Injuries to teeth and gums are common among children of all ages. If a child breaks a baby tooth, then first of all you need to remain calm and competently provide pre-medical care, while trying not to scare the baby. Most often, children are injured when they accidentally fall or when trying to chew hard food or an object. Therefore, children of primary preschool age, who are not yet accustomed to being careful, are most at risk; they may fall hard on the playground or injure their oral cavity with a foreign object.
Symptoms
To suspect that a child has broken a front tooth is quite simple:
- Violation of the shape and integrity of the dental crown. Upon examination, you may notice a chipped tooth and a defect;
- Appearance of a crack. Characteristic of an incomplete fracture, part of the tooth may wobble, but not break off;
- Strong pain. The pain can be localized in the tooth, gum, or even spread to the entire jaw, depending on the severity and nature of the injury. Pain in the jaw occurs with impacted fractures, which are most often the result of trauma. Young children who cannot say what happened begin to cry and refuse food;
- Swelling, redness, bleeding of the gums. In some cases, the fracture is also accompanied by injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity. In severe cases, pathological mobility of adjacent teeth may appear.
Prevention of childhood dental injuries
First of all, it is important to instill in children a sense of caution from an early age. You should teach your child to fall safely, placing his hands correctly, and to take care of especially vulnerable places. When playing sports, you should use a helmet to avoid injury. It will protect not only your head, but also your teeth. If the helmet is not provided for by the uniform, you can get by with a mouth guard. It is recommended to order a mouthguard individually based on impressions of the child’s teeth, then it will accurately replicate the anatomy of the jaw and reliably protect against damage.
What complications can there be?
The main complications of fractures of primary teeth are:
- Formation of a malocclusion (if a broken tooth has fallen out or been removed);
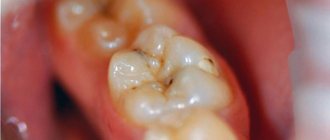
- Pulpitis. Damage to the enamel and tooth crown facilitates the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the pulp, where after some time an inflammatory process can develop;
- Periodontal abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis and other purulent complications. They are a consequence of advanced infection after tooth trauma.
If a child breaks his molar front teeth, it is important to make sure that the roots of the teeth are not damaged. Injury or fracture of the root of a permanent tooth is dangerous because the tooth may have to be removed from the roots, and expensive implantation will be required to restore the dentition.
Tooth dislocation in a child
It is not always possible to determine a dislocation on your own. Parents are required to examine the baby after an injury. If the tooth is rotated or tilted, there is no need to try to put it back in place. This way you can hurt the child. You need to see a doctor as soon as possible. He will determine the condition of the tooth root and decide whether to remove it or save it.
At the same time, if the crown is visually intact, it is possible that the root could have broken as a result of injury. This damage is not visible upon inspection. It can only be determined by an x-ray in a clinic. In some cases, it is possible to save the tooth and avoid removal.
How are they treated?
The dentist determines treatment tactics depending on the severity of the injury and the condition of the tooth. The following methods are used:
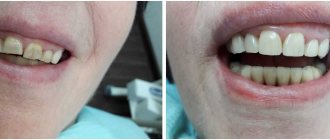
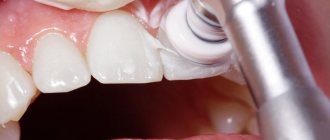
- Tooth restoration. Suitable only in cases where a small piece of the tooth has broken off and the pulp is not involved in the pathological process. Various types of composite materials are used to restore the integrity and normal appearance of the tooth;
- Depulpation. This procedure is used for more severe fractures when the child has symptoms of pulpitis. The process removes the infected pulp, which allows you to save the tooth and prevent the child from developing a malocclusion;
- Delete. A radical measure that is used in cases where it is no longer possible to save the tooth.
If a child knocks out a baby tooth, what should you do?
In a situation where a child breaks a tooth at the age of 1, there is no need to panic. You need to calm the child, pick him up, examine the oral cavity and try to find a broken or knocked out tooth. If it comes out intact with the root, it is necessary to protect the wound from infection by applying a sterile swab. For prevention, you should see a dentist. If a small piece is broken off, and even more so a red dot is visible, you need to immediately go to the dentist and have treatment. The procedure will be similar for older children with trauma to their baby teeth.
First aid
If you see a small chip on a tooth, but nothing bothers your child, then make an appointment with the dentist as planned. Many parents do not know what to do if their child breaks a front molar. Your actions should depend on the child's condition. If there is bleeding from the gums and severe pain, then you need to immediately go to the nearest dental clinic to see a doctor. If there is slight pain, but overall health is not affected, then you can give an anti-inflammatory drug (for example, paracetamol) in an age-appropriate dosage and make an appointment with a doctor the next day.
What to do if a child breaks a tooth?
The front incisors are especially affected. The cause of injury can be blows, falls, careless games with peers. The doctor’s tactics depend on how exactly the tooth broke:
- If a piece breaks off, a red dot is not visible upon examination, that is, the pulp is not open, you need to visit the dentist as soon as possible and have the chip filled. Without protection, fabrics will deteriorate.
- If a red dot is visible when the chip is chipped, it means that the pulp has been exposed as a result of injury. Contacting a dentist should be urgent. Before visiting the doctor, do not give your child hot or cold drinks.
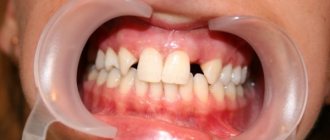
- If it is broken to the gum edge, it is worth looking for the broken piece and determining whether the root has fallen out or whether it remains in the hole. In any case, visiting a doctor is mandatory.
- If a tooth is knocked out, you can put it back in the socket within 5-10 minutes and after that go to the dentist. You can treat the root with saline solution or clean water, but not with alcohol or peroxide. The dentist will secure it to the adjacent ones with a splint so that it does not fall out. After some time, the tooth will become fixed in the jaw. This tactic is especially used in a situation where the front standing unit is knocked out.
- If the tooth is mobile, but there is no visual change, the help of a doctor is also urgently needed. You can break only the root, but the fracture will be deep in the tissues and the tooth will remain in place, but will be mobile.
Thus, no matter whether one unit is damaged or several, no matter how badly it is damaged, you need to visit a pediatric dentist. He will already tell you what to do in a specific situation and how the recovery process will go.
Why do chips appear on teeth?
Enamel is a durable transparent fabric. It reliably protects the tooth from destruction. However, there are a number of reasons why it may still break:
- eating too hard food
- mechanical injury (fall, blow)
- damage (cracks) in the enamel
- malocclusion
- untreated caries or incorrectly installed filling
- hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles
- partial absence of teeth, due to which the remaining ones are heavily overloaded
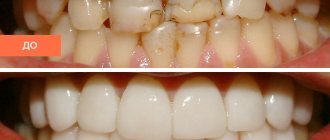
If a piece of a tooth breaks off, you need to seek help from a dentist, because over time, even a small chip can grow larger. The doctor will restore the beauty of your smile and comfortable eating, relieve psychological discomfort and increased sensitivity of teeth.
Damage to hard dental tissues
- Ifraction of enamel. It is a crack on the surface of the tooth without loss of dental tissue.
- Fracture within the enamel. Belongs to the category of chips without complications, but with the loss of some tissue.
- Enamel-dentin fracture. The fracture has no complications, and is distinguished by the passage of the chip line simultaneously along the enamel and dentin. Part of the dental tissue is lost.
- Enamel-dentin-pulp fracture. Refers to the number of fractures with complications, which result in exposure of the pulp.
Doctor's actions in the clinic
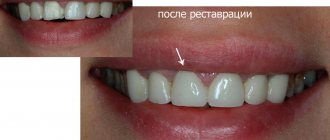
If the parents manage to bring in a broken tooth, the dentist performs hygienic treatment of the oral cavity, puts the tooth in its original place and fixes it. If a tooth is missing, cosmetic restoration is performed using photocomposite materials, a crown or a prosthesis, which replace the missing part of the tooth. When the child grows up and reaches adulthood, dental implantation can be performed.
Pediatric dentists at our clinic are professionals in aesthetic restoration of children's teeth. We carry out procedures taking into account the structural features of the child’s jaw, so that in the future it will form correctly. Thanks to the latest dental equipment of the clinic, we can restore teeth that have been destroyed almost below the gums - so that the new ones are indistinguishable from the real ones.
Tooth fracture - symptoms and treatment
Transverse (horizontal) fracture
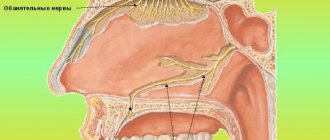
In case of a fracture of the crown part of the tooth without damage to the pulp, caries may develop in the absence of treatment and subsequently pulpitis and periodontitis. In case of a fracture accompanied by exposure of the pulp, acute pulpitis is a complication. The occurrence of pulpitis is accompanied by pronounced pain in the area of the causative tooth with irradiation (spread) along the branch of the trigeminal nerve to the area of neighboring teeth or antagonist teeth. The pain mainly occurs at night. Without appropriate treatment, acute pulpitis can turn into chronic pulpitis, and later into periodontitis, characterized by the symptom of an “overgrown tooth” (the feeling that a tooth has come out; you cannot bite on it, as it causes pain). You can clearly identify the causative tooth by performing percussion - tapping on the tooth. Pain also occurs when eating hot food.
In the absence of treatment, after some time the process of pulp sclerosis begins - degeneration, pulp atrophy, its replacement with connective tissue. As a rule, there is no acute pain at this stage, but chronic inflammatory processes - osteitis or radicular cysts - begin to develop in the bone surrounding the tooth.
Vertical tooth fracture
This injury is incompatible with the continued existence of this tooth in the alveolus. Without treatment (in this case it involves tooth extraction), the situation leads to the rapid development of an inflammatory local process - dental periodontitis, which can later develop into periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), osteomyelitis (chronic inflammation of the bone, which leads to resorption of bone tissue in the area of the lesion). ) and into extensive inflammation of soft tissues - an abscess of the maxillofacial area.
In this case, a purulent infiltrate appears around the tooth, melting the surrounding tissue. The patient's general condition worsens, the temperature rises, and swelling of the buccal or submandibular area occurs. Without appropriate treatment (tooth extraction, opening of periostitis or abscess), the process quickly becomes diffuse. In this case, phlegmon of the soft tissues of the face and neck may occur. Such a rapid and dangerous course of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity is due to the structural features of the cellular spaces of the face and neck. Cellular spaces are located between the muscle fascia. They are loose connective tissue. A distinctive feature of this tissue is the rapid development of purulent inflammation in it, which then spreads to nearby muscles and tendons.
Complications of a fracture also include resorption (external and internal) of the tooth root after injury. It appears after a few months. Resorption can be in the area of the apex (apex) of the root or in the area of the tooth root fracture. It occurs due to the lack of a “replacement callus”, which should restore the tissues of the tooth root - dentin and cement. The symptoms are quite sparse. This may be tooth mobility or pain when biting on a tooth. As a rule, it is possible to clearly diagnose resorption after an X-ray examination. This situation is a late complication of a tooth fracture. The tooth must be removed [9].