Pain after tooth extraction: how long does it last, and is it normal? These and other questions concern patients after dental procedures. Pain syndrome is normal in several cases: early postoperative period, complex removal, simultaneous implantation.
Normally, pain can persist from several days to a week, and its intensity should decrease. The appearance of symptoms such as increased pain, swelling, inflammation, bleeding or the appearance of purulent exudate is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
How does a postoperative wound heal?
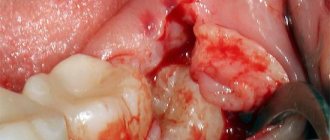
How long the area hurts after tooth extraction depends on many factors. The healing process after tooth extraction is a complex and lengthy process. Removal occurs with a rupture of the dentofacial connection, namely the connection with the alveolar process and the jaw bone.
The recovery process lasts about two to three weeks. Much depends on the surgical protocol, the clinical situation and the characteristics of the body.
Main stages:
- Formation of a blood clot. Forms 1.5-3 hours after extraction. The function of the clot is to protect the wound area from pathogens and secondary infection.
- Active tissue regeneration. The affected mucous membranes are restored, after 3-4 days swelling and inflammation decrease.
- Formation of granulation tissue. After 4-6 days, granulation tissue forms on top of the clot - the basis of a new epithelial layer.
- Granulation proliferation. After a week, the granulation tissue grows, completely covering the socket.
Already on the eighth to tenth day, the wound is completely healed and by the end of the second week a new epithelial layer is formed.
After two weeks, bone tissue begins to renew. After six months, the bone tissue in the area of removal becomes completely healthy.
How to remove formation
Before removing the cyst, the dentist will prescribe additional procedures that will help safely get rid of the purulent accumulation. To do this, it is necessary to fill the diseased teeth and clean the root canals. Surgical intervention includes the following stages:
- The patient is given an anesthetic.
- The soft tissue is cut to open access to the root of the chewing element and remove the cyst. If necessary, the gums on adjacent teeth are cut.
- The cortical plate is removed using a drill. As a result, the doctor has the opportunity to get to the root of the tooth on which the tumor has formed.
- Resection of the root apex is performed, while the tooth structure is preserved and the cyst is removed.
- If the removal is successful, the doctor cleans the root canal. Cleaning helps neutralize residual pus and infection that cause inflammation.
- A bone-like substance is installed to completely restore the structure of the damaged unit of the dentition.
After this, the doctor schedules an appointment to conduct an examination and determine the presence or absence of complications after cystectomy. During the examination, the specialist determines whether the tumor has begun to develop again.
Causes of pain
The occurrence of pain after tooth extraction is associated with damage to nerve endings, vascular structures and soft tissues. The peak intensity of pain occurs in the first hours after the cessation of anesthesia. The symptom persists for about 12 hours.
In case of incisions in the gums or damage to the bone tissue, as well as after implantation after removal, toothache may persist for 2-3 days. Pain syndrome also occurs in the case of displacement of the dentition towards the formed void. Therefore, doctors recommend prosthetics as soon as possible after extraction.
When deletion is indicated
Modern dentistry strives to preserve teeth and their roots whenever possible, but this is not always possible. Dental surgeons remove teeth with cysts for the following indications:
- the infectious process was caused by an advanced form of periodontal disease;
- there is a vertically located crack on the root of the tooth or on itself;
- the dental root canals are impassable, as a result of which therapeutic treatment becomes impossible;
- severe tooth decay, and restoring it does not make sense (too expensive and time-consuming);
- the tooth is located entirely in the cavity of the neoplasm;
- the cyst has grown into the nasal cavity, or the size of the tumor is more than 10 mm;
- the root of the tooth has fused with the neoplasm;
- the tooth is very loose.
The dentist decides to remove a tooth with a cyst after a thorough examination of the patient, which includes examination, history taking, radiography or visiography.
Pain during difficult removal
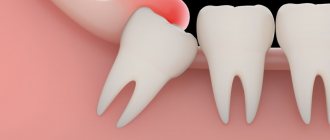
The duration of pain after complex extraction (wisdom teeth, impacted or dystopic incisors) is associated with damage to a larger tissue area. Often such an operation involves making an incision in the gum, sawing out the roots, extracting tooth fragments, and draining an abscess, which increases the scope of the surgical intervention. If your ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal, this may indicate nerve damage.
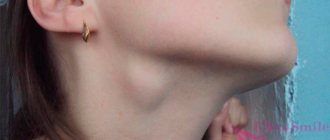
In some cases, patients complain of persistent discomfort and pain for up to a week. Clinical manifestations such as swelling, swelling of the gums, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, fever, and malaise are also common.
Dangerous complications of long-term pain
Ignoring pain and tissue swelling can lead to serious complications that may require surgery.
When the inflammatory process is advanced, purulent foci form in the tissues, increasing the risk of pus spreading through the bloodstream throughout the body. The development of phlegmon and destruction of the jawbone is likely. With a hematoma, a thickening of the clot may occur, which will inevitably lead to the need for surgical intervention, the appearance of scars and an increase in recovery time.
Types of pain
The nature and type of pain depends on the type and surgical intervention, the duration of the operation, and the complexity of the clinical process. Clinicians distinguish the following types:
- Aching. It is felt immediately after the anesthesia wears off. Keeps for about 2-4 days. The jaw may ache when opening the mouth or chewing.
- Intense, enduring. Occurs during extraction of a complex tooth with drainage or opening of a purulent cavity.
- Phantom. Occurs after traumatic surgery and may be felt from time to time. Phantom pain occurs with weak immunity and a low pain threshold.
It is difficult to say how intense the pain will be in each specific case, which is why it is so important to follow medical recommendations to prevent complications.
What to do during the recovery period
After surgery, swelling, pain, and inflammation may be observed in the area of the gum where the cyst was removed. If the patient conscientiously follows the doctor’s recommendations, the symptoms will disappear after a short period of time. To avoid negative consequences and re-development of the disease, the doctor recommends following some rules:
- To brush your teeth, you need to purchase a brush that will not cause bleeding or irritation of the gums.
- The diet that must be followed during the recovery period should not include solid, overly hot or cold foods. In addition, avoid consuming foods that are not capable of causing irritation of soft tissue, which, in turn, will cause a re-inflammation process.
- The patient should give up bad habits that can negatively affect the integrity of the teeth and soft tissue after cystectomy. It is not recommended to smoke or drink alcoholic beverages.
- It is necessary not to take medications that can cause an allergic reaction or are included in the list of other contraindications. With such a reaction of the body, the structure of the teeth and soft tissues will be disrupted.
If the patient carefully follows all medical recommendations, the risk of re-formation of the cyst and inflammation will be reduced.
What else can pain indicate?
Severe pain after removal may indicate the development of complications. Pulsating pain that radiates to the ears and submandibular lymph nodes is not normal. The most common causes of complicated postoperative pain are the following factors:
- Violation of treatment protocol. Unfortunately, mistakes do occur, especially in the removal of complex teeth. The techniques and approaches used in different clinics may differ from the standards. Errors include leaving fragments of materials or a splintered tooth root behind.
- Alveolitis. Occurs in the absence of a blood clot. The disease complicates natural healing and interferes with normal tissue regeneration. That is why doctors do not recommend touching the wound with your tongue or rinsing your mouth intensively.
- Dry hole. One of the common complications and the cause of long-term pain after tooth extraction. Despite the moisture of the mucous membranes, bone tissue is visible at the bottom of the wound opening. This problem is typical for smokers during periods of hormonal surges. The doctor seals the wound with a swab containing medication.
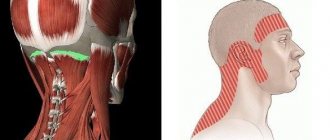
- Trigeminal neuritis. Long-term pain persists when a tooth in the mandibular row is removed if the trigeminal nerve is damaged during the manipulation. Damage may be accidental due to structural anomalies or multiple branching of nerve structures.
The likelihood of complications developing is low if the removal protocol, medical recommendations after extraction, and timely response to alarming manifestations are followed.
Treatment methods
The choice of a specific treatment method depends on the cause of the problem and the complexity of the situation as a whole. An integral part of therapy in this case is the use of appropriate medications - antibiotics and vitamin complexes, designed to facilitate the rehabilitation period. It may also be necessary to antiseptically treat inflamed tissues and place medicine inside the socket to fight infection.
Treatment of alveolitis Treatment of this disease involves complete cleansing of the socket from inflamed tissue, antiseptic treatment of the cavity, followed by placement of a medicinal product inside. Such compresses can be carried out either one-time or consist of a course of several procedures - it all depends on the severity of the inflammatory process. Additionally, antibacterial drugs and oral baths with antibacterial agents are necessarily prescribed, which promote tissue restoration.
Price:
from 3,000 rubles more about the solution
Treatment of facial nerve neuralgia An unsuccessful tooth extraction can lead to facial nerve neuralgia. Often the problem manifests itself in the form of minor inflammation of the nerve, which is accompanied by numbness in a certain part of the face. To solve the problem, drug therapy is carried out using anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsant drugs, as well as physiotherapy and electrical stimulation. Surgery can be performed to restore the integrity of the nerve, but this is a last resort and is usually necessary in advanced stages.
Price:
from 4000 rubles more about the solution
How can you reduce pain?
In the early postoperative period, it is important to follow basic recommendations that reduce the risk of negative manifestations:
- maintain the integrity of the blood clot - do not touch the wound with your tongue, rinse vigorously with solutions or water, just take an antiseptic or herbal decoction into your mouth, hold for a few minutes and spit;
- after a complex removal, take broad-spectrum antibiotics - this is important to prevent the infectious process;
- taking symptomatic medications for up to 2-3 days - in the first days, medications help reduce pain and inflammation;
- use a gel with a cooling effect for intense pain;
- do not eat for two hours after surgery, and eat solid food in the area of manipulation for 5-7 days.
You can reduce the pain if you chew a piece of ginger or propolis on the healthy side of the jaw, apply ice through a handkerchief to your cheek or chin, and rinse with the following ingredients:
- tea tree (10 drops per 500 ml of boiled water);
- steep chamomile decoction;
- decoction of eucalyptus and string;
- soda-salt solution (1 tsp soda, 1 tsp salt, 500 ml water).
The temperature of rinsing solutions should be comfortable - neither cold nor hot. Herbal solutions are best used as an alternative 3-5 days after surgery. In the early period, it is better to rinse the wound and oral cavity generously with water-based antiseptics.
The appearance of pain after tooth extraction is associated with trauma to the deep layers of the jaw structures. The tooth can hurt from several hours to 3-7 days, depending on the severity of the clinical situation and the scope of medical intervention. If questionable symptoms or other signs indicating complications appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Treatment of a cyst under an extracted tooth
The neoplasm is treated surgically. An x-ray is taken first. The image shows the area where the capsule is localized, its size, complications, for example, bone melting after rupture of the bladder with advanced pathology.
The doctor removes the cystic sac, cleans the cavity of pus, if there is any, and carries out an antiseptic treatment. When using a laser, the operation is performed practically without blood, and wound healing is faster. In any case, you need to take antibiotics to prevent relapse.