Bleeding is considered to be the loss of blood from the body. Bleeding can be both external and internal. Blood can flow both from body tissues damaged for certain reasons, and from natural orifices of the human body.
Healthy people can survive 15% blood loss without serious consequences. Blood from the mouth is a fairly rare phenomenon, and most often its occurrence indicates serious problems with a person’s health. What are the causes of blood from the mouth?
Why does blood appear on teeth and how to deal with the problem
Bleeding gums are an alarming symptom that does not occur on its own, but is a sign of poor oral health. The problem cannot be left to chance. To find out the reasons for its appearance, you need to consult a dentist: if your gums are bleeding, this may indicate the development of a serious oral disease or an infection. In addition, the lack of timely treatment contributes to the appearance of bad breath, which will reduce the quality of life and lead to the development of complexes.
Causal factors for bleeding
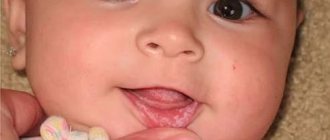
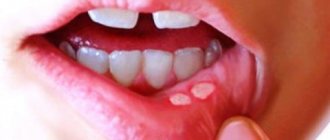
Normally, the gums are pink, smooth, dense, and fit well to the teeth. Any changes, including the appearance of bleeding, should be cause for concern. Various reasons can provoke the occurrence of an undesirable symptom.
Oral diseases
Often the problem begins as a result of bacterial activity. Under favorable conditions, namely insufficient oral hygiene, they actively reproduce. Because of this, a soft plaque forms on the teeth, which calcifies over time. This is how tartar appears. These are already solid deposits that provoke the development of an inflammatory process, which threatens the appearance of the following diseases:
- Gingivitis. When the disease occurs, the marginal part of the gum and interdental papillae become inflamed. In addition to bleeding, redness and swelling are formed in those areas where the mucous membrane comes into contact with dental plaque.
- Periodontitis. The disease manifests itself as a result of untreated gingivitis. In this case, the pathological process moves to periodontal tissues - those that hold the tooth in the socket.
The appearance of gingivitis and periodontitis is possible not only in an adult, but also in a child. According to statistics, tartar occurs in 2/3 of all high school students, and 1/4 of school-age children experience gingivitis.
Other diseases
The cause of bleeding may be vitamin deficiency. It is difficult to determine which vitamins are lacking when it occurs, because an imbalanced diet in general has a bad effect on oral health. But it is worth introducing foods containing iron, vitamin C and potassium into your diet. If you have an unpleasant symptom, you must also exclude the following diseases and pathologies:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes;
- AIDS;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- fragility of blood vessels;
- infectious diseases of the throat and nose;
- allergic reaction to medications, materials used in dentistry, toothpaste.
Bleeding gums are common in pregnant women and teenagers. This is explained by hormonal changes in the body. Expectant mothers often note that their gums hurt and swell. This condition is short-term and goes away on its own.
Common reasons
As already mentioned, blood in the mouth can occur due to poor oral hygiene. Incorrect brushing technique (strong, intense pressure) can lead to injury to the gums. Thus, using a hard toothbrush is a constant traumatic factor. Wisdom teeth are often difficult to clean. Due to problems with access, the brush hurts the gums. Bleeding may also occur for the following reasons:
- wearing braces or dentures;
- malocclusion;
- incorrect dental treatment of teeth or gums;
- smoking - bleeding occurs due to toxins that irritate saliva and weakened immunity in smokers;
- burn and injury to the mucous membrane with a sharp object;
- chipping of an old filling.
Taking certain medications can sometimes cause a decrease in the rate of saliva production. Since it resists bacteria, this can provoke a sharp development of pathogenic microflora.
Survey
To identify the causes of vomiting with blood, a gastroenterologist prescribes a comprehensive examination, which is aimed at studying the morphological and functional features of the gastrointestinal tract. Instrumental studies have high diagnostic value; laboratory tests help determine the severity of hemodynamic and metabolic disorders. The examination plan includes:
- Endoscopic methods
. To accurately determine the location of bleeding and visualize the defect in the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract, an endoscopy is performed. If necessary, during the procedure, coagulation of the affected vessel is performed, and a biopsy is taken from pathologically changed areas of tissue. - X-ray examination
. X-rays with oral contrast are performed only after vomiting has stopped and the condition has stabilized. The method is informative for diagnosing organic changes and hernial formations. Contrast leakage beyond the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract indicates perforation or fistula tracts. - Sonography
. An abdominal ultrasound is prescribed to quickly assess the condition of the abdominal organs. Sonography is used to identify space-occupying formations in the gastrointestinal tract, hernias, and diagnose liver diseases. To assess linear blood flow in the hepatic and splenic veins, Doppler sonography is performed. - Laboratory methods
. A general blood test is necessary to determine the degree of blood loss and the severity of anemic syndrome. If hereditary defects in the hemostatic system are suspected, an extended coagulogram is performed with determination of prothrombin time and other coagulation parameters. Sometimes serological tests are prescribed.
For possible primary disorders in the vascular system, contrast angiography is performed; radioisotope scintigraphy is recommended to assess the condition of the liver parenchyma. Additionally, macro- and microscopic analysis of stool is performed; to exclude intestinal bleeding, the Gregersen reaction to occult blood is informative. If hematemesis is combined with signs of hemorrhagic diathesis or general infectious syndrome, consultation with other specialists is required.
Before arrival
Symptoms accompanying gum disease
Pathologies that cause blood from the mouth may be accompanied by a number of other unpleasant symptoms:
- swelling of the gums;
- pain when pressing or eating solid foods (sometimes the pain is quite severe);
- itching and discomfort in the gum tissue;
- bad breath;
- tooth mobility (with advanced dental diseases).
Even if nothing bothers you throughout the day, and blood appears only when brushing your teeth, this may indicate a problem.
Treatment
It is important to remember that hemoptysis is only a symptom. It is important to treat the underlying condition and make efforts to stop the bleeding. If these are inflammatory processes (pneumonia, bronchitis), a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy in combination with drugs to regulate blood clotting are indicated. Regular cleansing of the bronchi from bloody sputum (sanitation) is also indicated.
If this is a tuberculosis lesion, anti-tuberculosis therapy is necessary, including surgical interventions on the affected lesions (cavities). For injuries and abscesses, the solution to problems is surgery; for cancerous lesions, tactics are selected individually, depending on the stage. Source: Ittrich H, Bockhorn M, Klose H, Simon M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemoptysis // The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemoptysis.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017 Jun 5;114(21):371-381. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0371..
How to quickly stop bleeding from gums
What to do if you need to quickly stop bleeding from your gums? For this purpose, you can use one of the following methods:
- Rinse your mouth with cold water or mint mouthwash. Decoctions of herbs - chamomile, oak bark, fir, calendula - help reduce the manifestations of unwanted symptoms.
- Apply a cotton swab soaked in chlorhexidine to the bleeding area. You need to press it tightly and wait until the bleeding stops.
- Glue a special protective homeopathic strip. You can buy it at the pharmacy.
No matter how long your gums bleed, you cannot put off a visit to the dentist. The problem will not go away on its own, but will only get worse.
How to eliminate constant bleeding gums
To carry out successful treatment, it is important to find out why the gums are bleeding. You should not self-medicate, since the problem requires an integrated approach, which consists in eliminating the cause and restoring the health of the gums. Only a doctor can tell you how to treat a disease that causes bleeding. Different techniques may be needed.
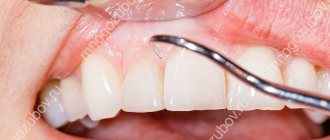
Professional teeth cleaning
If dental plaque provokes complications in the form of bleeding, it is necessary to thoroughly clean your teeth. This does not mean ordinary hygiene procedures at home, but hardware cleaning in a dental office. The doctor uses ultrasound to crush the tartar, the particles of which are washed out with a mixture of water and air. You need to carry out a hygiene procedure twice a year. Unfortunately, not all patients comply with such recommendations.
Air Flow technology is used to remove soft deposits. In this case, finely dispersed soda is supplied along with water. After the procedure is completed, the teeth are polished, which further prevents the accumulation of plaque.
Such actions are sufficient for diagnosed gingivitis. The doctor will also tell you what to do to restore the mucous membrane. This may include rinsing or taking certain medications. Professional teeth cleaning is used if gingivitis has progressed to periodontitis. But this is only the beginning of treatment. Let's talk about ways to eliminate the disease further. If periodontal pockets have formed, you will need powerful ultrasound devices, such as Vector. In this case, the periodontist should deal with oral hygiene.
Rinse with solutions
Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity can be carried out in the form of rinses based on the following agents:
- "Furacilina";
- "Rotokana";
- "Miramistina";
- "Chlorhexidine";
- alcohol solution "Chlorophyllipt".
Soda-saline solution also helps. You can add a few drops of iodine to it. It is better to use solutions through an irrigator - this increases their effectiveness. In case of bleeding, you need to use special toothpastes, including Parodontax, Lakalut, Colgate Total Pro. The compositions should not have a bleaching effect.
Drug therapy
To eliminate bleeding gums, the doctor may prescribe ointments and gels. They are applied to the problem area after rinsing the mouth. The following drugs are in demand in dental practice:
- "Metrogil Denta" - has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, often prescribed for stomatitis, after tooth extraction;
- “Asepta” is a propolis-based gel that quickly relieves inflammation;
- "Kamistad" is a drug available in two forms (for children and adults);
- "Elugel" is a strong antiseptic that effectively fights pathogenic environments.
For inflammatory processes, the doctor may prescribe medicinal bandages, antibiotics (in some cases), and a course of vitamins.
Gum curettage
For periodontitis with the formation of deep periodontal pockets, the following surgical techniques are used:
- Closed curettage. To carry out the procedure, the doctor uses a special instrument – a curette. With its help, the doctor cleans the roots of the teeth. The tool penetrates to a depth of 3 mm.
- Open curettage. The technique is used when the deposits are deeper. It involves the following actions: peeling of the gums, cleaning and antibacterial treatment, suturing.
The disease can be cured using an integrated approach. Therefore, it is important to follow all doctor’s recommendations even after the procedure.
Medicines
The choice of medications is determined based on the type and stage of the disease. Miramistin, chlorhexidine, furatsilin can be used for rinsing the mouth. In the presence of inflammation, you can use ointments that have anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effects. Infections are treated with the following:
- antibiotics;
- antiseptic drugs;
- antifungal agents;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamins.
Home treatments can be used as aids. Good results are shown by rinsing with herbal infusions of calendula, chamomile, and yarrow. To eliminate pain and strengthen soft tissues, use propolis tincture or a solution of soda and sea salt.
Preventive measures
To avoid gum problems, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- Perform high-quality and correct hygiene procedures aimed at oral health. It is necessary to select care products that will not injure the mucous membrane. You should brush your teeth morning and evening. Use dental floss with caution. Instead, you can use an irrigator, which will help effectively remove food debris. Your toothbrush should be changed every three months.
- Balance your diet. The body must receive all the necessary vitamins and minerals. To strengthen teeth and gums, it is important to eat solid plant foods, such as apples and carrots.
- Give up bad habits, in particular smoking. Toothpicks should be used with caution.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist - at least twice a year. This will allow timely detection of oral diseases.
Paying close attention to your oral health will help you maintain a beautiful and healthy smile for many years.
"Diclofenac"
Another NSAID drug. Relatively safe, good pain relief.
Tablets are recommended for toothache. They contain from 25 mg to 100 mg of diclofenac sodium.
The medicine is prohibited:
- children under 6 years of age (if the dosage is more than 25 mg), and adolescents under 18 years of age (if the dosage exceeds 100 mg);
- for erosions and ulcers of the digestive organs;
- if the patient is intolerant to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women.
Prescribe with caution to people with heart, kidney and liver failure.
- Bleeding in the middle of the cycle: causes
Diclofenac will relieve pain faster and more effectively if you take it half an hour before meals. The maximum dose per 24 hours is 150 mg, divided into 2 to 3 doses.