Afty Bednar
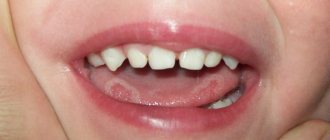
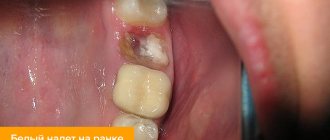
This disease affects children. The disease manifests itself as ulcers, which are covered with a plaque with a clear yellow tint. The main reason that causes the disease is insufficient oral hygiene. Erosions of traumatic origin can form due to rough mechanical rubbing of the soft tissues of the mouth. Therefore, from early childhood, parents should teach their children to properly brush their teeth and rinse their mouths. The selection of toothpaste and brush is important. Hard bristles often damage delicate tissues. It is better to use a brush with soft bristles.
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivostomatitis
A white sore appeared on the tongue, then an abscess appeared? The erosive area could have formed during a period of weak immunity. If you ignore this problem, a complication may develop in the form of gingivostomatitis. This disease is very unpleasant.
- With systematic hypothermia and damage to the body by viral infections and allergic stomatitis, a necrotic form of the disease often appears.
- Ulcers are diagnosed in the oral cavity, a sharply unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, the temperature rises, saliva is released, and a gray-yellow coating is visible on the muscle organ.
- Ulcers with uneven edges have a noticeable greenish coating and bleed.
The disease usually affects young people, more often men. Patients note pain while eating, swelling of soft tissues. The epithelium becomes cloudy. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the severity of the lesion. Antibiotics, anti-allergy medications, vitamins P and C are prescribed. In severe cases, necrotic tissue is removed.
Tuberculosis
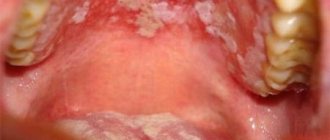
If tuberculosis of the airways is diagnosed, this negatively affects the condition of the oral cavity. Patients notice a dense white coating on the tongue that cannot be removed by brushing. The disease is due to the fact that tuberculosis bacteria have penetrated into the soft tissues of the muscular organ. Pathological tubercles develop on the mucous membrane, then ulcers. Their size is gradually increasing. Ulcerations are loose, shallow, bleeding. Their edges are uneven. In such patients, the temperature rises, weakness appears, and the ulcers are sharply painful. Increased sweating and weight loss are noted. In addition to general therapy, local treatment is recommended, and oral sanitation is prescribed when remission occurs. Pathological soft tissues are treated with antiseptic agents.
Syphilis
When an ulcer under the tongue does not heal for a long time, one can assume an infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum. After an incubation period (three weeks), ulcerations appear in the mouth. They are diagnosed throughout all phases of the pathology. At first, mucosal lesions are painless. Discomfort and mild pain gradually appear. Ulcers can take 120-150 days to heal. Scars form at the site of the lesion.
When examining the ulcer, it has an oval or round shape. Their edges are smooth, raised, the infiltrate is similar to cartilaginous tissue. The bottom of the ulceration is bright red, the top is most often covered with a dark gray coating in the form of a roller. General therapy for sexually transmitted diseases is carried out in a hospital. Local procedures include sanitation of the oral cavity during remission.
HIV
In a third of patients suffering from immunodeficiency, the oral cavity is covered with ulcerations. Gum tissues, cheeks, palate, lips are affected. An ulcer appears under the tongue in the frenulum area. For this disease, specific treatment is prescribed. It is carried out by infectious disease specialists. Dentists provide care to such patients in all clinics, carefully observing safety precautions.
What is glossitis?
Glossitis (from the Greek glossa (tongue) + suffix –itis) is an inflammation of the tongue. The reasons for its occurrence are different. Glossitis can develop as a result of a viral or bacterial infection, or as a result of another disease in the body. In addition, there are some other factors that provoke the development of the disease. These include mechanical, chemical and thermal damage to the oral cavity; nicotine; food that is too spicy or too hot; alcohol; caramel; some components present in toothpastes.
Glossitis has the following forms:
- folded
- diamond-shaped median
- desquamative
- hairy black
- Gunter's
- interstitial
According to the duration of the inflammatory process, acute and chronic glossitis are distinguished. The acute form of glossitis manifests itself as inflammation of the tongue, a change in its structure or color. Symptoms of the chronic form are more varied, but in most cases the disease is diagnosed by the presence or absence of papillomas - fungal growths on the tissues of the tongue. There are cases when the cause of the disease can be identified only after comprehensive medical research. True, this happens quite rarely and, as a rule, is associated with the presence of congenital, hereditary diseases.
Traumatic factor
Every person can experience mechanical damage to the tongue. It could be:
- biting;
- regular use of a rough toothbrush;
- damage during dental therapy;
- tissue damage from teeth, dentures, braces;
- irritation from food or medications.
Treatment of tongue sores resulting from injury occurs quickly and without complications. For the first few days, the damaged mucous membrane will react to all irritants. But the reaction will become less and less every day, and over time it will completely disappear.
Main symptoms of glossitis
Glossitis, the symptoms of which are very diverse and largely depend on the cause of the disease and the stage of development of the process, but the following signs are almost always present:
- coating on tongue uneven with spots
- ulcers in the oral cavity of varying depth and extent
- color changes (general or in the form of local spots)
- swelling of the tongue, the presence of “imprints” of teeth on its lateral surfaces and other sores
- limited tongue mobility
- bad breath problem
- salivation disorder
Often these changes are accompanied by a decrease in taste sensitivity, a burning sensation and pain at the slightest movements of the tongue while eating and when talking. Sometimes, as the inflammatory process progresses, there is a deterioration in general health: an increase in temperature, enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
General recommendations
For stomatitis in adults, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The dentist can perform initial treatment of the oral cavity, then the patient will need to perform all the manipulations independently at home.
Antiseptic treatment of the entire oral cavity is a prerequisite for the successful treatment of stomatitis and the rapid recovery of the affected mucosa. For “disinfection”, solutions containing chlorhexidine, furatsilin or metronidazole are used. Dentists also recommend rinsing with a soda solution every 2-3 hours.
Locally in the affected areas, it is necessary to remove heavy plaque using gauze and apply anti-inflammatory and regenerating gels or ointments to the areas where ulcers accumulate. The procedure is unpleasant, but significantly speeds up recovery.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, subject to all prescriptions and recommendations of the dentist, takes no more than 10 days. Symptoms of the disease disappear after 3–5 days; a few more days are required to restore the affected tissues.
Types of disease
Depending on the prevalence of the process and the predominance of a certain nature of changes, the following are distinguished:
Catarrhal glossitis
It is manifested by swelling, redness of the tongue, and the appearance of plaque on its surface, but the process does not extend to its deeper layers. Most often, catarrhal glossitis occurs with superficial injuries and burns of the tongue (chemical, thermal), oral candidiasis (disturbance of the balance of normal microflora), various forms of stomatitis, infectious diseases (viral and bacterial nature), as well as with a number of diseases (anemia, hypovitaminosis , metabolic disorders, diseases of the digestive system, etc.).
Ulcerative glossitis
It is usually manifested by the formation of single or multiple small ulcers on the tongue (the so-called aphthae, hence another name for it - aphthous glossitis). Ulcerations are often accompanied by bleeding, severe swelling, severe pain and deterioration in general condition. This type of glossitis can develop from catarrhal glossitis, and also be a manifestation of diseases of the oral cavity, gum diseases, and diseases of internal organs.
Purulent-phlegmous glossitis
It is a severe form of inflammation, spreading not only to the deeper layers of the tongue, but also to other tissues of the oral cavity; the nearby lymph nodes are also involved in the process. In this case, the patient’s condition is serious, with severe intoxication and elevated temperature, so such patients are usually treated promptly. Antibiotics for this glossitis are a mandatory component of treatment.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults is a reaction of the immune system to certain types of irritants, which are any substances. The causes of stomatitis have not been clearly identified; presumably, the body exhibits an individual reaction to certain substances or microorganisms.
Possible causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults:
- bacteria and infections of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of an infectious or viral type;
- respiratory diseases (ARVI, influenza, etc.);
- frequent injury to the tongue by orthopedic or orthodontic structures;
- damage to the tongue due to a chipped tooth;
- fungal infection;
- bad habits (smoking or alcoholism);
- burning the tongue or eating “spicy” foods.
In addition to the listed causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, inflammation of the mucous membrane can be caused by the herpes virus (herpetic stomatitis).
Special types of glossitis and their treatment
In addition to the above types of glossitis, dentists distinguish special types of glossitis, characterized by the development of limited specific changes in the tongue. These include:
Desquamative glossitis
It appears in the form of a “geographical” tongue, which has a “variegated” pinkish-red appearance, somewhat reminiscent of the outlines of the continents on a geographical map. In some cases, with the development of the inflammatory process, thinned areas cleared of plaque may change their position and shape within a short period of time (2 - 4 days). In such cases, desquamative glossitis is also called wandering glossitis. This can usually be observed with exudative diathesis, diseases of the digestive system, helminthic infestations, metabolic disorders, blood diseases, pregnant women, etc. Desquamative glossitis involves standard treatment, which leads to a gradual cleansing of the surface of the tongue and the disappearance of associated complaints in the patient.
Median rhomboid glossitis
It is characterized by the presence of a local thickening of the epithelium, usually located in the middle of the back of the tongue. In this case, the thickened area of the epithelium has a diamond-shaped or oval shape and can change its color from red to bluish. Rhomboid glossitis most often occurs in chronic diseases of the digestive system and is prone to chronicity and recurrence. Depending on the form of glossitis (flat, tuberculate, papillomatous), appropriate treatment is carried out: laser therapy, surgery, etc.
Atrophic glossitis
It often develops with insufficient intake of vitamins A and E. It usually appears as a single bright red, smooth spot that occupies the entire surface of the tongue. The focus of atrophy can persist for quite a long time without progressing. Sometimes the tongue decreases in size. Histological examination reveals dilation of blood and lymphatic vessels, swelling and inflammation in the papillary layer. Often, atrophic glossitis is a symptom of tongue damage due to gonorrhea.
Gunter's glossitis
Appears with a deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid. It most often occurs with blood diseases (usually anemia associated with impaired hematopoietic processes). In this form of the disease, the surface of the tongue is bright crimson in color and, due to atrophy of the papillae, has a “varnished” appearance. Gunter's glossitis involves treatment of the underlying disease by a therapist or hematologist.
Mycotic, candidal, or yeast glossitis
As a rule, it is a consequence of intensive antibacterial therapy, as a result of which the normal microflora in the patient’s body was suppressed. The disease manifests itself as swelling of the tongue, an accumulation of white plaque on it, with pronounced longitudinal and transverse grooves. Very often, mycotic glossitis occurs in young children and the elderly, as well as in people with weakened immune systems. Candidal glossitis requires treatment with antifungal drugs.
As an additional means for the treatment and prevention of glossitis, many experts have recently begun to recommend the use of an ultrasonic brush for oral hygiene.
Manifestations of tongue glossitis in children
In children, glossitis usually occurs at an early age - from 1 to 5 years. The causes of this pathological process have not yet been fully studied and can be very diverse: from infection to poor heredity. Externally, glossitis in children is manifested by the appearance of spots on the tongue, which slightly swells and itches. Itching and a burning sensation are the most unpleasant signs of glossitis, since a small child begins to scratch the tongue, thereby contributing to the appearance of microcracks with their subsequent infection. However, the disease does not pose a threat to the child’s life. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky does not recommend panicking about this and self-medicating by giving the baby serious medications. As a rule, multivitamins and a gentle regimen will have a positive effect within a week.
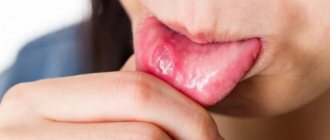
Signs of pathology
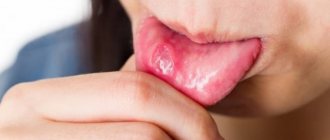
Sores on the tongue can appear in different places, and the process of their formation goes through several stages:
- In the first stage, swelling and small blisters appear on the tongue.
- Next, bubbles appear.
- The wounds are covered with a layer of white or yellow plaque, and a red border appears.
There are no age preferences for sores on the tongue; they can appear in children and adults. The frequency of their formation varies from several times throughout life, while in others they may appear with enviable regularity.
Usually the sores go away quickly, but if the wound on the tongue does not heal, then you should visit a doctor and find out the cause.
Features of glossitis during pregnancy
The causes of glossitis of the tongue in pregnant women are due to the fact that the immune defense weakens to allow the fetus to develop, which means that the body during this period becomes practically defenseless in the face of various bacteria and viruses. The second risk factor is a lack of vitamins and minerals obtained from food.
According to statistics, most often pregnant women experience a picture of desquamative and Gunter's glossitis. Symptoms that should alert you during pregnancy include:
- Profuse drooling. During the period of bearing a child, a woman already secretes a larger amount of saliva than usual, but a sharp increase may indicate the onset of glossitis.
- "Lacquered Tongue" A specific symptom that indicates the development of B12 deficiency anemia.
- Color change. White spots on the surface of the tongue alternate with spots of rich red color.
- Refusal of food. Acute glossitis in pregnant women is characterized by severe pain in the tongue during chewing and speaking, which, among other things, affects appetite.
As for the treatment of glossitis in pregnant women, the safety of the fetus comes first. Therefore, all therapy is exclusively local in nature (sprays, rinses), eliminating the penetration of the drug through the placenta. It is recommended to adjust your diet in such a way as to remove any foods that irritate your tongue.
Attention!
In order to avoid complications that can negatively affect the health of the fetus, treatment of glossitis during pregnancy must be carried out under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist monitoring the woman.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose glossitis in adults, the following basic methods are successfully used today.
- Examination
An experienced dentist in 95% of cases is able to diagnose glossitis based only on visual data. - RPR test
A special test that detects antibodies to the cardiolipin antigen. - Scraping
It is taken from the surface of the tongue to exclude syphilis, whose symptoms are similar to glossitis. - PCR
The most modern and accurate diagnostic method for identifying a wide range of infectious pathogens.
Treatment of glossitis depends on the form of the disease and analysis of concomitant diseases, but in any case it should be comprehensive:
- enhanced oral hygiene;
- general strengthening therapy aimed at increasing immunity;
- local treatment with antiseptics;
- strict diet;
- targeted medications (for example, for candidal glossitis - antifungal agents).
You can find out more about how to treat glossitis of the tongue in the article.
See a doctor urgently
It is necessary to urgently contact a specialist if:
- A large number of ulcers, wounds and neoplasms appear in the oral cavity.
- Open wounds appear, accompanied by severe pain.
- The sores appeared due to wearing dentures or artificial structures in the oral cavity.
- Sores have appeared on the tongue and are bleeding.
- The general condition worsens, the temperature rises, weakness.
- Sores and sores quickly increase in size.
- I have a headache and a feeling of fullness in the mouth.
If the listed symptoms are present, only a doctor can tell you how to treat wounds on the tongue.
Is it worth treating glossitis with folk remedies?
If you have a question: how to cure glossitis, don’t waste time looking for folk remedies! If you notice characteristic symptoms that do not go away for more than a day, you need to seek help from a specialist. Treatment of glossitis should be carried out only by a dentist, who will determine the cause of the changes in the oral cavity, carry out all the necessary therapeutic and diagnostic procedures, prescribe a set of therapeutic measures that the patient can perform at home, and also monitor the entire treatment process, making changes to it as needed. necessary adjustments. Moscow dental clinics are presented in the “Search” section on our website.
Glossitis, like other periodontal diseases, is fraught with many complications, so treatment with folk remedies can only serve as an aid in complex therapy.
In order not to come face to face with glossitis, it is enough to brush your teeth regularly, including brushing your tongue, and do not skip preventive examinations at the dentist. In addition, doctors recommend avoiding excessive consumption of spicy foods and spices, limiting the intake of alcoholic beverages and smoking. Remember, disease is easier to prevent than to treat.