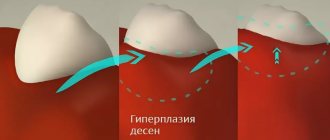
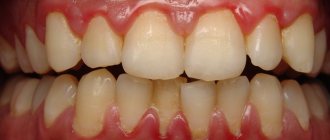
Gingival fibromatosis is an overgrowth of gum tissue. A typical manifestation of fibromatosis is hypertrophy of the gum edge or its entire surface. Gum tissue affected by fibromatosis is quite dense and has a pale pink tint combined with a roll-like shape. This pathology is most typical for young patients, as well as for children during the period of eruption of molars that replace milk teeth.
Fibromatosis is twice as common in women. Patients complain of enlargement and growth of gum tissue, as well as plaque accumulating on the teeth and under the gums. Minor bleeding is often observed during meals. Treatment for this type of pathology in most cases consists of surgical excision of the overgrown gums.
Reasons for appearance
Fibroids on the gums most often appear in children under 10 years of age and adolescents. In adults, the pathology is less common. The growth of a tumor can be provoked by the following factors:
- permanent tissue injury from fillings, artificial crowns, dentures, solid food,
- stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis,
- taking certain medications - estrogens, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine.
In children and adolescents, the growth of fibroids is usually due to a hereditary predisposition; in adults, it is caused by injuries to the mucous membranes.
Causes of gum fibromatosis
Gingival fibromatosis is a genetically predetermined pathology characterized by a dominant type of inheritance. The main cause of the pathology is a mutation of the SOS1 gene. In addition to genetically determined fibromatosis, there is also a form of the disease that arises as a result of long-term use of certain types of medications. For example, inflammation of the gums and interdental papillae of the marginal type occurs in those who take medications for epilepsy, as well as as a result of taking immunosuppressants and calcium channel blockers.
It is also possible that fibromatosis may occur while taking hormonal contraceptives, which in some cases lead to hypertrophy of the gum tissue. Some experts associate the manifestations of fibromatosis with diseases of the endocrine system. Some hypertrophic changes in gum tissue are also characteristic of Down syndrome.
Symptoms
A benign tumor forms slowly and does not cause discomfort, so it may remain undetected for some time. If the fibroma reaches a large size and is constantly injured, the following may occur:
- swelling and redness of the gum tissue,
- discomfort and pain of varying intensity.
Constant trauma to the tumor can lead to the beginning of active growth and transition to a malignant form, infection, loosening and tooth loss. Therefore, at the first signs of fibroma, it is important to consult a doctor.
Types of diseases and their characteristics
The pathological process is more often diagnosed in adults, but this is also possible in childhood. There are two main types of hyperplasia:
- Limited. The second name is focal, it is diagnosed in the case of an increase in the volume of tissue in a small area (affects 1-2 teeth). The clinical picture develops slowly, the color of the mucous membrane does not change, and there is no pain. The gums can cover the tooth only 1/3 of its height.
- Generalized. It is characterized by the presence of several areas with a pathological process at the same time, often they merge together. There are no clear boundaries of the overgrown tissue; a large number of tubercles can form. The clinical picture is aggravated: the patient complains of a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the mouth, pain, discomfort during chewing, and a change in diction.
Gum growth occurs slowly, the clinical picture is often blurred. To carry out effective treatment, it is necessary to identify the problem in time. Often, a limited type of gum fibromatosis transforms into a generalized one over time.
Symptoms of hyperplasia in dentistry, stages of progression
Regardless of the type of disease, dentists identify 5 symptoms of fibromatosis:
- increase in gum volume, its visible growth;
- filling the interdental space;
- hiding the crown part of the tooth by lifting the gums;
- a denser structure in places where it increases;
- pale gum color.
The listed symptoms are not necessarily present at the same time; it all starts with a slight enlargement of the gums. Pain and discomfort bother you much later, when the process has already started. The severity of the clinical picture depends on the stage of severity of the disease:
- the first stage - the cushion between the teeth is visually determined, does not present any inconvenience;
- the second stage - the gum tissue grows by half of the tooth root, the increase in volume is determined visually;
- third stage – the tooth enamel is almost completely hidden behind the overgrown gum tissue, the structure becomes smoothed and dense, and bleeding develops.
It is highly advisable to seek dental help at the first stage of the disease so that treatment is quick, effective and without complications.
Treatment methods
Fibroids on the gums are usually removed with a laser or radio wave method. The operation lasts up to 40 minutes. If the neoplasm is large, to prevent deformation of the mucosa, the wound surface is covered with a flap formed from adjacent tissues.
If fibroma is formed due to tissue injury from a filling, crown or prosthesis, you can do without surgery. The tumor may shrink or disappear after the provoking factor is eliminated. In this case, treatment includes refilling or replacing the prosthesis.
Tooth cyst
A dental cyst is a formation resembling a capsule, localized in the area of the apex of the root canal of a problem tooth, in the bone tissue of the jaw. Standard sizes
neoplasms -
from 0.5 to 2 cm
. Contents: serous exudate. The shell consists of connective tissue.
Causes of cysts:
- Dental or somatic diseases (for example, sinusitis, sinusitis).
- Chronic periodontitis - the root membrane and peri-root tissue become inflamed.
- Consequence of traumatic injuries.
Types of cysts
Dentists distinguish several types of such neoplasms. A cyst happens:
- Radicular
, located next to the root of the tooth. In the vast majority of cases, this is a consequence of inflammatory processes (for example, periodontitis). - Follicular
, adjacent to the crown. Formed when a formed but not yet erupting tooth bud becomes infected. - Paradental
. It is typical for heavy growth of the eighth molars - the tissues become inflamed, the process is difficult. - Teething
. Occurs during the period of change from primary teeth to permanent ones. - Retention cysts
are formed as a result of the outflow of secretions in the salivary glands. Typical localization is the sublingual area, mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips, and bottom of the tongue. - A keratocyst
occurs during pathological primary development of the unit. - Residual
- a consequence of complex or poor-quality tooth extraction.
Symptoms
The initial stages of cyst formation are asymptomatic. The first signs appear when the cyst has already reached a fairly large size - 0.5 cm or more. The capsule puts pressure on the tissue, and vague sensations begin, causing discomfort.
An increase in formation leads to painful sensations that do not go away after taking analgesics. When intensive formation of pus occurs in the capsule, the pain intensifies and swelling appears. Sometimes the temperature rises. Symptoms of a mature cyst are a fistula in the gum, gumboil.
Treatment of cysts
Dentists try to save the tooth, so they choose gentle techniques in each case. Deleting a unit is possible only in advanced or exceptional cases.
Therapeutic methods:
- Antiseptic treatment. In case of a cyst or granuloma, purulent exudate is pumped out of the cavity and disinfectant and anti-inflammatory drugs are administered.
- Using a laser. The beam not only removes the formation, but also has a disinfecting effect on the tissue.
Surgical methods
applicable if the cyst is located in a dangerous place, or its size is quite large (more than 2 cm, usually 3-4 centimeters). The surgeon opens the cyst, removes the pus, injects an antiseptic, and sutures it. Less commonly, the front part of the capsule or the neoplasm with the root of the tooth or its fragment is removed.
Mechanism of development of hyperplasia
The mechanism of development of the hypertrophic process remains not fully understood. However, scientists have discovered that the pathogenesis of the disease is influenced by impaired calcium transport. This leads to increased production of collagenase, which causes the gums to grow. Hyperplasia develops gradually, so patients do not pay attention to it right away.
Stages of the disease:
- First: the tissue covers a third of the tooth, there are no signs of an inflammatory process.
- Second: covers half of the tooth, bleeding may occur, especially with mechanical impact.
- Third: overlap from two-thirds to the entire crown, sometimes even the cutting edge and chewing surface are covered with soft tissue, granulations are visible over the entire surface.
Signs of oral fibroma
Fibroma looks like a pink hemispherical formation, rising above the general surface of the mucous membrane and having a wide, strong base or thin stalk. Fibroids do not cause pain. Its surface is smooth and does not have any growths, unlike papilloma. As a rule, no changes in tissues and mucous membranes are observed in the area of the fibroma, but in some cases ulcerations may appear over the neoplasm. In this case, an infection develops followed by inflammation, expressed in redness, swelling and pain in the area where the fibroma is located.
A standard fibroma in the oral cavity grows slowly, almost unnoticeably. And if it is constantly exposed to trauma, then the growth of the tumor may slow down, and the tumor itself will be within the initial stage of development. It is worth considering that constant injuries lead to complications: the tumor degenerates into a malignant one.
Fibroma looks like a pink hemispherical formation, rising above the general surface of the mucous membrane and having a wide, strong base or thin stalk. Fibroids do not cause pain. Its surface is smooth and does not have any growths, unlike papilloma. As a rule, no changes in tissues and mucous membranes are observed in the area of the fibroma, but in some cases ulcerations may appear over the neoplasm. In this case, an infection develops followed by inflammation, expressed in redness, swelling and pain in the area where the fibroma is located.
A standard fibroma in the oral cavity grows slowly, almost unnoticeably. And if it is constantly exposed to trauma, then the growth of the tumor may slow down, and the tumor itself will be within the initial stage of development. It is worth considering that constant injuries lead to complications: the tumor degenerates into a malignant one.
Gum cancer
This dangerous neoplasm is worth highlighting separately. Mutation cells begin to divide uncontrollably, which is why a red tumor forms on the gum. The disease progresses quickly and over time can develop into jaw cancer.
What are the symptoms?
- General weakness;
- increased body temperature (37 C°);
- loss of appetite;
- constant drowsiness.
The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis after a detailed examination. As a rule, treatment is long and painstaking. With timely medical intervention, the outcome is favorable.
Manifestations of the disease
The following clinical symptoms allow you to recognize gum fibromatosis:
- In the initial stages, swelling or enlargement of tissue of a tumor nature.
- On the mucous membrane you can see thickenings that gradually increase.
- Increased gum volume without signs of swelling.
- Filling interdental spaces with soft tissue.
- Overlapping of the teeth with the edges of the gums.
- Injury to overgrown areas during cleaning (this can cause bleeding and inflammation).
- Increasing intensity of tissue color (the gums become bright pink).
If you notice any signs of fibromatosis, you should immediately contact your dentist. If you ignore the problem, unpleasant complications may develop:
- decreased quality of daily hygiene with an increased risk of developing infections;
- pain when eating;
- redistribution of chewing load;
- development of periodontal diseases.
Complications
If a lump appears on the gum, you should immediately consult a doctor. Otherwise, pathological processes worsen, which can provoke various complications. Among them:
- infectious processes (cellulitis, abscess, likelihood of developing sepsis);
- loosening and loss of healthy teeth;
- malignant degeneration of growth tissue.
Lack of treatment for the appearance of fibroids can lead to dangerous consequences. However, with timely treatment the prognosis is favorable. As for prevention, proper oral hygiene, exclusion of traumatic factors, regular preventive examinations with a doctor, and timely treatment of identified dental diseases will help reduce the likelihood of a benign growth.
If left untreated
In almost all cases, the disease leads to the appearance of associated problems, which are considered complications in dentistry. Enlargements of the interdental papillae and gum margins lead to the formation of deep periodontal pockets.
Food debris can accumulate in them and bacteria can grow. It is impossible to empty the pockets yourself.
Such a complication very quickly degenerates into tartar, which causes inflammation of all tissues. Sometimes they detach from the tooth, which causes trauma.
The disease at stages II and III leads to bone atrophy in the affected areas of the upper jaw, osteoporosis, and destruction of the partitions between the teeth.
Loosening of the teeth, decay of the alveolar processes are observed, and dystopia develops (displacement of the teeth towards the tongue, cheeks, or rotation around its axis).
If the disease progresses in children, then there may be a delay in the change of bite and germination of permanent (molar) teeth, which in the future will adversely affect the development of the dental system.
Forms
There are 2 forms of this pathology. They differ from each other only in the area of damage to the oral cavity.
Focal
The second name for this form of fibromatosis is limited. This is a fairly rare form of the disease that progresses slowly. With it, only those tissues that are localized in the area of the tubercle of the upper jaw grow.
In isolated cases, such growth appears on the lingual part of the (inner) gum near the lower jaw. They do not differ in color from healthy tissues and are painless.
Why is it so important to sanitize the oral cavity during pregnancy? We'll talk about this in our article. In the following review you can read about how to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
The areas that have increased in size have a rounded shape and a fairly smooth surface with a dense, uniform consistency. The formations are covered by a third of the crown of the teeth (less often completely).
They prevent the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. Pathology threatens the collapse of the partitions between the teeth and the development of osteoporosis.
Generalized
This form is characterized by the formation of several pathological areas at once. Gradually increasing in size, they unite into one large lesion. As a result, the crowns of the teeth are almost completely covered by overgrown tissue.
The generalized form is of 2 types:
- diffuse – tissue growth occurs uniformly;
- nodular - overgrown tissues have a large number of nodules.
The development of the disease occurs slowly. Having grown, the pathology becomes a serious obstacle to the correct implementation of oral hygiene procedures and interferes with normal nutrition, since these tissues interfere with biting and chewing food.
Over time, both forms of the disease turn into a serious cosmetic defect that affects the psychological state, developing depression.
Growth on the gum: how to treat
The treatment plan is developed by the doctor based on the nature of the growth, so in no case should you self-medicate. It is important to understand that if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, serious complications can arise.
If the cause is an infection, then it must be removed. In case of periodontal inflammation, professional oral hygiene is performed. If the cause is periodontitis and complicated pulpitis, then first the lump is opened and pus is pumped out of it, and then conservative or surgical treatment is carried out.
If there is no pain, for example, with epulis or ecostosis, then the decision about surgical intervention is made together with the patient.
Varieties of epulis
Conventionally, there are 3 types of epulis:
- Fibrous. The neoplasm is dense, the basis is coarse fibrous tissue. Characterized by slow growth. There is no pain or bleeding.
- Angiomatous. The tumor contains a large number of blood vessels and is localized mainly in the lateral parts of the jaw. With this form of the disease, bleeding is observed even with slight pressure, for example, with a toothbrush or food. When pressed, the tumor is painless and has a soft consistency.
- Giant cell. The tumor can reach large sizes, displacing teeth that are located in the epulis growth zone. The mucous membrane of the epulis is bluish-red in color. On palpation, the neoplasm is painless, but may bleed moderately if injured.
Depending on the nature of the process, epulis can be benign or malignant. In the first case, the neoplasm is characterized by slow development and, as mentioned above, in most cases does not cause pain. The tumor size in this case rarely exceeds 10–20 mm. When the process becomes malignant, rapid tissue growth is observed. In this case, the process is often accompanied by pain, bleeding gums and affects the root canals of neighboring teeth.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
How to diagnose and how to treat gum hyperplasia?
The diagnostic algorithm is focused on not confusing the disease with other pathologies. Therefore, the examination should be trusted only to a qualified dentist. The Nurimed Clinic offers a modern algorithm for confirming hypertrophy:
- examination of the oral cavity (allows the doctor to suspect a problem);
- X-ray examination to exclude similar pathologies;
- histological analysis of tissues taken for biopsy (a conclusion on the benign quality of the process and cellular composition is required).
After confirmation of the diagnosis, which is impossible without histology, treatment of gingival hyperplasia is carried out. Modern dentistry offers safe, painless surgical removal of overgrown gum tissue. The dentist peels off and removes excess tissue, after which the mucous membrane is sutured. This procedure is considered minimally invasive and does not require special recovery. In some cases, the dentist prescribes a number of medications to prevent complications.
An additional stage of treatment is sanitation of the oral cavity. Manipulation allows you to eliminate infectious processes that could cause hyperplasia. Also, professional cleansing can reduce the risk of inflammation and relapse of hypertrophy.
In the case of drug-induced fibromatosis, it is recommended to consult with your doctor and, if possible, change medications. To prevent re-growth, the cause of hypertrophy must be eliminated: the bite is corrected, tartar is removed, inflammation is treated, the balance of hormones is controlled, and so on.
Types of oral fibroids
- Dense (hard) fibroma . The formation consists of coarse connective tissue fibers containing a small number of nuclei, tightly adjacent to each other. This type of fibroma is most often located on the gums or hard palate.
- Soft fibroma . The neoplasm has a softer structure due to the formation of thin and loose fibers, the structure of which contains a large number of nuclei. This tumor is localized on the tongue and inside the oral cavity on the cheeks. In some cases, mixed neoplasms such as fibrohemangiomas or fibrolipomas may occur.
- Fibroma from irritation . This neoplasm is not a tumor and is quite common. It develops as a result of damage by mechanical or chemical means. This fibroma is located on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and looks like a pink papule with clear boundaries. As it grows, a dense, rounded nodule appears. With constant trauma to the fibroma, lumpiness and ulceration may appear on its surface.
- Symmetrical bean-shaped fibromas with a dense consistency are usually located near three molars on the surface of the gums of the upper jaw. Such a tumor is not a true fibroma, but is an overgrowth of the gums and is accompanied by tissue scarring.
- Lobular fibroma . This neoplasm is distinguished by a lumpy surface that occurs as a result of reactive hyperplasia of the gum tissue when it is regularly injured, for example, by a removable denture.
- Fibrous epulis . This neoplasm of dense consistency is located on the gums and has slow growth.
Diagnosis of fibroids of the upper and lower jaw
The doctor will not prescribe treatment until he is sure that the diagnosis is correct. To do this, diagnostic procedures are carried out, the results of which will confirm or refute the fears of doctors.
First, the patient is asked to describe the symptoms. The dentist examines and palpates the tumor. However, this is not enough to develop therapeutic tactics, since it is extremely important to determine the depth of tumor growth into soft tissue. For this purpose, an ultrasound examination is performed.
In difficult cases (ulcers, development of an inflammatory process in a pathological area of the gum, etc.), a biopsy is indicated. After surgical removal of the tumor, fragments are necessarily sent for histological analysis.
The examination is necessary not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to identify the factors that provoked the disease. A full dental examination is carried out to confirm the presence of inflammation. In addition, one cannot do without radiography, orthopantomogram and other images in different projections.
If a person has dentures, a consultation with an orthopedic dentist may be necessary. This is necessary to eliminate the possible traumatic effects of artificial elements on the mucous membranes.
Differential diagnosis
Biopsy remains one of the most informative methods for distinguishing fibroids from other benign neoplasms. The study is indicated for suspected papilloma, lipoma, epulis of various structures, neurofibroma, cyst, squamous cell carcinoma, wart, etc.
If the growth is localized on the tongue or sublingual part, it is extremely important to differentiate it from all existing seals. Timely diagnostic measures make it possible to detect cancer at the earliest stages and provide high-quality therapy with a short recovery period.
What it is
Epulis is a tumor-like neoplasm that develops on the alveolar process of the jaw. It also has other names - epulid, supragingival, giant cell granuloma. More often it is localized in the area of incisors, canines and small molars of the upper jaw, less often the tumor is detected in the lower jaw. The growth has a round or irregular shape and a wide stalk; the size of the formation varies from 3 mm to 5 cm.
Despite the fact that such a tumor looks frightening, it practically does not cause concern to the patient, unlike, for example, a burn, with the exception of a violation of aesthetics and the sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity. Large tumors may cause difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
If epulis is accompanied by bleeding, infection may occur, which will lead to complications.
The disease mainly affects adults, but the neoplasm can also appear in children; in the latter, it occurs during teething. Studies have shown that women are more susceptible to developing epulis than men.
Brief description of the disease
In addition to fibromatosis, this disease in dentistry is called hyperplasia or gingival hypertrophy.
It is characterized by the progressive, uncontrolled formation of new connective tissue cells in the gums and periodontium. From them fibril tissue is formed, which is a causative factor in the increase in the size of the gums.
According to statistical data, the disease is rare, its mechanism is not completely clear.
Diagnostics
A visual examination alone will not be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. Fibromatosis is a benign tumor disease.
When diagnosing, it is important to differentiate it from other tumor diseases. A histological study of the structure will help to accurately determine the type of tumor. This study is carried out on material taken from a biopsy.
Differential diagnosis of fibromatosis is carried out with symmetric fibromas, osteomyelitis, periodontitis, hypertrophic gingivitis. This is done due to their clinical similarity of manifestations.
X-rays are used to evaluate the condition of the entire bone structure. Additionally, an orthopantomogram is prescribed, which will help clearly identify destructive areas of the alveolar process.