From this article you will learn:
- why do gums bleed during pregnancy,
- what is pregnancy gingivitis,
- how to carry out treatment correctly.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
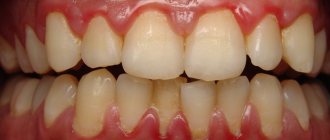
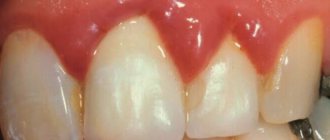
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is a process characterized by bleeding gums, as well as hypertrophy of the gingival papillae, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. This condition is usually called the term “gingivitis in pregnant women”, and according to statistics, it is observed in 75% of women - for a period of 2 to 8 months. Most often, gingivitis occurs in the area of the front teeth, and it affects only the gingival margin at the necks of the teeth (including the gingival papillae).
Clinical studies show that more than half of all women with gingivitis during pregnancy already had a mild form of chronic catarrhal gingivitis at the beginning of pregnancy, which is practically asymptomatic. Thus, an increase in the content of estrogen and progesterone in most cases led to an exacerbation of pre-existing gingivitis, and was not the root cause of its development. We will tell you more about the causes of inflammation below, because... there are other factors to consider.
Chronic catarrhal gingivitis –
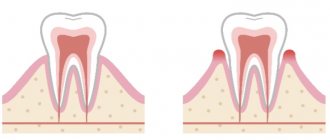
But pregnant women can experience not only gingivitis, but also a more serious gum disease, in which inflammation spreads from the superficial part of the gums to deeper tissues. This disease is called periodontitis, and with it there is destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, destruction of the dental-gingival attachment, suppuration from periodontal pockets, and over time, tooth mobility also occurs. And this disease already indirectly affects the fetus, which requires mandatory treatment.
How is catarrhal gingivitis treated in pregnant women?
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women begins with professional teeth cleaning: plaque and tartar are carefully removed, and the teeth are polished using special brushes and pastes. The next stage is anti-inflammatory therapy. For this purpose, the dentist prescribes the use of anti-inflammatory rinses, applications and toothpastes. The correct diet is very important - you need to reduce the consumption of carbohydrate foods and avoid frequent snacking. And of course, you need to take good care of your oral hygiene.
Why does gingivitis occur during pregnancy?
Tens of millions of microorganisms live in the oral cavity. Slight swelling of the gums leads to an increase in periodontal pockets, which become an excellent reservoir for the life and reproduction of bacterial microflora. In addition, microorganisms do not lack nutrition, since pregnant women like to pamper themselves with sweets, and carbohydrate foods are the best substrate for the development of bacteria.
Swelling of the gums, leading to an increase in periodontal pockets, excessive salivation, an acidic environment in the mouth, an increased feeling of hunger - these features that accompany pregnancy are the main factors contributing to the rapid growth of oral microflora. And this, in turn, provokes inflammation of the gum tissue - gingivitis.
How are treatment methods chosen depending on the stage of pregnancy?
The first trimester of pregnancy is associated with the risk of spontaneous abortion, so during this period interventions should be as necessary, and the indications for them are acute pain or severe swelling of the gums. Tartar can also be removed, but it is still better to postpone this manipulation for a while. In the second trimester, you can carry out complex treatment, including professional cleaning and taking antiseptics. And in the third trimester, a visit to the dentist should be as short as possible, so you should limit yourself to only hygiene procedures.
Whims or symptoms of gingivitis during pregnancy?
The first symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women begin to appear between 8 and 12 weeks. Expectant mothers, as a rule, suffer from two forms - catarrhal and hypertrophic; ulcerative gingivitis develops less often.
Catarrhal gingivitis
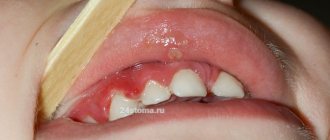
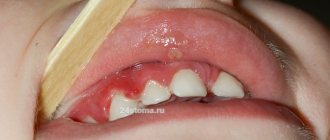
This form of the disease is manifested by the formation of a fairly large amount of soft yellow plaque on the surface of the teeth, swelling of the gums, their soreness and significant bleeding when pressed with a sharp object. Catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by the spread of inflammation over the entire surface of the gums, sometimes the process affects the tissues of both the upper and lower jaws.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
The first symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis usually appear no earlier than the twentieth week of pregnancy. Inflammation affects the lower jaw, gums in the area of incisors, canines and small molars. The hypertrophic form of gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the volume of gum tissue, an inflammatory process in it and bleeding. Gum pockets also appear - grooves formed between the tooth and gum due to the growth of gum tissue.
Ulcerative gingivitis
The most severe form of gingivitis occurs in pregnant women. It occurs against the background of serious health problems accompanying pregnancy, in the last trimester, or under the influence of stressful situations. The main signs of ulcerative gingivitis are severe itching, burning, bleeding of the gums, swelling and ulceration.
Experts' opinion
As a result of clinical experiments using the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Kazan State Medical Academy, the complex use of anti-inflammatory drugs from the Asepta line contributed to faster relief of inflammation, the combined use of balm, gel, rinse, toothpaste and vitamin-mineral complex mutually enhanced the therapeutic effect did not require daily visits to the dentist.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-lechebno-profilakticheskie-sredstva-dlya-individualnoy-gigieny-polosti-rta Silantieva E.N., Berezina N.V., Krivonos S.M. Complex treatment of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis using drugs from the Asept line, Practical Medicine journal
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
What to do if your tooth hurts during pregnancy and you can’t get to the doctor
For starters, you can drink something painkiller. Paracetamol is considered the safest. Unlike other analgesics, if the recommended dosages are followed, it will not harm the fetus.
Before meeting with your doctor, you can also try to reduce pain with warm rinses. For this, decoctions with an anti-inflammatory effect are used: oak bark, sage, chamomile. You can rinse approximately once every one and a half to two hours.
Severe pain is relieved with novocaine applied to a tampon and applied to the gum in the area of the diseased tooth. However, this method should be used with caution during pregnancy. In any case, you cannot self-medicate; you should quickly see a dentist.
Sign up at Clarimed at any time convenient for you, we work around the clock. Call: +7 (495) 316-96-16 or sign up at klarimed24.ru. If the pain is severe, we will try to see you immediately.
During pregnancy, you need to fill your diet with calcium-containing foods: milk, cottage cheese, cheese
Therapy
| Service | price, rub. |
| Primary consultation and examination with a doctor | For free |
| Initial consultation with an implantologist, orthodontist, orthopedist (orthopantomogram is required) | For free |
| Repeated examination without prescribing treatment | For free |
| Examination by a doctor with prescription of medication | 500 |
| Help for antenatal clinics, hospitals, sanatoriums | 500 |
| TREATMENT OF CARIES | |
| Treatment of caries “without drilling” ICON technology – 1 tooth | 3000 |
| Treatment of caries (filling, anesthesia, lining) | 2700 — 4200 |
| Treatment of deep caries (filling, anesthesia, x-ray, lining) | 3800 — 5100 |
| Artistic tooth restoration (frontal group of teeth) | 4800 — 6700 |
| Restoration of a chewing tooth (filling, gasket, anesthesia, x-ray, pin) | 3600 — 4600 |
| NERVE REMOVAL – CANAL TREATMENT (depulpation) is carried out in two visits, payment in stages, includes x-rays, anesthesia, canal treatment, temporary filling | |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 1-canal tooth, without the cost of a filling | 4400 — 5500 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 2-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 6500 — 7600 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 3-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 8600 — 9700 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 4-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 10700 — 11800 |
| Installing a seal | 3200 — 3600 |
Consultation is free.
Teeth cleaning
| Service | price, rub. |
| Initial consultation with a doctor | For free |
| Comprehensive professional hygiene (including ultrasonic removal of dental plaque, Air-flow, polishing, varnish coating) Promotion | 4000 3600 |
| Ultrasound removal of tartar – 1 tooth | 400 |
| Removal of pigment plaque with the “Air-flow” system – 1 tooth | 400 |
| Plaque removal using the Air-flow method – 2 jaws | 3300 |
| Ultrasonic dental plaque removal – 2 jaws | 3300 |
| Teeth whitening Opalescence Boost | 12000 |
| Skyce installation (including the cost of decoration) | 2000 |
All initial consultations are free.
How and with what to treat gums for pregnant women
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is one of the most common reasons for visiting the dentist during the difficult but joyful period of waiting for a baby. According to statistics, complaints about bleeding gums and other manifestations of periodontal disease during pregnancy can be heard from 75% of women.
If your gums are swollen during pregnancy, this is a good reason to visit the dental clinic. After all, the reason why gums hurt during pregnancy can be either relatively harmless gingivitis or much more serious stomatitis or periodontitis. In fact, these are consequences of the same pathological processes, but at different stages, so you should go to the clinic after the first alarming symptoms appear (for example, bleeding, ulceration, swelling and soreness of the gums).
The main task of a dentist when treating gums for pregnant women is to stop inflammation and prevent further spread of infection, using the most gentle methods possible. And the earlier treatment is started, the lower the risks of developing serious periodontal diseases, tooth loss and the impact of negative processes on the fetus.
What procedures are allowed during this period, and which are strictly prohibited?
Pregnancy imposes a number of restrictions on treatment, including dental treatment.
Acceptable:
- Treatment of caries, especially in the very initial stages. If the tooth is barely touched, you can even do without anesthesia. In case of increased sensitivity, use a spray with a minimal content of adrenaline.
- Fluoridation, enamel whitening. These manipulations are classified as absolutely safe procedures.
- Gum treatment. It can be carried out in any trimester using anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Installation of crowns and removable dentures. It will not harm either the expectant mother or the child.
- Removal of a tooth. At the level of modern medicine, it is considered a relatively safe manipulation for pregnant women, but it is performed in extreme cases
Forbidden:
- Dental implantation due to the need to take strong medications.
- Removing "eights". Severe trauma to the jaw occurs: a large wound surface can become a source of infection.
- Bite correction. During pregnancy, a woman's body loses a lot of calcium, so braces are likely to cause tooth decay. If pregnancy occurs already during treatment, it is interrupted until the birth of the child.
- Use of general anesthesia for pain relief.
Carrying out local anesthesia with special preparations containing a minimum percentage of adrenaline and calculating the correct dosages is not considered dangerous to the fetus.
Diagnostic features
A correct diagnosis will help determine how to treat the disease. To do this, it is important to assess the degree of tissue damage. The following methods are used in the diagnostic process:
- visual examination with measurement of the depth of periodontal pockets and assessment of the functional state of the periodontium;
- taking anamnesis;
- X-ray examination.
Based on the results, the doctor will draw up a periodontogram, which gives a complete picture of the condition of the periodontium. It is a special table in which X-ray data, measurements of the depth of periodontal pockets, tooth mobility, level of attached gums and depth of recession are entered.
Symptoms of the appearance of loose gingival tissue
If the gums are loose and soft, you should pay attention to the presence of other undesirable manifestations. Inflammation of the gum tissue is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dry mouth and viscosity of saliva are signs of a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity;
- increased sensitivity of soft tissues;
- itching and burning;
- bad breath, which subsides slightly after brushing your teeth;
- the formation of cones and growths.
Bleeding gums also indicate tissue problems. This symptom may occur when brushing or applying pressure to the teeth. The taste of blood is sometimes felt when chewing food.
Recommendations to help avoid problems
In order not to become one of the pregnant women suffering from gingivitis (and, according to statistics, there are more than 60%), you must adhere to simple rules.
- Carry out the necessary hygiene procedures regularly: brush your teeth using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and do this as thoroughly as possible, use floss and antiseptic rinses.
- Avoid excessive amounts of sweets and consume sweets, chocolate and cakes in moderation. It is strongly recommended to refrain from chewing toffee and caramel, since the remains of viscous delicacies can accumulate in the periodontal space of swollen gums, provoking particularly active proliferation of microorganisms.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits, paying special attention to foods containing vitamin C.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women cannot be postponed until later. Occurring due to changes in hormonal status and the growth of microbial microflora, it provokes even more active proliferation of bacteria, which in the most severe cases can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus.
How inflammation can affect the health of mother and baby
Pregnant women worry that problems with teeth and gums may affect their condition and the health of the child. Indeed, gingivitis is a dangerous, insidious disease.
Possible complications after gum inflammation:
- Discomfort and pain cause unpleasant sensations and make the expectant mother nervous, which negatively affects the course of pregnancy;
- There is a possibility of periodontitis and tooth loss;
- Intoxication of the body under the influence of microbes has a detrimental effect on the development of the fetus;
- An advanced inflammatory process increases the risk of miscarriage.
Negative consequences can be avoided by promptly consulting a doctor. Experienced, qualified specialists, using modern equipment, will solve the problem without harm to mother and child.