Home / Articles / Impacted fang
It has long been known that teeth can fall out too early and humanity is trying to combat this problem in every possible way. Recently, another problem of a slightly different nature has appeared - teeth began to erupt ahead of time, and this leads to another problem - an impacted tooth. Most often, this happens in childhood, while adults are faced with impacted teeth at the time of the eruption of the so-called “wisdom teeth” or eights. What is an impacted molar or canine tooth, why does it need close monitoring, and should it be removed?
Causes of impacted teeth
- Due to injury or damage to the jaw;
- If the child’s primary fangs were pulled out prematurely;
- Incorrect location of the tooth germ;
- Dental crowding, which means teeth are too close together;
- Inflammatory diseases of baby teeth and gums;
- The presence of “extra” teeth (supercomplete);
- Poor nutrition;
- Rickets;
- Exhaustion or weakness of the body.
The main prerequisite for the appearance of retention is the peculiarities of the child’s development in the embryonic period (lack of minerals in the body, thickening of the mucous membranes, low fetal growth rate).
Why do fangs erupt incorrectly?
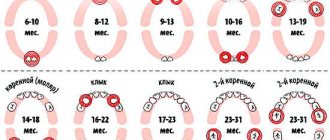
In children, under the milk teeth in the jaw bone in the second row there are the rudiments of permanent teeth, and even deeper, in the third row, permanent fangs. Therefore, during the period of change in occlusion, the “three” canines erupt last, and the first permanent teeth become “sixes”, at the site of the eruption of which there were no milk teeth at all.
- If for any reason a child prematurely loses a milk “four” or “five,” the sixth tooth will move into the vacant space, and there will simply be no room left for the canine to erupt. He will have to crawl out either outside the row or on the palatal surface.
- The cause of pathology can also be crowding of teeth, caused by the small size of the jaw, when there is simply no room in it for the physiological placement of large complete teeth.
Types of location of an impacted tooth
| Fine | The tooth has a vertical position and grows upward very slowly. Baby teeth and canines can grow properly. “Wisdom teeth” are rarely positioned normally. |
| Horizontally | The impacted tooth forms a right angle to the healthy one, located horizontally. This situation is detrimental to a healthy “neighbor”. In such a situation, it is necessary to remove the impacted tooth, which is performed only surgically. |
| Obliquely | An impacted tooth grows at an angle toward the cheek or tongue. If such an anomaly does not cause inconvenience to a person, then removal is not necessary. |
Contraindications to the procedure
The list of contraindications for removing a fang on the upper jaw includes:
- Cardiovascular pathologies – myocardial infarction (suffered earlier six months ago), bacterial endocarditis, hypertension.
- Diseases of the urinary system - pyelonephritis in the acute stage, glomerulonephritis, renal failure.
- Diseases of an infectious and viral nature - hepatitis, acute respiratory infections, influenza and other pathologies transmitted by airborne droplets.
- Exacerbation of psychological problems - manic psychosis, epilepsy.
- Pregnancy at 1, 2 and 9 months.
- Poor clotting .
- Cancer – acute leukemia.
- Malignant tumors located in the maxillotemporal zone.
Symptoms of tooth impaction
In most cases, an impacted tooth is detected on an x-ray at the dentist or at an appointment with an ENT doctor. Retention in a child can be determined if one of the elements of the jaw row is absent for a long time or if a baby tooth is not replaced by a permanent “brother” for too long. The eruption of an impacted tooth is usually accompanied by inflammatory processes. The child may be bothered by swelling of the gum tissue and jaw, pain and aches, numbness and tingling in the retention zone.
On palpation of the gums, thickening and hardening are noted, reminiscent in shape and outline of an unerupted tooth.
Features of the procedure
The canines on the upper jaw have one root located laterally. In cross section, part of the element resembles the outline of a triangle. In 30% of cases, the apex of the canine root has a curved structure. The outer part of the root is thicker than the inner one, but both sides of the alveoli are thicker in width than the incisors. Due to the listed features of the structure of the fangs, some difficulties arise when removing them from the socket.
During the operation, the doctor should place the fingers of the left hand in the same way as when removing incisors on the upper jaw. When removing an element from the right side, the patient's head should be slightly turned to the left and vice versa. This position of the patient will be more comfortable at the time of surgery.
The canines on the upper jaw are removed from the socket using wide forceps. During the operation, the element swings alternately towards the lips and palate with rotation around the longitudinal plane of the fang. The doctor makes the first movement of the instrument towards the outer wall of the alveoli, since it has a thinner structure.
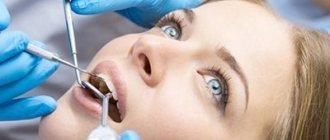
Preparation and stages of tooth extraction
The next dislocation is performed towards the palatine alveolus, and then the specialist performs rotations. The procedure consists of successive rocking and rotation of the element until the nerve fibers and tissues surrounding it are completely ruptured.
Due to the anatomical features of the canines on the upper jaw, when extracting them, a specialist has to make a lot of effort.
Removal of impacted teeth
If there are no complaints at all about the impacted tooth, and it does not cause any inconvenience (cysts do not form near it, the mucous membranes of the mouth are not injured), then removal may not be necessary. But if the impacted tooth is not removed, then it is necessary to undergo an X-ray examination of the mouth 2 times a year.
However, there are a number of cases when it is necessary to remove an impacted tooth:
- Retention causes constant inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- The occurrence of various paradental or follicular carpal formations, abscess, osteomyelitis in the gum tissue;
- Injuries and scratches of the oral mucosa that are caused by retention;
- An impacted molar or canine is also dystopic (improperly positioned in the dental arch) towards the cheeks or tongue.
The main factors on which the decision is made to remove impacted teeth are:
- The likelihood of injury during surgery,
- The location of the canine or molar and ease of access to them,
- Possibility of complications.
In most cases, the operation is painless and eliminates the possibility of pain even after the anesthesia wears off.
The removal of an impacted tooth itself takes place in several stages:
- pain relief by local anesthesia,
— an incision in the gum above the impacted canine and removal of a flap of tissue of the mucous membrane and periosteum,
- sawing out the bone to the dental crown using a drill,
- removal of a fang or molar from the bone using forceps (special biomaterials are left in its place).
Removal of premolars located on the upper jaw, canines and molars of the lower jaw has its own characteristics:
- Due to the fact that the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw are sometimes located close to the sinus, their removal must be carried out with the utmost care.
- In the case where the maxillary sinus has nevertheless been opened, medical treatment of the hole is not carried out, and the place where the bone has been broken is immediately sutured.
- Then a biomaterial is placed inside, which will promote rapid and painless overgrowth of bone tissue.
- The previously removed flap of mucous tissue and periosteum is returned to its place and sutures are applied.
- When removing impacted teeth in the lower jaw, the dentist must determine their location as accurately as possible, calculating their proximity to the mandibular canal. The safest way to access such teeth is through the vestibule of the mouth.
How is tooth extraction performed?
Before removal, the doctor conducts a survey to find out if the patient is allergic to anesthetics and medications. The doctor also asks the patient about the presence of trophic diseases (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis) and pathologies of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, arrhythmia, etc.). This is necessary for the correct selection of anesthesia.
Then the doctor administers anesthesia (usually conductive torus for the lower jaw and infiltration for the upper jaw) and waits for the effect to occur.
Simple removal consists of 5 steps:
- applying forceps to the tooth;
- moving them so that the cheeks are under the gum;
- tool fixation;
- luxation (swinging) - necessary to detach the periodontal ligament, which holds the tooth in the bone;
- traction (luxation) - removal of a tooth from the alveolus. This is done by tilting the tooth in the direction of least resistance (where the alveolar wall is thinner) and simultaneously pulling the tooth outward.
For complex extractions, the doctor uses an elevator - a chisel-shaped instrument with a pointed end, which is carefully inserted into the hole and, with its help, pushes the tooth out from the top of the root.
In the process of atypical removal, a surgical field is formed: the doctor dissects the mucous membrane, peels off the flap with the periosteum and removes the bone substance located above the tooth. The tooth itself is removed using an elevator, but often during the removal of wisdom teeth, the doctor is forced to saw it into pieces with a drill, extracting each root and crown separately.
Start of orthodontic treatment
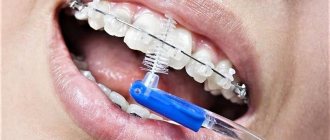
Before installing braces, the patient must undergo professional teeth cleaning by a hygienist. The specialist cleans the teeth, removes all plaque (soft and hard), checks the condition of the gums, polishes the enamel and gives recommendations on how to care for your teeth while wearing braces. Patients who decide to start treatment with braces receive a starter hygiene kit, which includes an orthodontic brush, toothpaste, brushes, dental floss, monobrush, and wax.
Damon metal braces are fixed:
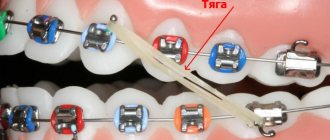
Treatment with braces at this stage is aimed at expanding the dentition in the areas of the 2nd and 4th teeth (special springs are installed on the brace system).
After 5 months, the next stage begins - the return of the fangs to the dentition. The second arch holds the anterior incisors in a stable position.
Stage of wearing orthoelastics (12 months after fixing braces):
Is it possible to put braces on fangs?
Dystopia can and should be corrected for both a five-year-old child and an adult. The question of how this can be done will be decided based on the complexity of the anomaly formed, the degree of its neglect and, of course, the age of the patient.
If the reason for the lack of space is an erupted wisdom tooth, you will have to get rid of it to get the necessary free space in the jaw. You can install metal or sapphire braces, which will move the canine to the place of the least valuable, previously removed first premolar. Finally, surgery may be performed to reposition the displaced eye tooth.
Even the best braces in Moscow will not make the correction process quick. The easiest way to return the fangs to the correct position is for 14-15 year olds. How long do adults need to wear braces ? At least 1.5–3 years - it all depends on the type of orthodontic structure, the material of the clasps and the patient’s dental characteristics.
Removal of lower incisors
Removing the lower incisors is the easiest procedure. Due to the fact that the incisors have only one flat root. The presence of additional roots in these teeth is extremely rare. Removal occurs under local anesthesia. During this procedure, the patient takes a sitting position. The doctor's hands securely fix the patient's jaw. In such cases, the surgeon uses beak-shaped forceps. First of all, the tooth begins to dislocate in the labial side, and then in the lingual side, a slight rocking is allowed.