- Facial neuritis is an inflammatory disease that causes partial, unilateral paralysis or paresis of the face.
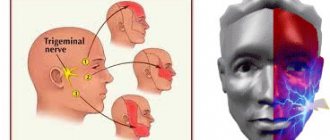
The facial nerve is responsible for contractions of facial muscles and consists primarily of motor fibers. It is one of twelve paired cranial nerves. It begins in the brain and, branching, innervates the face. Its inflammation can occur both at the base (in the core area) and throughout, involving one or more branches. Depending on this, the symptoms of the disease vary.
In most cases, treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve is carried out using conservative methods, and only in the most severe cases (for example, with injuries with a complete rupture of the nerve canal), if therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment is used.
At the Tibet Clinic, treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve is carried out without surgery, using reflexology and physiotherapy. Positive results are achieved in 97 - 98% of cases.
As a result of treatment, contractions of the facial muscles and facial symmetry are restored, spasticity and other symptoms disappear, and the inflammatory process is stopped. These results are long-term and persistent.
Symptoms
A common characteristic sign of the disease is immobilization and distortion of part of the face, in which it turns into a sedentary or completely motionless mask. Additional symptoms depend on where the inflammation occurs.
The facial nerve is a paired nerve; when it leaves the brain, it divides into two symmetrical branches. One of them is responsible for the innervation of the right side, and the other is responsible for the innervation of the left side of the face.
As a rule, inflammation affects only one of the two symmetrical parts, so the symptoms of neuritis are almost always unilateral. Contractions of the facial muscles become difficult or impossible, this manifests itself when trying to frown, smile, close an eye or raise an eyebrow. The face becomes distorted and asymmetrical.
The corner of the mouth and the edge of the eye are lowered, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out. When you try to close your eyelids, the eyeball turns upward (Bell's palsy). When you try to close your eyelids, a gap remains between them, this is called lagophthalmos or “hare's eye.”
Since the facial nerve consists primarily of motor fibers, inflammation of the facial nerve results in muscle symptoms. Sensitive, painful symptoms (in the form of neuralgia) are not typical for such neuritis.
However, the common nerve cord includes the intermedius nerve, which consists of sensory fibers and provides the sensation of taste to the outer two-thirds of the tongue, as well as the functioning of the salivary glands. Therefore, with neuritis of the facial nerve, symptoms such as disturbance, partial loss of taste, and increased salivation (drooling) are possible.
Another possible symptom is tear gland dysfunction, dry eye, or watery eyes. A combination of these two symptoms is possible - the so-called “crocodile tears”, when the eye becomes abundantly moisturized when eating, but remains dry the rest of the time (Bogorad syndrome).
Paresis or paralysis of the face usually develops within 24 hours after the appearance of pain behind the ear - the first sign of neuritis. As the disease progresses, symptoms such as hearing loss or intolerance to loud sounds (hyperacusis) are possible.
Ear pain with neuritis can radiate to the back of the head, temple, and be accompanied by loss of coordination, dizziness, and hearing loss. The complex of these symptoms is called Hunt syndrome.
Disruption of the innervation of the external eye muscle with neuritis of the facial nerve is manifested by convergent strabismus. Along with the characteristic signs of inflammatory damage to the facial nerve, symptoms of concomitant diseases may be observed, for example, shooting pain in the ear with otitis media. Or symptoms of cerebrovascular accident due to atherosclerosis.
From the point of view of Tibetan medicine, inflammation of the facial nerve, like other neuritis and neuropathies, refers to disorders of the governing basis Wind (Rlung - Tib.).
This is a light and cold base that has a great influence on other control systems of the body. Its disorder usually manifests itself not only with local symptoms (neuralgia, numbness, paresis, paralysis), but also with metabolic, immune, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, excretory, reproductive systems, as well as hormonal regulation.
Sanzhizhapova Avgustina Dondopovna Reflexologist, neurologist Experience 39 years
Central palsy - facial nerve
Central paralysis of the facial muscles (facial muscles) is observed as a result of damage to the corticonuclear fibers going to the nucleus of the facial nerve. Central paralysis is characterized by dysfunction of the muscles of the lower half of the face, which have unilateral cortical innervation. The main symptom of central paralysis is the smoothness of the nasolabial fold on the side opposite to the lesion. In some patients with central paralysis of the facial muscles, mild deficiency of the orbicularis oculi muscle can be detected. Central paresis of the facial muscles is usually observed in combination with central hemiparesis, or hemiplegia. In contrast to peripheral paralysis, with central paralysis of the facial muscles, the conjunctival reflex, brow reflex, and corneal reflex are preserved, and there is no degeneration reaction.
Causes
Inflammation of the facial nerve can occur due to its compression by a tumor, aneurysm of a vessel, or swelling of soft tissues with the development of “tunnel syndrome.” In this case, damage to both the root and the trunk of the nerve canal is possible.
The inflammatory process may spread to nerve tissue from the adjacent area. In particular, neuritis can occur against the background of inflammatory disease of the middle ear (otitis).
Often the cause of nerve damage is a viral or other infection, such as herpes or paramyxovirus (mumps).
An ischemic cause of inflammation is also possible, that is, a violation of the blood supply to the nerve due to vascular atherosclerosis or stroke. The provoking factor for the development of the disease is usually severe cooling of the face in a cold wind, rain or draft. This especially often occurs against the background of emotional experiences, stress, psycho-emotional overload or overwork.
Another possible cause of inflammation is trauma received, for example, during deep dental treatment or surgery.
Neuritis of the facial nerve occurs when there is an imbalance of the Rlung base, the main causes of which are poor nutrition, hypothermia (especially exposure to cold wind), stress, overwork, lack of sleep, psycho-emotional overload, negative emotions and mental trauma.
Wind imbalance can occur against the background of fasting, low-calorie diet, strict diet, abuse of dry, rough foods high in plant fiber.For example, a strict diet based on raw vegetables, greens, lettuce, citrus fruits can provoke an imbalance of Wind, which, on the one hand, manifests itself as restlessness, anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and on the other hand, increases the risk of neuritis and neuropathies, in particular the facial nerve.
Kulbuzhev Murat Sultanovich Reflexologist, neurologist Experience 30 years
Classification
Neuritis of the facial nerve can be primary or secondary.
The primary form of inflammation occurs as an independent disease in a healthy person due to hypothermia. This type of neuritis is called catarrhal neuritis.
The secondary form of inflammation develops against the background of infection, otitis media or another disease.
In the vast majority of cases, the disease is acquired, much less often it is congenital.
The congenital nature of the disease may be indicated by Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome - swelling of the face combined with folding of the tongue.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules for the prevention of facial nerve neuropathy can reduce the likelihood of pathology occurring. This is especially true if there is an increased risk of developing the disease. Doctors recommend:
- avoid hypothermia and facial injuries;
- observe safety precautions at work to prevent eye damage;
- consult a doctor in time for infections and otitis media;
- control blood sugar levels;
- promptly diagnose and treat chronic diseases.
Diagnostics
Thanks to the characteristic symptoms, establishing a diagnosis for neuritis of the facial nerve does not cause difficulties. Diagnostics is aimed mainly at determining the causes, nature of the inflammatory process, as well as concomitant diseases.
At the initial appointment, the doctor examines and palpates the face, assesses the degree of muscle spasticity and movement disorders. At the same time, he pays attention to the smoothing of natural folds (nasolabial, frontal, etc.), as well as to the non-closure of the eyelids (the inability to close the eye).
For this purpose, several standard tests are performed in which the patient is asked to close his eyes, try to smile, close his eyes, frown, wrinkle his forehead, puff out his cheeks, blow, wrinkle his nose, raise his eyebrows, and bare his teeth. In addition, the taste sensitivity of the tongue is determined.
If additional data is needed, the patient is sent for an MRI or CT scan to identify possible lesions of the brain, blood vessels (in particular, the presence of a tumor, hematoma, aneurysm, etc.), and the presence of inflammatory foci.
To assess the affected area and disturbances in the innervation of facial muscles, electromyography (EMG) is used - a method for studying bioelectrical activity. Using electroneurography, the speed of signal transmission through nerve channels (fibers) is assessed.
In addition, a general urine and blood test and a biochemical blood test are performed.
Important! Eastern medicine views the human body as a single system. Inflammation of the peripheral nerves in this context represents a particular, local manifestation of a general imbalance, almost never the only one.
Therefore, when diagnosing neuritis, a doctor of oriental medicine assesses the degree of imbalance as a whole, identifies concomitant diseases, disorders, functional disorders of the nervous, hormonal, reproductive, immune and other systems.
A treatment plan is designed to address the common causes of all these disorders.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of facial nerve neuritis is usually carried out to restore its integrity, damaged by injury (rupture of nerve fibers). For this purpose, the nerve is sutured.
In addition, surgery may be performed if the cause of nerve inflammation is compression by a tumor, aneurysm, scar tissue, or other neoplasm. The cause of the compression is removed (an example of such an operation is neurolysis - removal of connective tissue proliferation).
Another type of surgical treatment is replacing the damaged portion of the facial nerve with a graft. Such operations are usually performed for injuries. The section of nerve to be transplanted is taken from the leg. The volume of plastic surgery is determined by the surgical plan. In particular, the transplant can be sutured to the facial nerve on the healthy half of the face. In this case, the signal from the brain will arrive to the facial muscles simultaneously on the right and left sides.
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where conservative therapy does not bring results. It can be carried out within 12 months from the onset of symptoms of neuritis. Carrying out the operation later does not make sense, since by this time the facial muscles have time to atrophy.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic provides each visitor with medical care of the highest level, regardless of his age and reason for visiting. We offer:
- screening diagnostic programs to assess health status;
- accurate and quick diagnosis of obvious and hidden pathologies;
- modern methods of drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage;
- minor surgical operations within the walls of the clinic;
- course treatment of chronic diseases in comfortable day care wards;
- organization of hospitalization in a specialized hospital if necessary;
- preparation of documents for sanatorium-resort treatment, selection of sanatorium;
- remote consultations with foreign doctors to obtain an alternative opinion;
- modern rehabilitation programs.
Facial nerve neuropathy is a fairly common pathology. To prevent it from leading to irreversible facial asymmetry, contact a specialist as soon as possible. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will always come to the rescue.