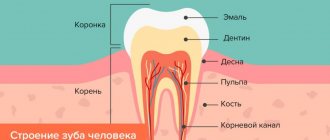
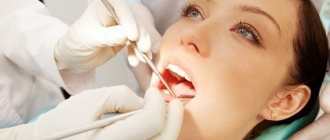
Almost every person on earth has experienced toothache at least once. It can be very difficult to tolerate, and sometimes simply unbearable. To avoid complications, one of which may be periodontitis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process of the apex of the tooth root, as well as in the tissues adjacent to it. This is a rather dangerous disease that can lead to even more serious problems, so you should not delay treatment. Periodontitis can occur as a result of advanced pulpitis or poor-quality canal filling.
Also, the causes of this disease can be an infection, injury, or the consequences of medication. According to statistics, this disease accounts for 45-50% of all dental diseases. People with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to rapid development of the disease.
Symptoms of periodontitis
It is impossible not to notice the symptoms of periodontitis. These include:
- The occurrence of severe pain that is constant;
- The appearance of painful sensations when chewing or touching;
- A clear feeling of which tooth hurts, with a feeling of bursting from the inside;
- Discharge of a small amount of fluid from under the tooth, accumulation of pus in the gums;
- The pain may be throbbing and radiate to the temporal or ear region;
- Bad breath;
- Visible swelling and redness of the gums.
Types of periodontitis
Depending on the nature of the processes occurring in the area of the tooth root, periodontitis has three forms.
- Chronic fibrous. A type of chronic periodontitis. This disease most often affects older people. The disease is practically asymptomatic, but during an exacerbation, pain may occur when chewing food. This form of periodontitis is manifested by fibrous changes in the periodontal tissue, that is, the tissue around the tooth becomes pale pink, and the tooth itself may become gray.
- Chronic granulating. It is also a chronic form of periodontitis. It is often the cause of complicated caries, and is characterized by inflammation in periodontal tissues. In this case, granulation tissue appears, which grows and can have devastating consequences for the bone.
- Granulomatous. Chronic stage of periodontitis with an inflammatory nature. Granulomas appear in the tissues at the apex of the tooth root, that is, formations that separate the infectious focus from part of the healthy tooth. Gradually, the tissue surrounding the tooth is destroyed.
In addition, according to the speed of the disease, periodontitis can be of the following types.
- Spicy. The disease acquires this form at the final stage. This form is characterized by rapid development, accompanied by acute pain (especially when eating hot food), redness and swelling of the gums, and the appearance of a fistula.
- Chronic. This form is characterized by sluggish processes due to unresolved inflammation. Pathogenic microorganisms constantly penetrate inside the tooth and contribute to its death, as well as damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth and bone destruction.
- Chronic in the acute stage. When the disease is in the acute stage, a person may experience a rise in temperature, a headache, a feeling of weakness, swelling of the gums and face, enlarged lymph nodes, and mobility of a damaged tooth.
Reasons for the development of the disease
- untreated caries or poor quality of filling, when an inflammatory process has developed again under the installed filling,
- preservation of the nerve under the crown - in this case (if the tightness of the prosthesis is broken, there is inflammation underneath) there is a high risk of pulp inflammation,
- tooth injury – inflammation penetrates from the outside, i.e. through cracks and chips that are located on the root or in close proximity to it,
- exposure to aggressive stimuli - temperature and chemical, for example, during previous canal treatment, naturally, with an incorrectly selected dosage of the drug.
Treatment of acute periodontitis
Any form of the disease requires immediate treatment. Surgical treatment of acute periodontitis involves opening the tooth for free access to the canals and mechanical cleaning using local anesthesia. It is also necessary to treat the canals with an antiseptic or administer antibiotics if necessary. Several treatment sessions may be required, during which the tooth is either left open or covered with a temporary filling. After the inflammation and pain are eliminated, a permanent filling is installed, after which an x-ray must be taken.
In some cases, periodontitis is treated surgically. If the nerve becomes inflamed, it must be removed. After completing treatment, it is useful to rinse your teeth with a soda solution for some time. Unpleasant sensations may occur for several weeks after treatment. But soon they will pass. If no repeated problems arise within six months, we can assume that the disease has been eliminated. Thanks to modern medicine, relapses of the disease occur in only 15% of cases.
Root canal infection
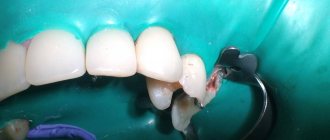
Penetration of microorganisms into the root canal can occur due to merciless preparation with pressure on the coronal pulp, careless amputation and removal of tissue from the orifice. The development and proliferation of microbes is possible due to the repeated use of tools, including burs and excavators. Infection of the root canal increases the risk of post-filling complications such as painful percussion, lack of positive dynamics after treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis. In preventing this complication, great importance is attached to careful isolation of the surgical field, since microflora can penetrate into the canal along with oral fluid. It is optimal to use protective equipment such as rubber dam and its analogues (Fig. 1). Before instrumental treatment, it is advisable to completely excise carious dentin from the walls of the carious cavity in order to prevent infection from entering the root canal.
Rice. 1. Treatment of pulpitis using a rubber dam.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis
Before starting treatment for chronic periodontitis, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the patient. To do this, probe and x-ray of the affected area of the jaw are performed. Based on the results, an effective treatment method is prescribed.
Periodontitis is treated in two ways.
- Treatment of the disease with a therapeutic method involves the use of antibacterial medications that have a wide spectrum of action, localize inflammation and relieve symptoms. Periodontal canals inside the tooth are treated with antiseptics, and general strengthening drugs are also used to accelerate tissue regeneration. It is also possible to use laser processing. Treatment lasts up to six months. The dynamics are monitored using x-rays.
- The surgical method is used if therapeutic treatment does not produce the desired results. It consists of removing the affected tissue, resection of the apex of the tooth, or its complete removal. If there is a large amount of pus, installation of elastic drainage is required. After the procedure, the patient must take medications prescribed by the doctor to avoid infection and to accelerate tissue regeneration.
Clinical researches
As a result of clinical experiments using the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Kazan State Medical Academy, the complex use of anti-inflammatory drugs from the Asepta line contributed to faster relief of inflammation, the combined use of balm, gel, rinse, toothpaste and vitamin-mineral complex mutually enhanced the therapeutic effect did not require daily visits to the dentist.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Mistakes in the treatment of periodontitis
Medical errors acceptable in the treatment of periodontitis, or errors arising for other reasons, can cause complications such as the appearance of a fistula, cyst and osteomyelitis. These complications are called local. But there are also general complications. These include intoxication of the body and infection (sepsis) of the blood. Therefore, to treat a disease such as periodontitis, you should contact only qualified specialists. All complications that arise during the treatment of periodontitis require immediate medical intervention. Let's take a closer look at local complications.
- Fistula. A fistula occurs as a result of poor-quality tooth filling, which causes bacteria to multiply inside it. An inflammatory process appears and a fistula is formed, through which pus is released. Treatment is carried out by taking antibiotics and antihistamines, as well as rinsing with saline solution. If treatment is carried out correctly, the fistula will close on its own.
- Cyst. The formation that occurs in the upper part of the tooth is called a cyst. It develops slowly and does not cause concern. As the size of the cyst increases, complications begin. The cyst is diagnosed using an x-ray and removed surgically using local anesthesia.
- Osteomyelitis. An infectious disease that can lead to the breakdown of the jaw bones. Diagnosis requires a complete examination, including a blood test, x-rays and other tests. For treatment, it is necessary to remove the diseased tooth and then take antibiotics.
It is known that the best prevention of diseases is their prevention. You shouldn’t put off going to the dentist for a long time, even if you have minor caries. Take care of your teeth, and then you will avoid serious dental diseases, have healthy teeth and a beautiful smile.
What determines the quality of filling?
The technique of filling root canals requires considerable skill from the dentist. Errors that negatively affect the effectiveness of treatment can occur at any stage. Inaccurate measurement of the length of the canals can lead to under- or over-filling of the canals, which almost always results in the development of inflammation of the tooth and surrounding tissues. If the length of the channels is determined incorrectly (not to the full length), they are also processed. The consequences of errors in measuring length include pain, neuralgia, swelling of the gum tissue, the development of periodontitis and other inflammatory diseases, and tooth extraction. Only in some cases can the canal be resealed without serious consequences. A control radiograph, which is required to be performed after filling, usually helps to detect an error in a timely manner.
In order to avoid errors when measuring length, clinics today use a special device - an apex locator. The device is connected to a file that is placed into the root canal. Using an apex locator allows you to record the moment the file reaches the root apex. In some cases, a radiograph with files installed inside the canals is used for more accurate control.
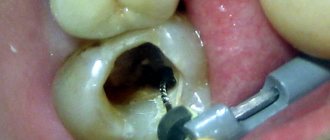
Doctors also make a large number of mistakes at the mechanical processing stage. Modern methods of filling root canals necessarily require preliminary expansion of the canals. The untreated channel, as a rule, has a too small and, moreover, variable diameter; inside the canals there are usually many narrowings and expansions that prevent high-quality filling. To eliminate them, mechanical treatment is used.
Cleaning and widening the canal can be done either with simple hand instruments or with a special endodontic handpiece. In the first case, the doctor literally performs all operations with his hands - independently determining the depth of immersion of the file, the force of pressure and the speed of rotation. You have to rotate the tool with your fingertips. Naturally, such a procedure does not always allow high-quality cleaning of the entire surface of narrow canals and sometimes leads to the tip of the instrument breaking off, which can cause poor-quality filling or pain after filling the root canal.
Mechanical processing using an endodontic handpiece is much more reliable and precise. The tip is connected to a microdrive, which ensures its rotation and also automatically controls the load and rotation speed to prevent breakage. The use of such technological tools makes it possible to achieve the highest quality of treatment and significantly reduce the risk of complications, but does not guarantee 100% effectiveness of treatment.