Vitamin A
Vitamin A or retinol enhances the protective properties of the skin and mucous membranes. With its deficiency, yellow pigmentation and hypoplasia of the hard tissues of the teeth may appear on the teeth, if this deficiency in the vitamin is revealed during the period of their development. If a deficiency of vitamin A occurs after teething, a disease such as hyperkeratosis and proliferation of the base layer occurs.
With an excess of vitamin A, an anomaly in the development of the jaws and tongue occurs, as well as an anomaly in dentin density.
Methods for diagnosing gingival bleeding
Before determining what to do if the gums are bleeding, inflamed and painful, or why there is bleeding between the teeth, the doctor must prescribe certain diagnostic tests to determine the causes of the disease and identify systemic diseases. For this, the following are shown:
- visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity;
- general blood test, urine test;
- coagulogram;
- stool examination;
- X-ray, CT.
Examining the mucous membranes, the specialist assesses their condition. What is important is the neglect of the inflammatory process, swelling, the severity of redness, the presence of plaque and stone.
In medicine, there are 6 degrees of bleeding (starting from zero and higher as the pathology develops). The method for determining the PBI index (from 0 to 4) is also used.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D - regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body, stimulates the growth and formation of bones, and participates in the formation of tissue respiration. With a lack of vitamin D, the well-known rickets develops, as well as dental caries. In addition, a lack of vitamin D leads to a primary state of calcium metabolism. There is an increase in the volume of the organic dentin matrix. Osteoporosis of the bone tissue of the alveolar process may develop, and in severe cases, enamel hypoplasia occurs. With a lack of vitamin D, as well as calcium and phosphorus, rickets occurs in children, and osteomalacia (mineralization disorder) develops in adults.
With insufficient amounts of vitamin D and normal levels of calcium and phosphorus, osteoporosis and resorption of dental cement develop.
With a lack of vitamin D and calcium, but with a normal amount of phosphorus, resorption of the jaws and hemorrhages into the bone marrow spaces may occur.
With a lack of vitamin D along with phosphorus, with a sufficient amount of calcium, rickets occurs.
With a lack of calcium and phosphorus and with normal vitamin D levels, alveolar bone resorption occurs.
With a lack of phosphorus and with normal levels of vitamin D and calcium, there is slow growth of the jaws, delayed teething, which subsequently leads to bite pathologies.
Hypervitaminosis D also leads to negative consequences. First, osteosclerosis occurs, then osteoporosis and resorption of the alveolar process. In addition, intensive formation of tartar occurs, hypercementosis and ankylosis occur. It should be noted that death can occur when large doses of vitamin D are administered.
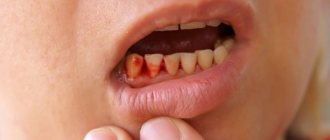
Why is there bleeding from the gums - what to do for treatment
Mucous membranes can bleed under the influence of various factors. They can be non-pathological (accidental injury, rubbing with dentures, orthodontic systems, taking certain medications) and pathological (the presence of systemic diseases, hormonal imbalance, etc.). Let's deal with each in turn.
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
The mucous membranes suffer from a lack of these substances and respond with reactions. As a rule, such symptoms clearly manifest themselves towards the end of the winter period, when vitamin deficiency is especially acute. The tissues do not receive enough essential components (C, D, E, potassium, etc.) and respond with a symptom - severe bleeding of the gums (we will look at how to deal with it below).
Quite often, a lack of ascorbic acid leads to the development of scurvy. The patient feels a loss of strength, lethargy, the appearance of rheumatoid pain, loosening of incisors, canines and molars. If the body lacks any elements, this negatively affects the functioning of internal organs and systems. Blood is just one of the symptoms indicating existing problems.
Dental procedures
When a person visited the dentist the day before, it is likely that for some time he will be bothered by the consequences of traumatic exposure. This especially applies to such manipulations as extraction of a unit or insertion of a pin or other structure during implantation.
As a rule, unpleasant signs disappear after a few days. The same applies to cases of using cheap orthodontic elements of low quality. Often the cause of bleeding gums (no treatment is needed here) is not pathological; the problem can occur after standard professional cleaning or installation of a filling.
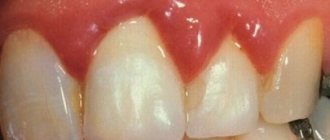
Gingivitis – inflammation of the upper mucosal epithelium
This is a disease of the oral cavity accompanied by an inflammatory process. The soft tissues swell, turn red, hurt, and in most cases bleed. If you neglect timely medical intervention, the symptoms will only worsen, especially at night. A person will not be able to fully rest and work.
The disease will penetrate into deeper layers and periodontitis will develop. The disease is easily treatable, but only if you consult a doctor in the earliest stages.
Stomatitis with ulceration
The patient's mucous membranes are affected, saliva flows profusely, and bad breath appears. Painful whitish ulcers and a dense yellow coating form. Children are more susceptible to the disease. The main reason why gums bleed, if bleeding occurs in this case, is poor oral hygiene. At first, soft deposits remain on the enamel, which subsequently harden and turn into stone. This is an ideal environment for bacteria to multiply.
A sharp decrease in immunity, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and allergies can also provoke the disease. The patient experiences severe pain when swallowing and chewing food and drinking.
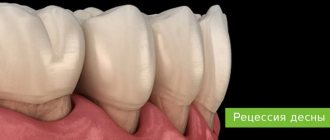
Periodontitis and periodontal disease
This phenomenon is observed in cases where inflammation is not cured in a timely manner and spreads to the deeper layers of the mucous membranes. The acute form is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. It is impossible to completely get rid of these diseases, but with a competent approach to therapy, stable remission can be achieved.
Mechanical injury
Sometimes the problem occurs when soft tissue is damaged and does not indicate a pathological process. This happens for various reasons (a home remedy for bleeding gums will not be effective if the traumatic effect continues):
- habit of biting nails, pen cap;
- brushing too vigorously;
- incorrectly installed crowns, fillings, implants;
- period of adaptation to the braces system, etc.
Don't panic. It is better to carefully examine the gum surfaces for signs of injury and consult a doctor. Even if the symptom really did not appear due to a pathological factor, the dentist will be able to prescribe healing and antiseptic agents that will speed up healing and prevent infection.
System-wide disorders and hormonal changes
All signs must be considered as a whole. For the above reasons, if the gums bleed heavily, treatment at home is only permissible if an accurate diagnosis is made in a medical institution. To do this, the patient should undergo a thorough examination and consult with specialists on all issues.
Possible indicators:
- hormonal changes due to pregnancy;
- deficiency of essential substances;
- diabetes;
- hemophilia;
- viral infections;
- autoimmune diseases;
- liver pathologies;
- oncology.
Because health problems can be very serious, if blood is detected, it is recommended to visit a doctor immediately.
Bleeding gums due to medication treatment
Certain medications provoke similar symptoms. As a rule, it disappears after stopping the drugs. However, if the symptom is pronounced and worries you greatly, it is better to go to the clinic to replace it with another medicine or completely cancel such therapy.
Similar symptoms occur quite often. In this case, it is important to determine which component caused the negative reaction. If this is not possible, treatment is selected carefully to avoid serious complications.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C - normalizes the permeability of the vascular wall, its strength and elasticity, and also increases its resistance to infection.
The human body is unable to synthesize vitamin C, so it must be obtained from food. With a lack of vitamins B and C, a disease such as scurvy or scurvy develops. In this case, bleeding, hemorrhages in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, joints are observed, and degenerative processes develop. Collagen formation is also disrupted and bone tissue formation slows down. Hemorrhagic gingivitis, rapid-onset periodontitis, occurs directly in the oral cavity.
What to do if your gums bleed constantly
Have you tried different methods and methods to combat bleeding, rinsed your mouth with different herbs and bought the best toothpastes, but nothing helps?
To cure sore gums, you need to perform a number of simple steps:
- Visit the dentist and have ultrasonic cleaning of dental plaque. They are the common cause of blood when brushing teeth and a bloody taste in the morning. Teeth brushing should be done 1-2 times a year.
- After brushing, you should definitely buy a new toothbrush (preferably medium hard or soft), since the old one has accumulated a large number of bacteria, which can cause your gums to bleed.
- If finances allow, get treatment from a periodontist. He will inject a special medicinal solution into the periodontal pockets - they will shrink, food debris will not accumulate in them and bacteria will not multiply.
- Buy an irrigator. This is a device that removes food debris using a water jet. It not only cleanses the oral cavity and makes teeth whiter and cleaner, but also strengthens weak gums by massaging them. Of course, in the first days of cleansing you will bleed more than usual, but after 2 weeks you will notice the result - your breath will become fresher, bleeding will decrease, and stones will appear much less frequently.
- Be sure to brush your teeth 2 times a day, use a mouthwash and, if necessary, floss if you do not have an irrigator.
- Use folk remedies. You can make a decoction of oak bark and rinse your gums with it 2-3 times a day; tincture of chamomile, linden or calendula is also suitable for these purposes.
- Eat carrots and other hard vegetables to strengthen your gums and teeth.
Don't delay treatment! Make an appointment now:
Foods necessary for healthy gums and teeth
In addition to vitamin-mineral complexes for teeth and gums, you should eat foods such as:
- hard vegetables and fruits: cucumbers, apples, beets, pears and carrots;
- citrus fruits: especially grapefruit and orange, which reduce bleeding gums;
- berries: cloudberries, lingonberries, cranberries and other forest products are especially useful for tooth enamel;
- dairy products: fresh cottage cheese and cheese can replenish calcium reserves in the body;
- nuts, in particular cashews and almonds;
- honey;
- seafood;
- eggs.
Causes of vitamin deficiency
Accordingly, the following factors lead to vitamin deficiency.
Nutritional factors. Here we can highlight:
- predominant consumption of foods in which vitamins are present in insufficient quantities and are absent altogether;
- malnutrition. Passion for fasting and other “folk” methods of weight loss often cause hypovitaminosis;
- excess sugar consumption;
- culinary processing or storage conditions that contribute to the destruction of vitamins in foods. The diet must include fresh fruits and vegetables;
Digestive disorders, in particular:
- defects in the mechanisms of vitamin absorption;
- dysbiosis – a disruption of the normal microflora in the intestines (for example, as a result of an infectious disease or antibacterial therapy);
- activation of pathogenic microflora;
- intestinal parasites;
Factors that affect the body as a whole and suppress the immune system. This is, first of all:
- unfavorable environmental conditions (increased background radiation, ingestion of heavy metals, pesticides and other highly toxic substances);
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
Uncompensated increased need for vitamins. The body requires more vitamins than usual when:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- stress;
- significant physical activity;
- work in low temperature conditions, etc.