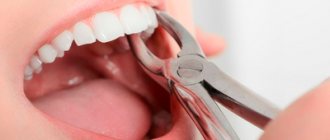
It may take one minute or an hour, using a drill and a scalpel, but there is no way to avoid it.
Tooth extraction is a surgical operation to remove a tooth from its socket. A basic dental procedure that can scare anyone. Fear of removal is due to the idea of ancient times, when they did not think much about the patient’s comfort, much less about good anesthesia.
The fear has not gone away, but approaches to dentistry have changed dramatically. Let's look at when it is necessary to be examined by a dental surgeon, what options are available for tooth extraction, and how to quickly recover after surgery. We will also consider frequently asked questions to the dentist.
Indications for removal:
- a painful tooth provokes the development of a cyst, negatively affects the function of the trigeminal nerve, causing its inflammation;
- abnormal position of the tooth, improper eruption, which affects the bite;
- constant injury by the edges of the crown of the mucous membrane, tongue due to the abnormal size of the tooth or its shape - this factor also affects the bite;
- multi-rooted teeth that provoke inflammation of the cyst - osteomyelitis;
- chronic inflammatory processes – periodontitis, impossibility of non-surgical treatment;
- advanced caries complicated by pulpitis, periodontitis, neuritis or odontogenic osteomyelitis.
After carrying out diagnostic measures, the doctor identifies the causative tooth and prescribes its removal. This happens in one session under local anesthesia.
Contraindications:
- Blood diseases
, which lead to disruption of its coagulation;
- Diabetes
. The disease prevents tissue regeneration, so when removed, the wound can take a very long time to heal. During this period, microorganisms that cause an inflammatory process can multiply;
- First trimester of pregnancy
;
- Allergic reaction to the products used
.
It is important to inform your dentist about any existing diseases. Indicate the medications you are currently taking. Under no circumstances should you hide the presence of allergic reactions, as this can be life-threatening. The removal of the lower wisdom tooth is carried out in the same way as the upper one. The operation technology is the same.
Does it hurt to remove?
A typical mistake made by patients before tooth extraction is the desire to start the procedure faster in order to “get over it” faster. In this case, the anesthesia does not have time to completely dissipate through the tissues and the patient will face a painful procedure. Therefore, you need to wait a certain time, which is suggested by the dentist.
Stress factors can also affect pain during surgery. During the effect of anesthesia, you need to remain as calm as possible, which will allow you to carry out the procedure quickly and with the least risk.
Causes of pain with anesthesia
It is worth noting that in rare cases, pain may occur. This may be caused by the following factors:
- The patient is a drug addict. These people may not respond to pain medications;
- Long-term use of painkillers;
- Severe purulent inflammation.
In most cases in modern dentistry, tooth extraction is painless. The appearance of pain is associated with the immediate location of the tooth.
Removal methods
There are two main types of extirpation - a simple removal method and a complex method.
Complex removal method
It is carried out in cases where there is no access to the tooth, application of forceps is impossible and additional access must be made through an incision in the gums. During a complex operation, the tooth is not removed immediately, but in parts.
For this, a whole set of special tools is used:
- laser,
- saw,
- scalpel,
- burs.
Complex removal may be indicated in the case of a cystic formation under the causative tooth, fistula, dystopic wisdom tooth, or retention. Contraindications to the procedure are pregnancy, allergies to anesthetic drugs, mental illness, problems with the endocrine system. But if certain conditions are created, extirpation can be carried out even in the presence of these contraindications.
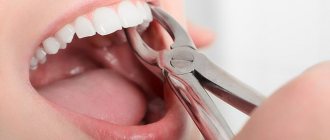
Simple operation
This method does not require additional preparation; it is removed by applying standard forceps, after which the bleeding stops and further measures are taken to restore the dentition.
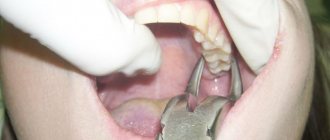
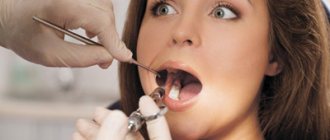
Molar tooth extraction procedure
The procedure will be the same in every dentistry. With high-quality modern equipment, the procedure is quick and painless. If a patient is afraid to have a tooth removed, then he must understand the consequences that such a decision will entail. One of them is pain, which may be stronger than after surgery under anesthesia.
Removal steps
How to pull out a molar, 8 stages of work:
- Examination and diagnostic procedures.
- Anesthesia of nearby areas.
- Ligamentotomy.
- Moving the forceps under the gum.
- Dislocation.
- Extraction.
- Inspection and treatment of the resulting hole.
- Stitching.
If the impacted figure eight is removed, then an additional tissue incision will be required. In this case, the gums are sutured after the molar is removed, and complete healing will take more time.
Until the next visit to the dentist, how the molar heals after removal should be monitored by the patient himself. If any unusual pain occurs, the dentist who performed the procedure should be contacted.
Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is necessary to increase patient comfort. It is inserted before the molar tooth is removed. But not all drugs have the same effect on the human body. Painkillers are divided into groups:
- Application – suitable only for simple procedures. Not used when working with adults.
- Infiltration – suitable for simple procedures, can be used to remove mobile incisors and molars.
- Conductive – used when complex removal is necessary or for complex work. Allows you to block the peripheral branches of the nerve to cover a large area.
- Intraosseous – the anesthetic is injected directly into the bone tissue, leaving the surrounding soft tissue sensitive.
- Intraligamentary – mainly used when working with children.
When selecting an anesthetic, the doctor should always find out about the presence of an allergy to any compound in order to select the correct composition for anesthesia. Thanks to these drugs, the patient does not have to wonder whether it hurts to remove a tooth.
Is it painful to remove a tooth root?
Thanks to modern anesthesia methods, the procedure is painless. Does it hurt to have a tooth pulled out? No, and discomfort appears only after the painkiller wears off.
Recovery after deletion
In the postoperative period, additional care for the socket is indicated to prevent complications. Possible complications are associated with the wrong choice of technique, an error during removal, systemic diseases, and improper care after surgery.
Bleeding very often occurs after surgery, which the dentist can treat with hydrogen peroxide and socket tamponade. If bleeding continues, the dentist uses hemostatic drugs to stop bleeding from the socket.
At home, after removal, you need to treat the hole with antiseptic drugs - this means rinsing the mouth with weak antiseptic solutions. To relieve pain, you need to take medications prescribed by your doctor. Swelling, inflammation, and itching may occur near the hole of the extracted tooth - you should contact your dentist with these complaints, as this is a sign of infection or the development of periodontal inflammation.
Hygienic procedures after removal remain unchanged, but direct contact of the toothbrush bristles with the socket should be avoided. While eating, you need to cover the hole with cotton wool and then rinse your mouth with warm water and soda.
Surgical dentistry has moved forward in many ways in terms of the technologies, drugs and techniques used. Today, the risk of inadequate surgery is practically absent, and the dentition can be restored in many ways. Surgical dentistry is directly related to orthopedics, orthodontics, and aesthetic dentistry, so the patient does not have to worry about an aesthetic defect after treatment.
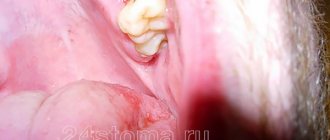
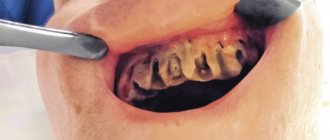
Dental roots affected by caries are a dangerous source of infection in the body.
When the carious process has destroyed not only the crown, but also the roots of the tooth, it is necessary to part with them as quickly as possible. Removing the root of a decayed tooth cannot be called a simple surgical procedure, but modern anesthetics and professional skills allow the doctor to carry it out quickly and without significant pain. If this is not done, rotting roots will create a serious health problem for the patient.
- Pathogenic microflora will spread to neighboring teeth.
- There will be a persistent unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- A cyst or granuloma may form around the root tip. Pus from the overgrown local formation will sooner or later release into the gum tissue - a flux will form, which will already capture the entire upper or lower jaw and “swell” the cheek.
- A persistent focus of infection will cause a significant decrease in immunity.
When treating gumboil, the patient's gums are first cut under anesthesia to allow the drainage of pus and to disinfect the source of infection. Without this manipulation, it is impossible to remove the tooth root, since it is impossible to inject an anesthetic into the gum tissue filled with pus. When sending a patient home, the dentist cannot even be sure that he will return to remove the root. Unfortunately, many avoid surgical intervention, which means they will soon face a relapse of the disease.
When is surgery necessary?
Wisdom teeth are more likely to develop pathological processes than others. There are several indications for the procedure:
- Dense or crowded teeth. As a result, the eruption of the wisdom tooth is complicated - it grows at an angle and causes pain. Inflammation occurs, and to solve the problem, surgery is performed to remove the wisdom tooth.
- Incorrect bite, requires braces. “Eights” can shift the dentition and cause pain when wearing braces. To avoid such problems, it is necessary to remove unerupted wisdom teeth.
- Lesions - caries, pulpitis, periodontitis become the reason for surgical intervention. Carrying out therapy is problematic, so they resort to removal.
At DENTA dental blades, you can undergo the procedure of wisdom teeth removal inexpensively - at a cost of 6,480 rubles. The price varies depending on the complexity and volume of work and the anesthesia used. To find out how much it costs to remove wisdom teeth, call us at the numbers provided.
In what cases should a wisdom tooth be removed?
Indications for removing the “eight” are:
- Abnormal placement of wisdom teeth .
Evenly growing third molars are rather an exception to the rule. Most often, these teeth grow at an angle, injuring the tongue, cheek, and moving other teeth. Sometimes the inclination is so great that wisdom teeth do not even show on the surface and can only be detected on an x-ray. Compared to our ancestors, the jaw of modern humans has decreased in length by almost 12 millimeters. That is why “eights” often simply do not have enough space in the jawbone. - Pericoronitis or too slow tooth growth . This pathology is not an absolute indication for surgery. More often, the dentist suggests that the patient simply remove the hood to avoid the development of an inflammatory process over the growing tooth. But if the patient goes to the doctor too late, then there is only one way out: removal.
- Caries . It is difficult to take good care of the “eights”. Bacterial plaque still remains on the teeth, and later, during a preventive visit, the doctor discovers carious cavities. You can suspect their appearance if the tooth begins to twitch when exposed to cold or sweet foods.
- Inflammatory process . It is also necessary to remove a tooth if an infection has been introduced into the soft tissues of the periodontium. It can provoke the development of flux or a cyst, and in this case the dentist will not hesitate.
Whether it makes sense to preserve a wisdom tooth, only a doctor can determine in each specific case.
Possible complications after tooth extraction
Complications can appear during surgery, as well as after it, and can be local or general. General: fainting, rarely – shock. Their cause is the patient’s psycho-emotional stress, sometimes pain due to poor-quality anesthesia.
Local complications:
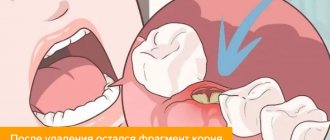
- Fracture of the tooth being removed (crown or root);
- Dislocation or fracture of a nearby tooth;
- Trauma to the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Dislocation or fracture of the jaw;
- Perforation of the bottom of the paranasal sinus;
- Pushing the tooth root into the maxillary sinus;
- Bleeding;
- Alveolitis.
What drugs are used for pain relief
Just a few decades ago, the only painkiller used by dentists was novocaine. Despite its low toxicity, it very often caused serious complications in patients: from an allergic reaction to anaphylactic shock.
The next step was the use of lidocaine. It is still used to this day in budget dental offices, and has an undeniable advantage: allergies to the drug occur extremely rarely. The problem is different: to prolong the effect of lidocaine, the dentist has to add a drop of adrenaline to it. Moreover, this is done “by eye”. And as soon as the doctor’s hand trembles a little, the patient is guaranteed such unpleasant symptoms as rapid heartbeat and dizziness.
It is much more comfortable for both the doctor and the patient of the dental clinic to deal with articaine anesthetics. These include:
- ubistezin
; - ultracaine;
- septanest
.
Firstly, such drugs are administered with a carpule syringe, which ensures that the injection itself is less painful. Secondly, the ratio of adrenaline and anesthetic in the drugs is adjusted to the nearest milliliter. This means that wisdom tooth removal will be painless, and the patient will not experience any side effects.
Important! If the patient is at risk, it is recommended to use an anesthetic that does not contain adrenaline.
What do patient reviews depend on?
Positive reviews will primarily depend on the experience and professionalism of the dental surgeon. It is better to find an experienced doctor rather than a young doctor straight out of medical school. Ideally, the doctor has experience in maxillofacial surgery and/or implantology. Read patient reviews about wisdom teeth removal in the comments to this article. We hope that our article on the topic: Wisdom tooth removal consequences photo - was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Qualified removal of third molars” (Asanami WITH.).