptics (Miramistin, chlorhexidine, furatsilin solution) is indicated.
Important! To treat unpleasant odor caused by diseases of the digestive system, upper and lower respiratory tract, abdominal organs, complex medical, physiotherapeutic and surgical (if necessary) treatment is prescribed: rehabilitation of foci of chronic infection in case of sinusitis, pharyngitis, treatment of gastritis, correction of IBS.
How does halitosis manifest?
Constant bad breath is one of the symptoms of periodontal disease2. With physiological halitosis, when there are no dental or general diseases, the unpleasant odor is a temporary phenomenon. It appears after eating specific foods (onions, garlic) and disappears some time after eating and brushing teeth6. If you notice bad breath in the morning or after intense physical activity, it is likely that you are not producing enough saliva or it is drying up quickly due to breathing through your mouth at night or during exercise6.
to come back to the beginning
Prevention
The main measure to prevent bad breath in patients of any age is high-quality oral hygiene and timely treatment of dental diseases. The tips and recommendations below can be used both to prevent halitosis and to improve the effectiveness of its treatment.
- It is necessary to carry out hygienic treatment of the oral cavity at least 2 times a day. You should brush your teeth immediately after waking up in the morning, and after your last meal in the evening.
- If you are prone to bleeding and the deposition of bacterial plaque, you should additionally use balms and rinses with medicinal herbs and natural antiseptics (Forest Balsam, Listerine, Asepta). Such products should be used in courses - 2-3 weeks every 3-4 months.
- Incorrect or irregular nutrition can provoke the appearance of an unpleasant odor, so it is important to adjust your diet and habits.
- After eating, you should rinse your mouth with boiled water so that there are no pieces of food left in it, which are a breeding ground for bacteria.
Persons who practice oral sex should brush their teeth (at a minimum, thoroughly rinse your mouth with water or mouthwash) after each contact.
Video - 10 ways to combat halitosis
Foul odor from gums is a common dental problem that can only be solved with an integrated approach. Treatment should begin with a visit to the dentist and a complete sanitation: removal of necrotic tissue, relief of inflammatory processes, extraction of teeth that cannot be treated or restored. If the cause of halitosis is diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or larynx, treatment also involves the sanitation of existing infectious foci. Any local remedies (oral sprays, rinses, chewing gums) only mask the problem for a short time, but do not solve it completely, creating conditions for the development of possible complications.
Associated symptoms
- If the cause of the fishy odor is trimethylaminuria, then accompanying symptoms will be the presence of a fishy odor in the urine, sweat, and vaginal discharge.
- In addition to halitosis, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and liver are characterized by symptoms such as deterioration in general health, weakness, nausea, and allergic skin reactions.
- In case of dental or nasal diseases, pain characteristic of them appears at the site of development of the pathological process (tooth, gums, sinuses), white or yellowish plaque, and sometimes increased body temperature.
Complications from rotten teeth
You should not self-medicate and put off visiting the dentist if your crown stinks. Untreated caries can cause complications that lead to tooth loss and can provoke common somatic diseases.
- Periodontitis
Periodontium is connective tissue, part of the complex mechanism that holds the tooth in the jaw. If microbes penetrate it, the tooth root becomes inflamed and periodontitis begins. It develops gradually and symptoms become noticeable when the disease has already become protracted. With advanced periodontitis, the roots become exposed and the gums begin to bleed. Cysts with purulent contents may form on the root. Treatment of periodontitis is complex and includes surgical methods: removal of the root apex, one root in multi-rooted teeth, tooth separation or root amputation.
- Pulpitis
When preparing for prosthetics, the pulp is not always removed. If it is not removed, it can become inflamed and cause a lot of trouble. Pulpitis, inflammation of the pulp, is accompanied by severe pain. Surgical treatment - depulpation, and then re-prosthetics.
- Cysts, abscesses
Any purulent formation can cause serious complications, because the infection spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream. If abscesses or cysts are not removed promptly, they can cause serious illnesses such as osteomyelitis.
A tooth has rotted under the crown: what to do?
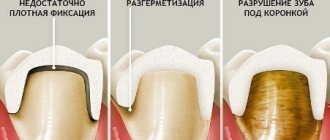
If a tooth rots under the crown, then you need to keep in mind that this process is no longer reversible. It will continue until the tooth tissue on which the crown rests rots completely, after which the crown falls out (Fig. 4). Signs that the tooth is rotting are the following symptoms:
- bad smell from under the crown,
- food getting under the crown,
- root caries is visible at the lower edge of the crown,
- the tooth under the crown has turned black (if the crown is made of metal-free ceramics, then its darkening can serve as a symptom of carious damage to the tooth tissue under the crown).
Caries of the tooth root under the crown on an x-ray (Fig. 5-6) –
The best diagnosis of this process is to contact a dentist, who will be able to detect caries even on surfaces that are difficult to inspect. The onset of carious lesions on the root surface at the lower edge of the crown can be difficult to diagnose if caries occurs on the lateral surfaces of the tooth root, i.e. in the interdental space (24stoma.ru).
In the latter case, a targeted photograph of the tooth is taken (Fig. 5-6), in which caries under the crown looks like intense darkening, unusual for healthy tooth tissue. Keep in mind that early contact with the dentist in such a situation can sometimes allow the tooth to be treated and a new crown installed. Late treatment, on the contrary, brings you closer to tooth extraction.