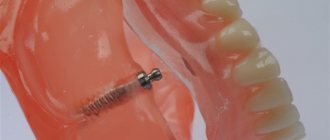
Although orthopedics as a science was formed not so long ago, people have been practicing dental prosthetics since ancient times. Animal bones, semi-precious stones, hard wood - everything that ancient doctors did not use as prosthetic material. But the methods of fastening were quite monotonous - using gold, less often silver, wire.
What are dentures made of now? The composition for prosthetics is selected for a specific clinical case, taking into account the patient’s wishes, indications and contraindications.
Content
- Composite
- Ceramics. Metal ceramics
- Ceramic dentures
- Metal alloys
- Plastic
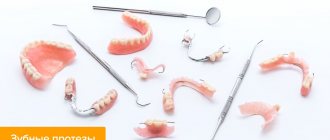
Modern materials for prosthetics help facilitate this process. Today, dentures are high quality structures that are barely distinguishable from real teeth and are comfortable to wear. They are made from various materials.
Modern prostheses:
- High quality;
- Wearable, with a long service life;
- Aesthetic;
- Ensuring the full functioning of the dental system.
Each of the materials from which dentures are made has its own characteristics.
This group includes:
- Ceramics;
- Metal ceramics;
- Plastic;
- Composites;
- Metal alloys.
The choice of the optimal option is carried out taking into account many factors.
PROMOTION
All-on-4 prosthetics turnkey!
120,000 rub.
Materials for dentures, their types and features, strengths and weaknesses.
— Composite
A composite is a polymer compound that may contain various additives. Typically, the composite contains quartz, silicon, porcelain dust and other options. Exposure of the composite to ultraviolet light makes it stronger and more durable. At first, composite was not as hard and was used more to replace front teeth, which are not as involved in the chewing process. However, modern changes that have affected the material allow it to be used more widely for prosthetics.
Composite materials are applied in layers, they are alternately applied to the extended tooth, and then irradiated with ultraviolet light and given the required size and shape. The doctor chooses a shade that matches the color of the patient’s teeth as closely as possible. Composites have a relatively low price and are stronger than plastic structures. Over time, they may fade, change color and may require replacement, which should be taken into account when choosing the type of prosthetics.
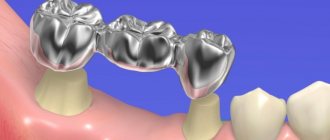
— Ceramics
This is a fairly popular material for dental prosthetics, because it has a number of advantages. Ceramic prostheses do not cause reactions from soft and bone tissues and have a high level of hygiene. The prosthesis is strong and durable and can withstand loads well. Ceramics is a material that easily meets the patient’s aesthetic needs and allows one to hide dental defects. The finished prosthesis is light and does not put pressure on the jaw, this is important for large-scale prosthetics, because then the weight of each element plays a role.
ledent.ru
Many are stopped by the price of the issue, but the cost of a ceramic prosthesis is justified by its quality, which is confirmed by long-term work with patients and assessment of the condition of the jaw after using ceramics.
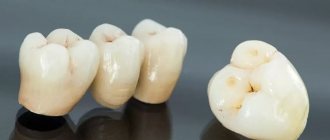
— Metal ceramics
Partial dental prosthetics and restoration of chewing elements are the most common field for the use of reinforced ceramic prostheses. They are based on a metal structure, which makes the final version more durable and prolongs its operation. Metal-ceramic dentures are of high quality at an affordable price, as well as an aesthetic appearance. This is the reason for the popularity of such designs.
They are used to replace severely damaged teeth, restore pulpless elements, and replace previous dentures that have worn out. Metal ceramics are used even in cases of pathological abrasion of teeth, which is a contraindication for the use of some other materials.
The advantage of the method is the possibility of widespread use of metal-ceramic prostheses - they allow you to restore several teeth, they are used in bridge structures, when the functional and anatomical parameters of the teeth are violated. Another advantage is the strength and long service life of structures. Metal-ceramics are preferred by patients and dentists for their beautiful appearance, versatility, reasonable cost and reliability.
Of the minuses, it is worth noting the fact that over time a metallic tint may appear along the edge of the gum, in the place where it is adjacent to the prosthesis. In some patients, metal cannot be used due to allergies. If gum recession occurs, the metal component of the structures may be visible from the outside.
— Oxide, zirconium dioxide
One of the most popular modern materials - it meets all the necessary requirements for prostheses. Crowns made from it have high aesthetics; it is possible to choose a color identical to the shade of the patient’s enamel. Zirconium structures are used to replace front, chewing teeth of different locations, because they are as strong and reliable as they are aesthetic. They can be used to form a bridge. The zirconium-based structure will last for several decades or more - just careful treatment and standard procedures for caring for the prosthesis.
The cost of zirconium prostheses may seem high - this is explained by the need for special technical equipment to form the structure. This is not surprising, because the material is really durable, not only in use, but also for the work of the technician. This price justifies the quality and durability of use. Cheaper materials are accompanied by a uniform decrease in service life and worse aesthetics.
— Metal alloys
Metal structures are certainly durable and strong; they do not change their position and appearance over the years. Basically, metals are used to replace lateral teeth, since the aesthetic parameters are low. Among the disadvantages, it is also worth noting the possibility of an allergic reaction. Metal can harm adjacent and contralateral teeth, because the alloy is much stronger than native enamel.
Crowns are made from alloys - these can be various compounds of chromium, cobalt, and nickel. The prosthesis performs its function well, but is not suitable for everyone. By the way, metal can affect and change the taste. Noble metals do not harm the body, are quite durable and have an appropriate price. We are talking about combinations of gold, platinum, palladium. Modern technology makes it possible to cast structures that ideally replace the loss and ensure a good fit of the prosthesis.
— Plastic (acrylic, nylon)
Used to form a removable denture. Acrylic has a lower cost, but this fact is accompanied by a number of disadvantages - acrylic absorbs odors well, which can cause discomfort, the material is stained and changes shade under the influence of tea, coffee and other food colorings. Plastic has a porous structure, which is a positive condition for the growth of bacteria. Such structures require careful maintenance, which will extend their service life and quality of use.
Nylon has the best performance for prosthetics. Structures made from it are light and flexible, resistant to deformation. They tolerate moisture well, are resistant to microbes and are safe for health. The aesthetic side is also a strong point of nylon prostheses - they are translucent and have discreet fasteners.
Composite
The composite is durable and has a long service life. Its only drawback is the high price. But if you need a prosthesis for life, it makes sense to resolve the issue in favor of this composition. Composite is a polymer with many additives that provide exceptional strength and make artificial teeth look like real teeth.
Prosthetics are carried out according to the following algorithm:
- A polymer composition is applied to the prepared area in layers, giving it the shape of a lost tooth;
- Each layer is dried with a special lamp.
As a result of this build-up, the tooth becomes stronger and regains its lost shape. The doctor may use a pin to strengthen the structure. The pin is installed into the remains of the tooth or directly into the root canal.
What is the best material for prosthetics?
The choice of materials for prosthetics is quite large. There is no clear answer to the question of choosing a prosthesis. It is best to answer this question from your attending physician. When selecting materials for the formation of a prosthesis, the dentist takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient, his anatomical data, the need for aesthetics, and capabilities. Options that are incompatible with local tissues and may cause a reaction or cause harm are immediately eliminated.
You also need to focus on what is most important to you - durability, price, aesthetics. A specialist will help you sort out this issue and choose the best option that will satisfy your basic needs and give good performance.
Ceramics. Metal ceramics
Ceramics for many years was considered the main material for prosthetics, despite the lack of high strength. This delicate material deteriorated over time, and prosthetics had to be started all over again. Modern ceramic and metal-ceramic prostheses have changed - they are reliable and strong.
The advantage of the material is lightness. Teeth made from it are almost not felt in the mouth. Aesthetic indicators are the best. Ceramics are used for both molars and front teeth.
When performed professionally, prosthetic structures are durable, their shade, translucency and shape are indistinguishable from natural teeth. The manufacturing process does not require much time and lengthy preparation. Treatment is carried out relatively quickly. Ceramics are suitable for patients prone to allergic reactions.
Technology and methods of prosthetics
Innovative technologies are also coming to dental orthopedics. The emergence of new materials and techniques allows for high-quality diagnostics (computed tomography, 3D modeling of future structures, etc.). From the initial examination to the stage of installation of dental prostheses, the orthopedic dentist has the opportunity to use the latest achievements of science. Today it has become possible in practice to manufacture high-precision durable orthopedic structures made of ceramics using milling machines using 3D models.
For all types of dental prosthetics, laboratory stages are mandatory, although today the use of innovative materials and technologies makes it possible to install dental prosthetics in one visit to an orthopedist. In this situation, the construction is manufactured on a special machine.
Metal alloys
As a rule, it is a compound of chromium, nickel and cobalt. The advantage of such materials is their increased resistance to mechanical stress.
Disadvantage: high allergenicity. In patients prone to allergic manifestations, adverse reactions occur frequently.
The preferred material is an alloy of platinum, palladium and gold. The prosthesis from it will be:
- Expensive, but safe and durable.
- Be comfortable and give a feeling of naturalness;
- With a ceramic coating, it will completely match the appearance of natural teeth.
Titanium is a popular and most modern solution in prosthetics.
Titanium prostheses:
- Durable;
- Safe;
- Lungs.
The only drawback is the lack of full compliance with aesthetic requirements. Titanium crowns are placed on the far molars. Here they are not visible to others, but they perform their task flawlessly.
Zirconium oxide remains the traditional choice:
- Lasting;
- Stable;
- Biologically compatible and safe;
- Meeting high aesthetic requirements;
- The color matches the natural enamel of the teeth.
Thanks to laser processing, artificial teeth made of zirconium dioxide completely match the natural shape of the tooth being restored.
What are dentures made from?
Modern dental prostheses differ from each other in aesthetic and functional parameters. Today, dentists use materials that are safe for the body and convenient to work with, with the help of which they can achieve the effect necessary for the patient and his health:
- composite;
- ceramics;
- metal ceramics;
- oxide, zirconium dioxide;
- metal alloys;
- plastic (acrylic, nylon).
Materials for making artificial crowns:
Materials for making artificial crowns
- Stainless steel (stamped);
- Alloys of gold and silver (all-metal cast);
- Cobalt-chrome, cobalt-nickel and palladium alloys (cast metal base combined or as an independent material);
- Plastics of cold (when mixing the components they harden in the oral cavity) or hot (when mixing the components they harden under heating and high pressure) polymerization (for clinical, i.e. directly in the office or laboratory production of temporary structures, respectively);
- Technical composites (temporary, laboratory-produced);
- Ceramic masses (for lining frames or making porcelain crowns);
- Zirconium dioxide (aluminum compound) is a modern standard of aesthetic prosthetics.
Disadvantages of nylon thermoplastics
- Uneven (point) distribution of chewing pressure due to the flexibility of the prosthesis and softening during use;
- Severe uneven atrophy of the alveolar ridge (this worsens the fixation of existing and subsequently manufactured prostheses);
- Absorb liquid and dyes (it is recommended to limit the consumption of strong tea, coffee, sour and hot foods);
- Impossibility of relocation and repair;
- Fairly high cost ;
- Difficulty in complete cleaning at home.
Therefore, their main purpose should be temporary prosthetics (from several weeks to two to three years). The period of adaptation to prostheses, of course, is strictly individual, but on average it is 5–10 days.
Description of the main characteristics of alloys
Hardness as the property of a material to resist the penetration of an indenter—another solid body—into it. This parameter determines the occlusal wear resistance and how the dentist can process and polish the prosthesis.
The yield stress is the stress required to cause permanent plastic deformation in tension. The proof strength is the stress that occurs at a strain of 0.2%. This parameter characterizes the strength of the alloy more than others. This is what people pay attention to first when choosing the design of a prosthesis.
The elastic modulus is another important property that determines the flexibility of a metal frame. An alloy with a high modulus of elasticity bends less under load than an analogue with a low modulus.
Elongation is the ductility of a material, measured as a percentage. The lower this indicator, the more fragile the alloy will be.
The melting temperature range is an important parameter to prevent frame deformation when firing ceramics.
Biocompatibility means that the alloy material is safe for the tissues of the body and humans in general. Non-noble alloys have mixed biocompatibility and should be used with caution.
Manufacturability is the maximum precision in manufacturing and processing of the frame.
The coefficient of thermal linear expansion indicates the compatibility of the alloy with ceramics. The main condition is that the coefficients of the alloy and ceramics must match as much as possible, and there should be no residual stress left in the finished restoration.
Preparation for prosthetics
Before proceeding with the manufacture and installation of dentures, it is necessary to carry out thorough preliminary preparation. If during the initial examination the doctor reveals diseases of the teeth, gums or other problems with the oral cavity, then you will need to undergo a mandatory course of therapeutic treatment. Also, regardless of the planned type of dentures, you should have your teeth professionally cleaned. If a patient requires microprosthetics using lumineers or veneers to improve their appearance, they will need to undergo whitening procedures in addition to cleaning. The presence of malocclusion and lack of space for implantation may require a course of orthodontic treatment.
How are they attached?
Several fixation methods are used for dentures.
On the closing valve. It is often called a “suction cup”; it is an element of the base, the basis of the structure, which in shape must exactly match the gum. When the denture is placed and bitten, air escapes from the gap between it and the mucous membrane. When completely sealed, a sealed space is formed, and the base is held as if on a suction cup. For more reliable fixation of a complete denture with a closing valve, special gels can be used.
On clasps. This fastening is used for conditionally removable, partial structures; they are mainly made of acrylic. Fixation is performed using metal hooks that are placed on the remaining teeth. Usually these are the incisors in the smile area, and therefore the clasps can be visible. Fixation is reliable, without the risk of displacement or accidental loss, the chewing load is distributed better than when using a locking valve.
On elastic clasps. They are used for structures made of nylon, made of plastic, pink in color, and invisible. Fastening is almost the same as when using metal hooks, but elastic clasps are more convenient, less damaging to the mucous membranes, and easier to get used to.
On attachments. These are composite micro-locks that can be used if the patient has preserved at least part of the dentition. One of the attachment elements is built into the base, the other is fixed to the supporting tooth and covered with a crown. The fixation is reliable, durable, the entire structure is protected from displacement, and transfers the chewing load well. Attachments are used with clasp dentures (having a metal base).
Advantages of nylon as a material for removable dentures
- Lack of so-called residual monomer - a substance that forms the basis of plastic powder and causes local allergic reactions (redness, swelling, itching of the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed) or even systemic in some patients;
- Biocompatibility (this is important for patients with diseases of the immune, endocrine, nervous systems, and gastrointestinal tract);
- The ability to withstand enormous loads when falling, hitting or bending while maintaining the original shape (elastic deformability - elasticity) - even if you drop the prosthesis on a tiled floor, nothing will happen to it;
- Lightness and grace, subtlety;
- Strength (the ability of the prosthesis to withstand chewing pressure without destruction);
- Greater aesthetics compared to acrylic dentures (“naturalness”);
- Subjectively, for patients - greater ease of use, both during primary and repeated prosthetics (comfort, quick adaptation and invisibility to others) - “soft dentures”.