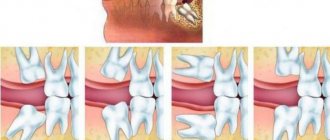
Fangs protruding from the dentition - the third pair of teeth, counting from the center - is a fairly common dental pathology, occurring in approximately 30% of dental clinic clients.
The canines are located at the corners of the jaws, directly behind the incisors, and differ from them in having a longer crown and root. Canine dystopia can manifest itself in different ways:
- their protrusion from a generally even row;
- hiding behind other teeth;
- an excessively long or, conversely, short crown;
- turning around an axis.
The “vampire smile” not only affects appearance, but also seriously impairs chewing function, and therefore requires qualified orthodontic treatment.
Formation of permanent teeth
Molars are formed from the epithelial dental plate. The appearance of their rudiments occurs only closer to the 5th month of fetal development inside the mother’s womb.
There are two groups of molars:
- Substitutes. This includes canines, incisors and premolars, which have temporary analogues.
- Additional. This group includes molars that do not have milk predecessors.
The growth of the primordial teeth of the replacement type occurs in the same alveolus as the temporary teeth; they are located behind the lingual surface of the primary teeth. Only after some time does the volume of bone tissue increase, ensuring their insulation.
Additional teeth are formed only after a year, since for this the jaw must reach the appropriate size.
Supernumerary teeth in children
The appearance of additional tooth buds is rare, occurring in only 2% of cases. The anomaly is associated with a disorder of embryonic development. A tooth that appears above a child's tooth is usually removed. But this does not always happen: if the tooth does not disturb the shape and aesthetics of the dentition, the dentist can leave it.
Sometimes supernumerary teeth are located outside the dental arch. The appearance of a tooth on the palate of a child is rare, however, this is no exception. There is no need to be afraid of this: it does not affect your health in any way. The Natadent clinic has a pediatric orthodontist who will help solve this problem quickly and painlessly.
At what age do they appear?
Statistics show that the beginning and completion of the change from temporary teeth to molars in most children occurs at approximately the same time. There are minimal differences only among children in different regions. The warmer the climate, the sooner the child will have permanent teeth.
The table shows age parameters that can be used to determine the approximate beginning of the eruption of molars according to several well-known authors.
| Set of teeth | Period of eruption of permanent teeth in children (in years) | ||
| according to Vinogradova | according to Lukomsky | according to Novak | |
| Central incisors | 5-6 | 6-9 | 6-9 |
| Lateral incisors | 7-9 | 7-10 | 7-10 |
| Fangs | 12-13 | 9-14 | 9-14 |
| First premolars | 9-11 | 9-13 | 9-13 |
| Second premolars | 9-11 | 9-15 | 10-14 |
| First molars | 4,5-7 | 7-8 | 5-8 |
| Second molars | 12-13 | 10-15 | 10-14 |
| Third molars | 18-25 | 15-24 | 18-20 |
The differences in the age at which permanent teeth appear depending on the author are due to the fact that they present the results of studies in different regions that were carried out with a serious difference in time (several decades).
Eruption of fangs in babies
The baby teeth in the baby’s mouth erupt in a certain order, according to which the eye teeth appear only after all the incisors and first molars. At the same time, the upper canines emerge somewhat earlier (at 16-18 months) than the lower ones (at 18-20 months). This rather late appearance of the eye teeth is explained by their deeper location in the jaw. And for the same reason, their teething is the most unpleasant for the child.
Most mothers know that the eye teeth are the hardest teeth for children. How long does it take for a baby to cut their fangs, the body temperature may be moderately elevated, and a runny nose may appear due to swelling of the oral and nasal mucosa. During this period, the child is very capricious, whiny, his sleep and appetite are disturbed. All this is a normal reaction of the child’s body to inflammation of the gums above the erupting tooth.
But if a child has a high temperature of up to 39 degrees or higher, accompanied by coughing, vomiting, diarrhea and general intoxication, it is important to remember that these are most likely not signs of teething, but symptoms of a serious illness.
How to relieve teething symptoms?
To make the appearance of a fang less distressing for the child, a number of methods can be used:
- Light gum massage . Using a clean index finger, gently massage the gum above the eye tooth for 1-2 minutes. It is advisable to repeat this procedure 2-3 times a day.
- You can let your baby chew on special teethers with a cooling effect , which should be placed in the refrigerator for a while before use. They are usually filled with sterile distilled water, so even if a child accidentally bites through the shell, it will not harm his health.
- with pain-relieving gels several times a day . They begin to act within a few minutes and relieve pain well over the erupting tooth.
- If the appearance of eye teeth is accompanied by nasal congestion, then to relieve this unpleasant symptom you can use children's vasoconstrictor drops (Otrivin, Nazivin, Quix).
- When the temperature rises above 38 degrees, it is necessary to take antipyretic drugs (Paracetamol or Ibuprofen), which are available in child-friendly forms: syrup or suppositories.
How many days such activities need to be carried out for each child is decided individually. In any case, you should consult your pediatrician.
Teething sequence
Almost all parents believe that the first molars should be incisors, which replace temporary elements of the dentition. But this opinion is wrong. Even before baby teeth fall out, at the age of 5-6 years, children receive their first molars, which are not on the list of primary teeth.
After this, the sequence of formation of a permanent bite is almost no different from the order of eruption of primary teeth:
- the lower and upper central incisors grow;
- lateral incisors appear on both jaws;
- lower and upper first premolars;
- fangs;
- upper and lower second premolars;
- second and third molars (you must understand that the so-called “wisdom teeth” sometimes do not penetrate the surface of the gums at all).
Teeth cutting in this order does not happen just like that, because it ideally corresponds to the speed of development and formation of the maxillofacial system. If the optimal sequence is followed, correct bite development occurs.
What teeth are called eye teeth?
Eyeteeth is a folk term, not a medical one. In common parlance, this is usually what the upper canines are called, and by analogy with them, the lower ones too.
Probably, the fangs received their special name due to the fact that next to them there are branches of the facial nerve, when irritated, severe pain occurs, spreading to the upper half of the face and radiating into the eyes. That is why, when a child develops baby eye teeth, it is accompanied by excruciating pain and other unpleasant symptoms. And because of this, removing fangs in adults is a very painful procedure that requires serious anesthesia.
Despite their name, eye teeth do not affect vision in any way. Although quite often dental patients express the opinion that if a fang is removed they can easily go blind, such a prejudice has no medical evidence and is erroneous.
Duration of growth
Typically, children say goodbye to their last temporary teeth at about 12-13 years of age, although the roots of baby teeth dissolve even earlier. By that time, the oral cavity already has molars that are actively growing, and their roots are at different stages of formation.
It is necessary to understand the approximate timing of growth and root formation in case of deviations. It is these indicators that are taken into account when choosing a treatment method.
Experts distinguish two main stages of development of the roots of permanent teeth:
- Stage of unformed apex.
- Unclosed apex stage.
At the first stage, the length of the root becomes maximum, but its walls are parallel to each other. The channel is of sufficient width; it ends in the area of the future apex with a bell. The periodontal gap can be seen only on the sides of the tooth root.
At the next stage, there is a gradual formation of the upper part of the root, the convergence of the root walls and the release of the periodontal fissure, the apical region of which is slightly enlarged.
Why do fangs erupt incorrectly?
In children, under the milk teeth in the jaw bone in the second row there are the rudiments of permanent teeth, and even deeper, in the third row, permanent fangs. Therefore, during the period of change in occlusion, the “three” canines erupt last, and the first permanent teeth become “sixes”, at the site of the eruption of which there were no milk teeth at all.
- If for any reason a child prematurely loses a milk “four” or “five,” the sixth tooth will move into the vacant space, and there will simply be no room left for the canine to erupt. He will have to crawl out either outside the row or on the palatal surface.
- The cause of pathology can also be crowding of teeth, caused by the small size of the jaw, when there is simply no room in it for the physiological placement of large complete teeth.
The completion of tooth root formation occurs at approximately this age:
| Teeth | Upper jaw, age | Lower jaw, age |
| Central incisors | 9-13 | 7-11 |
| Lateral incisors | 9-12 | 8-11 |
| Fangs | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| First premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| Second premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| First molars | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| Second molars | 14-15 | 14-15 |
Since the eruption of third molars does not occur at a specific time, it is impossible to establish a clear age at which their roots are formed.
X-ray results confirm the completion of the process of tooth root formation. The key signs are the absence of an opening at the apex, as well as a pronounced periodontal contour.
Thus, completion of dental growth, including full maturation, usually occurs only between the ages of 15 and 18 years. It is at this time that the maxillofacial apparatus already has the same dimensions as in adults.
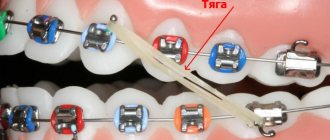
Features of canine correction with braces
The problem can be solved with or without tooth extraction. Both methods help to obtain the space that is missing, but necessary for the dystopic canine to be returned to its place. The choice of the optimal option depends on the clinical situation.
- If removal is not performed, free space is formed due to the gradual lengthening of the dentition with braces. The doctor must assess in advance how the process will affect the proportions of the face.
- If changes in appearance turn out to be negative (for example, the front teeth deviate noticeably forward), a pair of teeth will have to be removed - usually the first premolars.
There is no need to be afraid of removing completely healthy teeth. This method will be suggested by the doctor only if absolutely necessary - to improve chewing function, balance load distribution and maintain the health of the remaining teeth. Due to the free distribution of tooth roots, in this case a stable correction result that is not prone to relapse will be achieved.
Orthodontic patients often ask: is it possible to put braces on one jaw? Dystopic fangs are just that case. If there is a need for significant straightening of the canines with braces on the upper jaw and minor correction of the lower dentition, the lower bracket can be installed later, which is more financially beneficial for most patients.
Content:
- Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
- When do the first baby teeth fall out?
- Which baby teeth fall out first?
- Drop order
- At what age do radical units appear?
- Possible abnormalities in the child
- Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
As the child grows, the baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. This is a natural process, without which the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus is impossible. But parents should treat it with the utmost responsibility, since very often violations in the sequence of loss of temporary units cause serious malocclusions that have to be treated in the future.
Possible abnormalities in the child
Parents should know when to expect changes in their child's bite . Late change of baby teeth, like premature change, is undesirable. They speak of lateness when an eight-year-old child has not yet lost any of his incisors; they speak of early eruption if a five-year-old child has already lost many of his incisors and fallen out. It is important to find out the cause of the changes occurring and, if possible, eliminate it.
Factors due to which the bite changes earlier than standard periods:
- severe jaw injuries;
- congenital diseases leading to anomalies in the eruption of temporary and permanent units;
- advanced caries, due to which crowns and roots are destroyed faster than necessary.
As for a late shift, it is possible due to:
- rickets, calcium and vitamin D deficiency in the child’s body;
- hereditary characteristics of the dentofacial apparatus;
- some infectious pathologies.
Mouthguard as a preventive measure for the second dentition
In dental practice, mouth guards are worn by children over four years of age. At this age, the child is already consciously approaching wearing a trainer and can wear it for a long time. The device is made according to individual casts, taking into account the characteristics of jaw development. The material from which the mouthguard is made is soft and does not injure the mucous membrane.
From the age of two, children can wear removable plates to correct bad habits. If a child often sucks a pacifier or fingers, his bite does not develop properly. These children are more likely to have teeth growing in two rows. A soft plate will help avoid this.
In our clinic, parents trust doctors with their most valuable asset – their children. You can rely on our specialists in any situation. To confirm these words, we publish reviews from our grateful clients.
Natadent specialists know how to win over the youngest patients. Most guys leave the dentist's office without the same fears. True professionals in their field not only master their tools flawlessly, but also make every trip to them as comfortable as possible.