From the moment they appear, wisdom teeth often behave unpredictably, grow slowly and crookedly, and the growth process is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. Taking into account such features, it is considered quite natural that the wound bleeds after extraction of the “eight”. In this case, intermittent hemorrhages, which last up to 2-3 days and no more, are considered the norm. They are caused by damage to the periosteum and soft tissues during tooth extraction. When blood is released longer and negative symptoms are observed, then you definitely need to see a dentist to find out the cause of the incessant bleeding.
Causes of bleeding
As a rule, hemorrhage (hemorrhage) occurs as a response to damage during soft tissue surgery or as a result of exposure to certain medications. Such problems usually go away within a few hours after the procedure.
If an ordinary tooth can be pulled out without much difficulty and a cotton swab applied to the wound, then removing third molars is much more difficult. During the manipulation process, it is often necessary to saw the crown of the tooth and pull it out in parts. With deep and curved roots, it is almost impossible to extract them without damaging bone and soft tissue.
In addition, there are also other reasons why the bleeding does not stop after a wisdom tooth has been removed:
- high blood pressure;
- mechanical injuries of a large vessel;
- the patient is taking blood thinning medications, for example, Heparin, Aspirin and others;
- low blood clotting;
- the use of anesthetics, after which the blood vessels dilate. This increases bleeding and slows down the process of clot formation;
- the presence of concomitant diseases can cause heavy bleeding. These include hepatitis, scarlet fever, leukemia, hemophilia and others;
- Overheating of the body or high physical activity immediately after removal increases the risk of hemorrhage.
If immediately in the postoperative period the patient abuses alcoholic beverages or smoking, bleeding can occur as complications.
If wisdom tooth extraction cannot be avoided, then the patient needs to understand that bleeding after such a procedure is a natural and normal process. But even with relative safety, the release of blood requires careful monitoring by both the doctor and the patient himself.
Duration of bleeding, normal limits
One of the frequently asked questions by patients who are about to have a wisdom tooth removed is how long does the formed socket bleed and what to do if the bleeding does not stop.
As a rule, after 10-15 minutes after surgery, a blood clot forms in the socket; in some patients, approximately 30-40 minutes may pass before the clot appears. Under no circumstances should this clot be removed, because it protects the wound from infection.
Deviations from the norm are situations where bleeding continues after returning home. But some patients worry in vain, mistaking ichor for blood. If the bleeding in most cases stops within 30-60 minutes, then the discharge of ichor from the wound can be observed for up to 12 hours or longer.
Ichor is a yellowish or colorless liquid with a small blood capacity. Each person may have a different intensity of discharge depending on the characteristics of the body, but in any case this is not a cause for concern.
If blood is released from the wound uncontrollably for a long time, you should inform the doctor about this without waiting for complications.
How long will it take for gums to heal?
Healing times vary. They depend on two main factors:
- Difficulty of intervention. If the wisdom tooth has already erupted, then recovery occurs relatively quickly. If you had to make an incision in the gum and “cut down” part of the bone, it will take more time.
- Compliance with the doctor's recommendations, especially in the first 24 hours after the procedure.
In most cases, the function is restored within a week, and the person no longer experiences any discomfort. But some processes may continue to occur in the jaw for a long time. The bone is rebuilt, the shape of the face changes slightly.
The sutures usually dissolve on their own within 7–10 days. If non-absorbable suture material was used, the surgeon will invite you to remove the sutures after about a week.
Why doesn't the bleeding stop?
Depending on the physiological characteristics of the body, in some patients a clot forms immediately after surgery, in others the bleeding does not stop for a long time. The reasons for this condition may be different.
High blood pressure
A patient with hypertensive pathology often experiences bleeding from the socket, so if he has such a disease, he should inform the doctor about it before the operation. This will allow you to find an individual approach to a problem patient and prevent possible complications.
Poor blood clotting
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with coagulation disorders, then he is obliged to inform the doctor about the existing problems in order to prevent negative consequences.
Inflammation of the socket
After surgery, the doctor must treat the hole with an antiseptic. But even treatment is not always a guarantee that the bleeding will stop after wisdom teeth are removed. If the socket is a source of infection, the gums usually bleed. In such cases, you should not resort to self-medication, as this can lead to dire consequences. Only a professional specialist can correctly diagnose and prescribe effective treatment.
Purulent accumulations
Before performing any manipulation, the dentist must diagnose the patient’s jaw and make sure there are no pathologies. If there are already purulent accumulations inside the gums, this can provoke heavy bleeding, which is quite difficult to stop.
Damage to the integrity of blood vessels
Due to the irregular growth and location of wisdom teeth in hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity, the removal of such units is considered a relatively complex dental procedure. Vessels are almost always damaged by surgical instruments. Usually, after several hours, the bleeding stops, but the patient may simply not feel pain due to prolonged exposure to the anesthetic. If large vessels are damaged during surgery, bleeding may occur later and in such cases you should not hesitate to visit the dentist.
Failure to comply with medical recommendations
A rather complex procedure is the removal of a wisdom tooth; bleeding can occur in every patient, even if the operation is performed correctly. The reason for this is improper wound care, which leads to a deterioration in the condition of the hole and the development of an inflammatory process.
Types of pathology
Today, it is customary to distinguish several types of pathological bleeding: early and late, otherwise they are called primary and secondary. In the first case, we are talking about the fact that the blood does not stop for a long time immediately after the extraction of the diseased unit from the series. If the bleeding stopped quickly in the clinic, but started again at home, then secondary bleeding is occurring, and its causes should be investigated.
It is important to understand that during tooth extraction the surgeon applies quite a lot of force, which can damage blood vessels and unaffected soft tissues. This is why the appearance of blood is absolutely normal.
Only the dynamics of the development of the situation in the future and the patient’s well-being can indicate the beginning of the pathological process. To avoid complications, you should adhere to certain recommendations of a specialist, maintain oral hygiene and not injure the just operated area.
How to stop bleeding
Many patients simply do not understand the complexity of wisdom tooth extraction and when bleeding occurs after the procedure, they do not know how to stop the bleeding. If blood leaks from the gums within a few hours, you can consult a dentist or try to stop it yourself at home.
First aid with gauze swabs
Immediately after pulling out a tooth, the dentist washes the hole, treats it with an antiseptic solution and applies a gauze swab. After 15 minutes you need to spit it out. If this is not done, then after half an hour bacteria will multiply in the blood accumulated on the tampon, and this increases the risk of the inflammatory process.
If bleeding continues after spitting out the tampon, you should make a new tampon from a sterile bandage or gauze, apply it to the gums, firmly clamp your teeth and hold for about 20 minutes. If blood continues to accumulate in the oral cavity, then the procedure with a tampon can be repeated, only now it needs to be slightly moistened in a solution of Miramistin or hydrogen peroxide.
Home Remedies
the blood does not stop after the wisdom tooth is removed by the dentist , then you can use a cold compress. You need to apply a bottle of cold water or a piece of ice wrapped in a cloth to your cheek for a few minutes. Cold relieves pain well, reduces swelling and promotes the rapid formation of a blood clot.
Tea leaves have good tanning properties. To stop bleeding, you can apply a pre-wetted and cooled black tea bag to the place where the tooth was pulled out for 10 minutes. Just don’t apply a hot bag, as the clot that has already formed may melt.
Medications
When the gums bleed after tooth extraction, it is worth purchasing hemostatic drugs at the pharmacy, for example, Dicynon or Etamzilat. The tablets begin to act within 20 minutes after taking them, but the full effect is observed after several hours.
If you experience severe pain, you can take a painkiller. If, after visiting a doctor, an inflammatory process is diagnosed, then a course of antibiotics cannot be avoided; only a specialist must prescribe a specific drug.
In order not to irritate the gums even more, special hemostatic sponges can be applied to the wound. They perfectly normalize coagulation, have an antimicrobial effect and stop bleeding.
Symptoms of alveolitis
As a rule, the patient ignores the first symptoms of inflammation without due attention, considering them to be the norm after surgery. After tooth extraction, as already noted, pain within 24 hours is considered normal. As the hole heals, the pain subsides and completely disappears after a few days.
If the patient develops an inflammatory process, then the unpleasant sensations do not subside after a day or two, and 3–5 days after the operation, severe, throbbing pain in the socket occurs, which intensifies as the infection develops.
With alveolitis, patients may complain of both unbearable and moderate pain. Pulsation and pain are focused, as a rule, only in the removal area. However, in rare cases, the pain radiates to half of the face.
Other characteristic symptoms of alveolitis are:
- a sharp rise in body temperature;
- tooth sensitivity to hot/cold food;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- decreased appetite;
- increased salivation.
In rare cases, the disease causes weakness, increased fatigue, and secondary infectious foci appear on the oral mucosa.
Actions after surgery
To prevent hemorrhage and other negative consequences after the removal of a wisdom tooth, the following manipulations are performed directly in the dentist’s office:
- the alveolar socket is cleaned;
- the doctor examines the wound for any remaining tooth fragments;
- damaged tissues are treated with antiseptic agents;
- a tampon is applied.
If bleeding continues after 15-20 minutes, the doctor can inject hemostatic solutions, if large vessels are damaged, bandage them, apply hemostatic agents (fibrin film, sponge, aminocaproic acid, etc.), apply sutures or perform electrocoagulation (cauterization of blood vessels) .
Why is bleeding from a socket dangerous?
Intense bleeding from the gums often frightens patients - they fear dying from blood loss. However, the risk of death after tooth extraction surgery is minimal - this happens in isolated cases, and only with people who suffered from serious illnesses, alcoholism or drug addiction. But problems with internal organs and systems as a consequence of severe bleeding from the gums are quite likely, so it is not recommended to ignore severe bleeding.
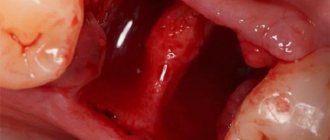
Blood clot after tooth extraction
Complications after wisdom tooth removal
Manipulations for the extraction of wisdom teeth should not be underestimated, since even if such procedures are carried out correctly, the patient may experience complications.
Edema
One of the most common consequences that occurs after tooth extraction is swelling. The reason for this may be partial damage to the tissues around the tooth. Usually the swelling goes away within 1-2 days. To speed up the elimination of swelling, this can be done by applying cold compresses to the cheek.
Fever
After a tooth is removed, the body’s natural reaction is to increase body temperature. This condition can last for 2-3 days. To improve your health, you need to take antipyretic drugs, but if the condition does not improve, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Soreness
Pain after extraction of the “eight” occurs due to damage to the periodontal tissues and nerves. If the pain cannot be tolerated, then for relief you need to take analgesics. When painkillers do not help, you should go to the dentist.
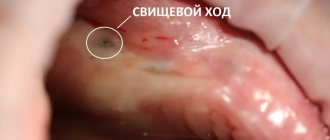
Suppuration of the socket
If the wound becomes infected, suppuration may occur. The reasons for the formation of pus may be non-compliance with medical recommendations and improper care of the oral cavity, as well as dental fragments remaining in the tissues after surgery. Self-medication in such cases is inappropriate; only a qualified doctor can prescribe adequate treatment and eliminate the cause of suppuration.
Dry socket
The blood clot must remain in the wound. It protects nerve endings and bone from microbial penetration. Therefore, on the first day after the manipulation, you should not rinse your mouth, and also do not eat hot food.
If a dry socket forms, this leads to increased pain, inflammation and alveolitis. In such cases, the doctor places a tampon with anti-inflammatory gel on the sore spot. Treatment continues until complete healing.
The wound is bleeding
In dental practice, there is only one known case in which a patient died after the removal of three adjacent teeth. The cause of death was not blood loss at all. The patient could not think of anything better after the operation than to drink a fair amount of alcohol and go to bed. Alcoholic drinks affect the liver, which increases bleeding. Due to alcohol intoxication, the sleep was sound, blood entered the respiratory tract, and the poor man choked.
In any case of bleeding due to an extracted tooth, the patient should calm down.
You only need to seek medical help in one case, if blood flows out of the wound in a stream.
If the patient is worried about bleeding, it is enough to make a tampon from sterile material and press it with your teeth to the wound for half an hour. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe special medications to stop bleeding. Doctors do not recommend using hydrogen peroxide in such cases.
If bleeding continues for more than a day, this is a symptom of a complication. Only a dentist, upon examination, will determine the cause of these complications and prescribe further treatment.
Precautionary measures
A wisdom tooth has been removed and the wound is bleeding – what to do in such situations? Hemorrhagic syndrome can be prevented with the help of hemostatic drugs, provided there are no contraindications.
In the first days after the manipulation, you need to brush your teeth with extreme caution and do not eat hot or hard foods. You should not stick your tongue into the hole, as such actions can damage the clot.
You should also avoid physical activity, visit the sauna, and take hot baths.
Before the procedure, you need to accurately and truthfully answer all questions asked by the doctor, especially about taking anticoagulants, aspirin and the presence of pathogenic diseases. Women do not need to hide the presence of menstruation and the use of contraceptives.
If you have high blood pressure or problems with blood clotting, you must notify your dentist.
In what cases should you seek medical help?
You should seek dental help after removing a figure eight in the following cases:
- with constant bleeding, the abundance of which does not decrease;
- with dizziness, severe headache and weakness;
- with sharp and severe pain in the gum area;
- with bloody discharge mixed with pus;
- when the elevated temperature persists for several days.
Swelling and swelling after the procedure are not a cause for concern. But when such swelling does not go away, then for your own safety it is better to visit the clinic as soon as possible.
Gums hurt
Often, after tooth extraction, the patient's gums hurt. Experts are confident that this is a natural reaction of the body to surgical trauma. In this case, the pain is moderate, but sometimes it indicates not only gum injury, but also inflammation. Medical statistics note that inflammation after tooth extraction occurs in 4% of operations. Gum pain as a result of inflammation becomes even more likely if not just one, but several hours of removal. How to determine whether a wound is healing? How to act in case of inflammation?
Normally, after a tooth is removed, a clot of dark blood forms in the socket, which over time acquires a white-yellow hue.
The duration of the pain depends on the level of injury and the appearance of inflammation; it usually hurts for no more than two days. The pain is much more serious if the inert tissue is severely damaged, which inevitably happens when cutting out bone using a bore. This surgical technique is used when it is necessary to remove a crown or extract a tooth in parts. In all other cases, prolonged pain indicates a medical error or problems in the body.
To relieve pain, the use of analgesics is allowed. Normally, they help a lot, but if the pill doesn’t work, this is evidence that the operation was performed incorrectly. Medical errors during tooth extraction occur frequently, especially in the following cases.
- When sawing out bone using a drill. Modern dental standards require the use of drill tips with a cooling component. But in domestic dentistry, most dentists use tips without cooling. As a result, the patient receives a burn, as a result of which superficial necrosis develops, accompanied by acute pain. If the pain does not go away after using NSAIDs, and a blood clot does not form in the socket, you will have to go to the doctor again. The doctor will clean the hole from dead tissue, after this manipulation the patient’s condition will return to normal.
- If there are sharp bones protruding from the socket. Such edges of protruding bones often injure the mucous membrane, especially if the bone is not completely covered by a clot in the socket. Most often, this problem occurs due to the fault of the surgeon who did not apply stitches to close the wound. The patient can independently determine the presence of cutting fragments by touching the tongue, as well as in case of severe pain when drinking drinks. In rare cases, bone fragments can be seen when examining the wound in the mirror.
- With mobility of parts of the bone in the wound. Sometimes the dentist does not notice significant pieces of bone that were formed when the tooth was rocked. Such pieces often cause pain and inflammation in the socket. The problem can only be corrected with a second visit to the dentist.
- Incorrect removal method. This is a common cause of complications after tooth extraction. Dentists have different experiences, so two doctors remove the same tooth in different ways. So, when removing, you can use forceps, but another doctor, to speed up the process, will divide the tooth into two halves and only then remove them.
- Excessive use of anesthetic, leading to spasm of the blood vessels of the gums. As a result of such an error, the hole after the operation does not fill with blood and a clot does not form. In an empty socket, the bone is exposed and reacts painfully to touch.
- The dentist did not apply stitches, which should be done even when removing some teeth with a single root. In the case of teeth with several roots, a suture is required in the vast majority of cases. A properly sutured wound reduces the intensity of pain and the likelihood of complications by half. With stitches, the wound heals much faster.
- The dentist did not prescribe antibiotics. These drugs are not always prescribed, but in difficult cases, inflammation and acute pain cannot be avoided without them.
Do not start taking medications without discussing with your doctor, relying on the recommendations of friends or the Internet. The pain normally lasts no longer than a couple of days and should be moderate. If the pain does not subside, bone particles are felt in the hole, the wound reacts to liquid, or an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth, you should immediately contact the dentist who performed the operation or any other similar specialist.
Professional assistance at the Berezka clinic
A dentist in a clinical setting stops bleeding in several ways, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual characteristics of the patient. It should be noted that each of the methods will be effective only if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Stitching
The damaged vessel is ligated over the hole or soft tissue is sutured. The boas of the method stop bleeding with equal effectiveness.
Electrocoagulation
The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia. They resort to this procedure if several capillaries are damaged. The tissues are dissected using a special tool, after which they are soldered, facilitating rapid healing of the wound.
Application of fibrin film
A fibrin film is applied to the place where the tooth was removed. In addition to the hemostatic effect, the film also has an anti-inflammatory, disinfecting and healing effect.
Tamponation
In this case, the dentist uses iodoform turunda. It is inserted into the hole in the same way as a gauze swab, but to a greater depth.
Hemostatic tube
The method is relevant for patients suffering from high blood pressure. The tube is carefully inserted into the hole and held until the AT is brought back to normal.
You can also use gelatin and collagen sponges to stop bleeding.
The dentist makes a decision on the need for additional treatment procedures based on the results of examining the condition of the wound after extraction.
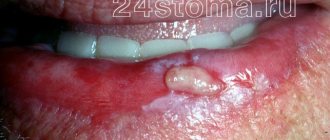
A growth has formed on the gum
After tooth extraction, there is often a complication such as the appearance of a lump on the gum. A growth in such a place indicates the onset of dangerous inflammatory complications. An infection can be caused if the clot is removed carelessly. Another source of infection is leftover food, so dentists prohibit patients from eating for several hours after surgery. During this time, a clot should form in the wound, protecting the gums from infection.
If a growth has formed on the gum, it may be an allergy to the anesthetics used or mechanical damage. Often a growth forms where the injection was given; such a new growth contains liquid inside, which in its structure is no different from a hematoma.
Such a lump will resolve in three days, unlike an infectious one, which often does not go away on its own and requires treatment.
Inside the growth, which is infectious in nature, there are purulent masses.
To determine the nature of the lump, the dentist performs palpation. By palpation, the doctor determines how hard the lump is and whether it contains liquid and pus inside. To make an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray or computed tomography may be prescribed. X-rays are not prescribed to pregnant patients. Based on the diagnostic results, the most appropriate treatment for the growth is prescribed.
- If there is no clot in the hole, it is cleared of inflamed tissues and treated with antiseptic materials. At the end of the manipulation, a hemostatic sponge is placed in the hole.
- The surgeon may decide to open the lump with a surgical instrument. After the procedure, the patient is invited to return for a follow-up visit in a few days.
- The general method of treating and preventing the growth is to take certain antibiotics.
Before coming to the dentist, the patient can rinse his mouth with furatsilin solution on his own. This drug cannot affect the size of the growth, but it will have an antimicrobial effect and reduce the intensity of inflammation. You can use dental ointments with an antibacterial effect. Folk remedies will not help get rid of the growth, but they can provide short-term relief. For this, soda and salt solutions are used. Rinsing should not be too vigorous, so as not to remove a blood clot that is beneficial for the body from the socket.
Benefits of wisdom teeth removal at Beryozka
If you need to extract a wisdom tooth in Balashikha, we invite you to carry out such a procedure at the Beryozka clinic. Advantages of our dentists' services:
- absolute painlessness and speed of manipulation are ensured by the professionalism and experience of dental surgeons;
- During surgical interventions, the clinic’s specialists use modern anesthetics;
- minimal trauma is achieved through the use of advanced technologies during operations, which prevents bleeding and promotes rapid healing of the wound surface.
Our clinic offers an objectively affordable cost for figure eight removal and each patient receives effective dental care.