Causes of dislocation Symptoms Classification Possible complications Diagnosis Treatment and prognosis If the tooth cannot be saved
Tooth dislocation is a dental injury in which an incisor or canine is displaced in the alveolus (socket) in a lateral or vertical position due to mechanical impact. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the upper incisors and canines are more often exposed to such damage. Anatomically, each dental unit consists of a crown and a root. The coronal part is located above the gum, the root is in the jaw bone (alveolus, socket).
Between the alveolus and the root there is a periodontal ligament, consisting of connective tissue fibers. Intertwined with the alveolus and root cement, the periodontium holds the root in the jaw. The combination of 3 elements (alveolus, periodontium, cementum) is called the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth
. It can be injured due to a blow, biting on a hard product or object, resulting in dislocation or subluxation of the root, its disposition in the dentition. Traumatic tooth dislocation in the lower jaw is less common than in the upper jaw.
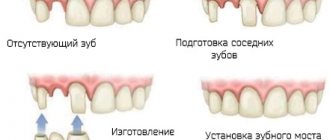
A timely visit to the doctor makes it possible to save the injured incisor and avoid removal. According to the severity of the injury, adequate treatment is carried out, including immobilization of the dental unit by fixing it to adjacent teeth. Even if the incisor has fallen out, but the root and crown are preserved, with prompt treatment it is possible to restore the tooth using replantation.
Symptoms
- Disposition of a dental unit in a row (from slight mobility to loss);
- severe pain in the area of injury;
- violation of chewing and speech functions;
- swelling, redness, increased sensitivity of the gums;
- Difficulty closing the jaws.
Dislocation of a baby tooth is one of the most common injuries in children under 3 years of age. The most threatening is an impacted tooth dislocation, since in this case the bone bottom may be destroyed, which will interfere with the formation of a permanent unit. Signs of tooth dislocation in children are similar to those in adults.
Varieties
This disease is classified into:
- complete;
- incomplete.
In the first case, the disease forms after an absolute rupture of periodontal tissues and the circular ligament of the tooth due to a strong blow to the crown. Often there is damage to the upper jaw of the front teeth.
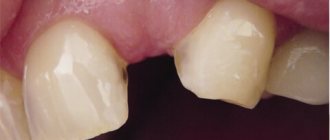
A complete dislocation clinically looks like this: upon examination, you can see that the tooth is missing from the dentition, and its socket is filled with a fresh blood clot and continues to bleed. Often there are concomitant injuries to the soft tissues of the lips - wounds to the mucous membrane, bruises, and so on. In order for the treatment to be complete and effective, the condition is assessed, namely the presence of carious cavities, the integrity of the root and crown, etc.
Incomplete luxation changes the position of the tooth in the row. The patient complains of mobility, pain, changes in his position and impaired chewing function. An examination of the oral cavity shows the displacement of the crown of the injured tooth in different positions. It can be highly mobile and very painful upon percussion, however, it is in its place in the dentition.
In this case, the gums are hyperemic and swollen, and ruptures may occur. Due to rupture of periodontal tissue, the circular ligament and damage to the walls of the alveoli, pathological dentogingival pockets can form, as well as bleeding from there. In the case of dislocation and oral displacement, its root is usually displaced vestibularly and vice versa. Often the patient has concomitant injuries - wounds, hemorrhages, bruises.
Classification
- Incomplete
tooth dislocation - the crown part is displaced in different directions or rotated around an axis, the incisor is movable, but is held in the socket. The dental unit responds to touch with sharp pain. The gum separates from the hard tissues of the crown, bleeds, turns red, and swells. Such an injury can be complicated by destruction of the pulp chamber (internal cavity with a neurovascular bundle), atypical changes in the root part (shortening, curvature). - Complete dislocation
of the tooth - the crown part with the root has completely fallen out of the socket, the gum is separated, swollen, and has acquired a bluish tint. There was a bleeding hole where the incisor was located. This type of injury occurs more often with primary teeth because they do not have a developed root system. - Impacted
tooth dislocation - implies a shift of the dental unit towards the jaw. The coronal part is completely or significantly immersed in the gingival tissue (visually, the height of the visible part decreases). The injury may be accompanied by root splitting, destruction of the jaw bone, damage to the pulp, and rupture of blood vessels.
Causes of dislocations
Dislocations occur due to strong and sudden mechanical impact. As a result, the tooth is displaced relative to the alveolus, and the connective tissue surrounding the tooth and its neurovascular bundle are damaged. The reason may be:
- blow to the tooth;
- biting hard food;
- contact with a tooth of a hard foreign body, such as a stone, while chewing food;
- bad habits, such as opening bottles with teeth, cracking nuts;
- inaccurate tooth extraction, leading to dislocation of the adjacent one [1, 2].
The incidence of dental injuries due to other dental diseases is increasing every year.
In this case, the frontal teeth, compared to the distant molars, are subject to injury more often due to lack of protection. It is curious that this problem is more often faced by men who often get into fights, engage in aggressive sports (boxing, martial arts), and practice extreme types of recreation. Naumovich Yu. Ya., Ph.D., orthodontist [3]
Diagnostics
Only a dentist can differentiate a root dislocation from a fracture. Not only the incisor is damaged, but also the periodontal tissues. A crack may form in the jaw bone. Comprehensive diagnostics includes:
- Orthopantomogram;
- sighting shot of the incisor;
- CT;
- three-dimensional scanning of the maxillofacial area.
The dentist makes a diagnosis based on examination, complaints, and X-ray results. The doctor analyzes the clinical picture and assesses the condition of the jaw bone in the injured area.
Tooth dislocation: photos and symptoms
Any injury has its own clinical picture. Tooth dislocation, photos of which can be viewed on dental websites, is also characterized by specific symptoms. During the examination, the dentist looks for signs to diagnose a luxated tooth.
The doctor also determines what type of tooth dislocation the resulting tooth is. The symptoms of each are slightly different. After analyzing the x-ray, treatment is usually prescribed.
Treatment and prognosis
The doctor determines how to treat a tooth after a dislocation based on the type of traumatic injury. The decision on the treatment method is made according to the condition of the jaw bone and the detected degree of displacement.
- In case of pronounced displacement,
the dentist pulls the incisor with special forceps to its previous position and fixes it with a splinting device. - If the tooth is slightly misaligned,
splinting is not always required; the unit often recovers on its own.
Partial dislocation of the front teeth involves the following stages of treatment:
- Reposition (the incisor is returned to the correct position);
- fixation with a splinting structure (splints, staples, mouth guards, etc.);
- depulpation and filling of dental canals (if the pulp is dead).
If an injury occurs, you need to seek help from a dentist as quickly as possible. Even with complete dislocation in the first 30-40 minutes
replantation can be performed while preserving the dental unit. During the procedure, the doctor implants the dislocated tooth into its own alveolar bed and fixes it with a splinting device. The wearing time of the splint is 4-6 weeks. If the pulp is damaged, it is first removed with further filling of the canals, then the cutter is inserted into place under anesthesia and secured with a splint.
Treatment of complete dislocation of teeth by replantation is applicable only to permanent units without cracks, chips in the enamel, or root damage. Replantation with preparation takes about 40-60 minutes, the replant healing period is 2-3 weeks, sometimes more.
Prevention of dislocations
Most injuries can be prevented by following these precautions:
- Think about the organization of the interior. Creating a non-traumatic environment is especially important for young children who have recently started walking, but adults also get dislocated teeth at home. There should be no protrusions or dangerous sharp corners in the room that could cause you to trip. Sufficient lighting must be provided in all areas of the space.
- Keep an eye on the child. Children of preschool and primary school age should not be left unattended during active games with peers, even on specially equipped playgrounds.
- Use of protective equipment when playing sports - masks, helmets, mouthguards, as well as comfortable shoes that prevent falls.
- Elimination of bad habits that lead to dislocations - chewing hard objects, opening bottles with teeth, etc. [3, 4].
Treating a dislocated tooth is difficult. Often it is not possible to save a tooth, and even with a favorable outcome of treatment, its service life is reduced. This is why prevention rules play such an important role. Simple safety precautions help prevent troubles and preserve the integrity of your teeth for life.
List of sources:
- Cherchenko N. N. Dislocations and fractures of teeth. Fractures of the alveolar process: educational and methodological manual. Minsk: BSMU, 2013. // URL: https://rep.bsmu.by/bitstream/handle/BSMU/1742/%D0%92%D1%8B%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%85%D0 %B8%20%D0%B8%20%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC%D1%8B%20%D0%B7%D1 %83%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%B2.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y (accessed 08/18/2021).
- Negametzyanov N. N., Aldasheva M. A., Zhanabaeva G. B. Clinical protocol for the diagnosis and treatment of dental injuries // URL: https://www.rcrz.kz/docs/clinic_protocol/2016/2%D0%BF% D0%B3/%D0%9F%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%8F/%D0%A1%D1%82% D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%8F/2%20%D0%9F%D0% BE%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D1%8F%20%D0%B7%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%B2%20%D0%B2%D1%81% D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%B4%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2% D0%BC%D1%8B%20%D1%83%20%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B9.pdf (date of access: 08/18/2021).
- Naumovich Yu. Ya., Ph.D., dentist-orthodontist, article “Dental injuries” // URL: https://www.roden.by/bolezni/travmy-zubov/ (access date: 08/18/2021 .).
- Morozova N.V., Vasmanova E.V., Vinnichenko A.V., Golochalova N.V., Khromenkova K.V., Ivankina E.O. Dental injuries in children: a textbook. M.: FGBOU DPO RMANPO, 2022. // URL: https://irbis.rmapo.ru/UploadsFilesForIrbis/30f79a8db3798e14e3481477e130db73.pdf (access date: 08/18/2021).
INJURY OF MILK TEETH. What to do?
Baby teeth can be injured just like permanent teeth, but first aid and treatment tactics are different.
An important feature that determines “what to do” is the proximity of the roots of baby teeth to the rudiments of permanent teeth. Therefore, in case of injury, the main concern is the preservation of future (permanent) teeth.
Nevertheless, if it is possible to preserve baby teeth without harm to permanent teeth, the dentist will act this way. The goal of treatment is to organize the healing process of the periodontium (tissues surrounding the tooth) and the pulp of the baby tooth, provided that this does not harm the formation of permanent teeth.
TOOTH FRACTURE. What to do?
As we wrote above, the following injuries include tooth fractures:
- chipped piece of enamel
- chipping of the crown within the dentin without damage to the dental pulp
- fracture of the tooth crown with damage to the pulp (blood is visible at the fracture site)
- tooth root fracture
Root fractures can be of more complex types:
In all these cases the recommendation is the same:
- If possible, find all the broken tooth fragments and place them in water
- No emergency visit to the dentist is required; make an appointment this day or the next .
Clinical picture
Each type of dislocation is characterized by a specific set of symptoms:
- with partial damage, significant discomfort occurs (mainly during palpation and chewing). During a dental examination, it is discovered that the unit is loose, deviated from the axis, the mucous membrane is reddened and swollen. Blood may bleed from the periodontal cavity;
- with complete dislocation, it is distinguished by the loss of the tooth element from the alveolus. A fresh clot is found inside the wound. The victim complains of pain;
- symptoms of intrusion: the height of the causative tooth is less than that of neighboring units. Sometimes the injured element is completely immersed in the bed. The pathology is accompanied by signs: significant pain, swelling of the surrounding periodontal tissues, bleeding of the socket.