Have questions?
Stomatitis is a disease in which the oral mucosa becomes inflamed.
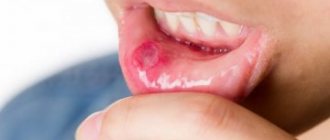
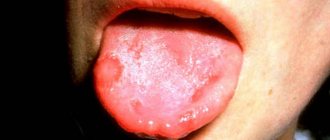
Stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of painful ulcers and wounds in the mouth, which cause significant discomfort to the patient. They are localized on the gums, tonsils, inner lips, cheeks, and under the tongue. The disease is most often bacterial or viral in nature and occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene or microtrauma of the oral cavity, through which microorganisms enter the soft tissues. It may also have an allergic or fungal origin. It mainly affects children, but often occurs in adults.
What to do if you have inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes
At the first suspicion of inflamed lymph nodes, you can conduct an independent diagnosis at home:
- Examine the neck area where inflammation is found. Perhaps it's just a boil or soft tissue damage.
- If point 1 is confirmed, then this area should be diagnosed in more detail. Gently touch this area with your fingers. If a ball can be felt under the skin, it means that this is clearly an enlarged lymph node.
- Next, we examine the discovered “ball”. If there are a lot of these balls, they are painless when pressed, then this indicates a compromised immune system. You should contact an infectious disease specialist.
- If pain occurs during palpation, as well as lumpiness and immobility of the node under the skin, then a serious diagnosis is needed in the clinic. Diseases of the throat and mouth are characterized by soreness of the lymph glands.
- If you suspect diseases of the ENT organs, you should visually examine your oral cavity for the presence of sore throat, as well as stomatitis, caries. A healthy oral cavity has clean mucous membranes without plaque, teeth are white without black spots. If a visual examination reveals problems, this means that this is the cause of lymphadenitis.
Very often, enlarged lymph nodes occur without obvious symptoms. To do this, you need to see a doctor and carry out a competent diagnosis from a specialist.
Based on the diagnostic results, the therapist refers the patient to the appropriate specialist: ENT specialist, dentist, surgeon, oncologist, hematologist. Inflammation of the lymph glands accompanies about a hundred diseases. With timely treatment of the disease, lymphadenitis also returns to normal.
If the patient has undergone treatment, and the nodes do not decrease within 3-4 months, then a full examination of the body should be done: donate blood for tests, do an ultrasound of the main organs, and consult with specialists.
Symptoms of mononucleosis
The incubation period of mononucleosis is on average 7-10 days, the maximum duration is 21 days.
Most often, the disease begins acutely, with a rise in temperature. If the temperature does not rise immediately, it usually occurs towards the end of the first week of illness. During the course of illness, the temperature may rise several times. It decreases gradually. In the evening, a slight increase in temperature may be observed for quite a long time. In some cases, no increase in temperature is observed.
Other symptoms may also be present in both pronounced and vague forms.
The acute period of the disease usually lasts 2-3 weeks. The recovery process can take quite a long time (up to several months). Swelling of the lymph nodes and a slight increase in the size of the liver and spleen persist the longest.
The main symptoms of mononucleosis:
Temperature increase
Mononucleosis is characterized by an increase in temperature to 38°C and above. A rise in temperature is accompanied by chills, body aches, and headache.
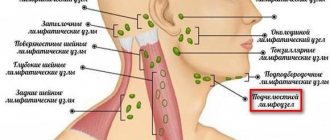
Enlarged lymph nodes
First of all, swelling of the cervical lymph nodes is detected. Sometimes axillary, inguinal and other groups of nodes increase.
Redness of the tonsils
There is redness and enlargement of the palatine tonsils. Quite often the whole complex of symptoms of angina appears.
Stuffy nose
The nose is stuffy, but there is no discharge from the nasal passages (no runny nose).
More about the symptom
Enlarged liver and spleen
With mononucleosis, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen is observed (reaches a maximum on the 4th – 10th day, but can manifest itself from the first days of the disease).
Rash
Various types of rashes may appear. The rash disappears after a few days, leaving no traces.
More about the symptom
Aphthous stomatitis
Gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, rheumatism, viral infections and hereditary predisposition lead to aphthous stomatitis. The disease occurs in a fairly severe form.
So-called aphthae appear on the oral mucosa - whitish ulcers with a diameter of 3-5 mm with a narrow red border. There is a deterioration in health, an increase in temperature, and pain in the area of the ulcers.
Aphthous stomatitis occurs in both acute and chronic forms.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Treatment of the oral cavity for stomatitis - Studiopedia
Herpetic (cold sore) stomatitis
It occurs in both children and adults. It is caused by the herpes simplex virus. The disease can be acute or chronic.
In a mild form of the disease, small blisters resembling aphthae appear on the mucous membrane.
In severe form, the rashes are multiple. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed and swells. Salivation increases. Characteristic symptoms include general malaise, toxicosis, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes. When eating, burning and pain are felt.
Symptoms and causes of stomatitis
The manifestations of the disease are clearly visible to the patient, since the inflammation causes him noticeable pain. There are many types of stomatitis, but they have common symptoms.
- In places where the mucous membrane is affected, redness occurs, this area swells and swells.
- The patient is bothered by acute, severe pain, which prevents him from chewing food or talking normally.
- A characteristic sign is the formation of single red ulcers on the mucous membrane with a white filmy dot in the middle.
- Salivation increases significantly, an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, and gums may bleed.
- In the acute form, enlargement of the lymph nodes and an increase in temperature to 39 degrees are possible.
A huge risk of developing stomatitis appears with a decrease in immunity, against the background of which bacterial and infectious infection of the body occurs. Risk factors are also various systemic diseases: gastrointestinal disorders, problems with hormone production, diabetes, anemia.
The immediate causes are:
- bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma, viral infection;
- complications of infectious ENT diseases;
- allergy;
- injuries, burns of the oral cavity (for example, when eating);
- the presence of massive tartar and plaque;
- poor oral hygiene;
- unbalanced diet;
- medications, toothpastes that significantly reduce salivation.
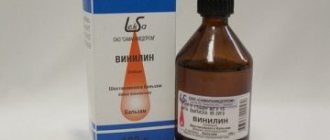
Home treatment for stomatitis
Home treatment of stomatitis using folk methods is aimed at solving two problems:
- For antiseptic and anti-inflammatory rinses.
- For these purposes, you can use herbal decoctions of calendula, chamomile, plantain and antiseptic ointments based on propolis, sea buckthorn and vitamin A.
- To stimulate the immune system by drinking solutions of rose hips, sea buckthorn, taking amaranth oils and other means.
- However, before home treatment, you need to consult a dentist, because very often it is necessary to eliminate not only local, but also general causes of stomatitis, such as Candida fungus or the herpes virus, not to mention more serious diseases.
How and what can be used to treat aphthous stomatitis in adults
Aphthous stomatitis is one of the variations of inflammation of the oral mucosa, which occurs with the formation of painful erosions (aphthae). In this case, the sick person experiences a feeling of severe discomfort. Treatment of the pathology is prescribed based on the reasons that provoked its development.
The main factor in the formation of aphthous stomatitis can be called various infections, as well as previous viral diseases. For example, this could be influenza, measles, herpes virus activity, staphylococci, etc. The disease must be treated under the supervision of a medical specialist.
How to treat stomatitis?
It makes sense to start the treatment process of any form of stomatitis with professional hygienic cleaning, removal of tartar and plaque. It is also necessary to cure caries, if present.
Next, the mucous membrane is treated with antiseptics. Throughout the day, you can rinse your mouth with warm solutions of calendula and chamomile. Thanks to such measures, catarrhal stomatitis can go away after 5-10 days. If it turns into aphthous or ulcerative, general treatment will have to be added to the local treatment. Contact the clinic for additional antiseptic procedures.
In the case of herpes stomatitis, antiviral therapy is indicated. Candidal stomatitis is treated with antifungal drugs.
If stomatitis is caused by any other disease (for example, gastrointestinal disorders), during treatment it is strictly recommended to follow a diet limiting coarse, sour, hot, cold and spicy foods.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults at SM-Dentistry
The SM-Dentistry doctor will carefully collect anamnesis and develop an individual treatment program aimed at eliminating symptoms, increasing immunity, and preventing relapses. If it is necessary to identify the systemic cause of the disease, you will be offered consultations with general and related doctors.
The most common types of this disease that our specialists encounter are bacterial and ulcerative. We also provide treatment for herpetic, aphthous, and candidal stomatitis. If the illness is of an allergic nature, we will refer you to a qualified allergist for consultation.
Treatment at SM-Dentistry includes a range of tools:
- imported high quality antiseptic preparations;
- antiviral, antifungal drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (gels, ointments) for healing the mucous membrane;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- vitamin therapy;
- developing a diet to improve immunity;
- if necessary - removal of plaque, stone, treatment of caries and other dental diseases.
In addition, you will receive detailed recommendations on oral hygiene.
Stomatitis causes a lot of unpleasant and painful sensations. In order to quickly and effectively get rid of them, contact SM-Dentistry (from 9 a.m. to 9:30 p.m. on weekdays, until 9:00 p.m. on weekends). To make an appointment, fill out an application on the website or call: +7.
Dentist consultation Professional teeth cleaning Plaque removal Treatment of caries Tartar removal
How does aphthous stomatitis go?
Doctors distinguish only 4 stages:
- Initial. During this period, body temperature increases and general malaise is observed. If you palpate the cervical lymph nodes, they are enlarged and painful to the touch. Lost appetite.
- Active. Redness appears on the surface of the mucous membrane. A little later, erosions form in their place.
- At the next stage, erosive formations transform into painful ulcers.
- The final stage. At this stage, healing of aphthae occurs, and discomfort, itching and burning in the oral cavity disappear.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Stomatitis Louise Hay table
With a decrease in immune defense and the presence of numerous chronic diseases (which is typical for all adults), aphthous stomatitis almost always passes into the stage of a chronic recurrent type.
Candidal stomatitis
This is a fungal disease typical of older people and children. As a rule, such stomatitis progresses against the background of decreased immunity, as well as with long-term treatment with powerful antibiotics.
Candidal stomatitis is characterized by the following symptoms: burning sensation in the mouth and larynx; white coating in the mouth and tongue; hyperemia and bleeding of the mucous membrane; an unpleasant taste in the mouth or a complete loss of taste.
The type of stomatitis described is considered contagious and can be transmitted both through household and sexual contact.
Content:
- The danger of herpetic stomatitis
- Causes of the disease
- Manifestation of herpetic stomatitis
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
The danger of herpetic stomatitis
Herpetic stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa, which is caused by a well-known infectious agent - the herpes virus. Simple forms of inflammation cause discomfort, but do not threaten the patient. However, there are situations when the disease becomes severe: in addition to pronounced ulcerative-necrotic inflammation of the oral epithelium, the respiratory tract, vascular wall, and even internal organs can be involved in the process. You need to know the manifestations of this disease in order to consult a specialist in time, carry out treatment, prevent repeated episodes of herpetic stomatitis (since infection with the herpes virus is accompanied by its lifelong presence in the body) and prevent possible complications.
Causes of the disease
The etiological factor causing stomatitis in this case is herpes simplex virus type 1. There are also HSV - type 2, the so-called “genital herpes”. It is transmitted only sexually and causes damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs; in this case, there is no herpetic lesion of the oral cavity. The mechanism of transmission of herpes simplex virus type 1 is carried out mainly by contact, much less often by aerosol. Infection occurs at an early age. The first episode of stomatitis is most often observed in childhood. This is primarily due to the fact that by the first year of life the child’s immune protection received from the mother weakens. Childhood is the main risk factor for developing the disease. In some cases, infection is not accompanied by any symptoms, and the child becomes a carrier of the virus. In this case, the disease can manifest itself at any age. For the development of the disease, predisposing factors are also necessary: a decrease in the body's defenses - hypothermia, stressful situations, hormonal disorders, exacerbation of chronic diseases. The herpes virus refers to microorganisms that have tropism (the ability to interact with certain tissues) for epithelium and nervous tissue. In this regard, the lesions will be localized on the mucous membranes and in the nerve formations of the body. Penetrating into cells, the virus begins to multiply and eventually spread throughout the body. Depending on the magnitude of the viral load, the disease will manifest itself at the time of infection or only after sufficient accumulation and reactivation.
Manifestation of herpetic stomatitis
Herpetic stomatitis as one of the forms of the disease occurs more often than others. The clinical picture is specific and allows, in most cases, to promptly recognize the disease and begin treatment. From the onset of symptoms to complete recovery, it can take from 3-5 days to several weeks. Most often, stomatitis begins with an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels. There may be mild symptoms of ARVI - redness of the mucous membrane of the nose, pharynx, tonsils. Lymph nodes can be involved in the process if the body overreacts to the introduction of the virus - most often this happens during the first episode of herpetic stomatitis. Lymph nodes in the head and neck area enlarge and become painful on palpation. The main morphological element of herpetic inflammation is the vesicle (vesicle). A vesicle appears on an inflamed reddish area of the mucous membrane of the lips, gums, cheeks or other area; it can be represented by a single element or multiple vesicles. During its development, the blister gradually increases (on average 2 mm, maybe up to 5 mm), bursts, and in its place an ulcer - aphthae - forms. Herpetic elements in the oral cavity and any other location are very painful. Sometimes there is severe salivation. In the case of moderate and severe cases, other organs are also involved, body temperature rises to 39-40 degrees, signs of intoxication are expressed - myalgia, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, severe weakness. A lot of vesicles appear; after rupture, they turn into deep ulcers and become necrotic.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you suspect a herpetic lesion of the oral mucosa, you should consult a dentist. In some cases, a consultation with a general practitioner and a dermatovenerologist may be indicated.
Diagnosis is not difficult: collection of complaints and examination makes it possible to make a correct diagnosis at an early stage. In diagnostically unclear cases, methods of special diagnosis of the pathogen may be prescribed - it is detected in scrapings from the mucous membrane (virological diagnosis is difficult), an increase in the titer of antibodies in the blood (a more effective method), PCR diagnostics, and others.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
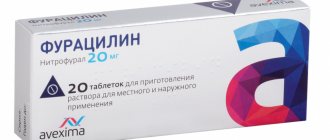
Treatment can be symptomatic - treatment of the oral cavity with solutions: hydrogen peroxide 3%, potassium permanganate 1:10000, furatsilin; it is possible to prescribe painkillers. Etiological treatment is prescribed when the diagnosis of herpes is confirmed. Specific antiviral drugs are used that act on the pathogen - Acyclovir, Valciclovir, Famciclovir. There are forms for local treatment in the form of ointments, as well as tablet and soluble preparations. In simple forms, antiviral drugs are applied only to the affected areas.
Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes with antibiotics
Antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck are used only as prescribed by a doctor. These drugs make sense if the infection is caused by bacteria. In addition, it is necessary to be very careful with this method of treatment, since antibiotics have negative side effects on the body.
When prescribing antibiotics, doctors give preference to drugs with a broad spectrum of action. The most common antibiotics are the penicillin group. In case of individual intolerance to penicillin, antibiotics of the following groups are prescribed:
- macrolides;
- sulfonamides;
- quinolones;
- cephalosporins.
For inflamed lymph nodes that accompany diseases of the ENT organs, the following drugs are most often prescribed:
- Amoxiclav;
- Azithromycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Tsiprolet;
- Cipronol;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Biseptol.
These medications should be taken according to the regimen prescribed by your doctor. The doctor competently determines the dosage in accordance with the patient’s age and body weight, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. It is strictly forbidden to take antibiotics on your own!
Causes of mononucleosis
Mononucleosis is caused by a type of herpes virus (Epstein-Barr virus). The route of transmission of infection is airborne droplets.
. The disease does not pose an epidemic threat. The virus quickly dies in the external environment. But it is present in saliva. A child who puts various objects into his mouth can become infected, especially if he is in a group of children in which there is a carrier of the infection. Therefore, outbreaks of mononucleosis sometimes occur in kindergartens.
Family foci of the disease are also recorded. Emphasizing this feature, mononucleosis is called the “kissing disease.” Most often it affects children aged from one to 10 years. The second peak in incidence occurs in adolescence. By the time they reach adulthood, most people are immune to mononucleosis.
Treatment of stomatitis
Many patients are interested in how to quickly cure stomatitis? Which doctor treats stomatitis in adults and children?
Most often, local treatment of all types of stomatitis is carried out by a general dentist or periodontist. Treatment of stomatitis in adults and children is carried out mainly symptomatically, but with mandatory consideration of the main cause of its occurrence. Medicines for stomatitis in adults are aimed at relieving swelling, pain and inflammation.
Local treatment of stomatitis begins with the removal of dental plaque, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory rinses of the mucous membranes, as well as anesthetic ointments and gels for the treatment of aphthae and ulcers are prescribed. Limit food, exclude hot, spicy and hard foods. If candidiasis is detected, then antifungal drugs are prescribed; if there is herpes, then antiviral drugs are prescribed.
The main common root cause of stomatitis, gastrointestinal diseases, immune diseases, etc. are always identified and treated. It is clear that this is not done by dentists, but by their colleagues - specialized doctors. However, the first person who can detect and pay attention to this and send the patient for examination to colleagues is the dentist.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Diseases of the oral mucosa - transparent blisters in the mouth
The most pressing question from many patients is: “How much does it cost to cure stomatitis? Where can stomatitis be treated inexpensively and efficiently?”
The price for turnkey treatment of stomatitis in dentistry in Livny and other large cities of Russia is determined by the causes of stomatitis. The cost of local treatment of oral stomatitis on a turnkey basis starts from 2000 rubles and can reach 20 thousand rubles or more. Prices for general treatment of stomatitis depend on the main pathogenic factor and concomitant diseases, such as systemic herpes, the presence of Crohn's disease, enteritis and other health problems.
Prices
| Name of service | Price, rub.) * |
| Initial consultation with a dentist-therapist | 1,500 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a dentist-therapist | 800 rub. |
| Treatment of caries (imaging, anesthesia, isolation of the oral cavity, installation of an insulating lining and filling made of composite light-curing imported material) | from 4,350 rub. |
| Comprehensive oral hygiene (OptraGate oral cavity isolation, AirFlow removal of colored plaque, ultrasonic removal of dental plaque, polishing with paste, preventive fluoridation of teeth) | 7,000 rub. |
We accept VISA, MASTERCARD, MAESTRO bank cards for payment.
Would you like us to call you back?
Treatment of stomatitis at home
To treat stomatitis at home, first of all, certain infusions and decoctions are used that have anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating and antiseptic effects. The most accessible options are calendula and chamomile.
Only rinsing the mouth with decoctions is effective, but also taking them orally. Rose hips are suitable for this. It contains a large amount of vitamins, strengthens the immune system, and helps in destroying harmful microorganisms. However, we should not forget that herpetic and candidal stomatitis cannot be cured with folk remedies, because these diseases are based on fungi that are not affected by the compounds described above.
Stomatitis and lymph nodes
Hello, the child is 1.6 months old, on Friday (June 14) at night the temperature rose to 38.5, Saturday and Sunday it stayed, there was only a runny nose and profuse salivation, they thought that fangs were coming out, on Monday they called a doctor, she said that it was stomatitis, she discovered one lump on the lip and one on the tongue, the gums are red, she also said that the red throat looks like a sore throat is attached, the submandibular lymph nodes have increased.
Prescribed: ecoclave 3 times a day Suprastin 1/4 tablet 2 times a day Panavir in the throat and on affected areas 3 times a day Interferon 5 drops 5 times a day Linex 1 capsule 3 times a day Genferon 1 suppository 2 times a day
Today the temperature has been rising for 5 days, but it doesn’t go down for long, all the symptoms persist, I started coughing.
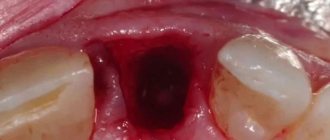
Ulcerative stomatitis
This is a more severe form of the disease than the previous one and can develop from its advanced stage.
Often the disease progresses in those who suffer from stomach ulcers or chronic enteritis. We include in the risk category those with diseases of the cardiovascular system and blood. Poisoning and infectious diseases increase the risk of developing ulcerative stomatitis.
Symptoms: the entire thickness of the mucous membrane is affected, the temperature can rise to 37.5, all this is accompanied by headache, weakness, and inflammation of the lymph nodes. Eating is uncomfortable due to pain.
Methods for diagnosing mononucleosis
Symptoms of mononucleosis are not specific. Therefore, diagnosis is based primarily on laboratory data. The necessary studies are combined in the profile “Diagnostics of infectious mononucleosis”.
General blood analysis
A complete blood count for mononucleosis usually shows an increase in the number of leukocytes and ESR. Characterized by a significant increase in lymphocytes and monocytes, together these varieties can account for up to 80-90% of the total number of leukocytes. The main symptom of mononucleosis is an increase in the number of specific cells - atypical mononuclear cells (which are altered lymphocytes) to a level of over 10%. However, they are detected no earlier than on the 5th day from the onset of the disease.
More information about the diagnostic method
Blood chemistry
Mononucleosis can manifest itself in the results of a biochemical blood test in the form of a two- or three-fold increase in the activity of ALT and AST. When the skin turns yellow (jaundice), bilirubin increases.
More information about the diagnostic method
Serological blood test
Using serological analysis, specific antibodies to the causative agent of mononucleosis, the Epstein-Barr virus, can be detected.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.